Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Which of The Two Is More Liver Specific and Increases More During Liver Disease
Which of The Two Is More Liver Specific and Increases More During Liver Disease
Uploaded by
Mariel Abatayo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesclinical chemistry
Original Title
Which of the two is more liver specific and increases more during liver disease
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentclinical chemistry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesWhich of The Two Is More Liver Specific and Increases More During Liver Disease
Which of The Two Is More Liver Specific and Increases More During Liver Disease
Uploaded by
Mariel Abatayoclinical chemistry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Which of the two is more liver specific and increases more during liver disease: Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
ALT for both, however they are present in other tissues as well so increased levels may indicate other tissue damage.
Hepatitis A is transmitted mainly via which route and is vaccine available?
Fecal-Oral
Yes
What are the three antigens for Hepatitis B and what time of infection are they present in:
Core (Present in acute infection)
Surface (Not infectious, but may indicate HBV. anti-HBs can also develop which makes patient immune to HBV)
E antigen (Acute and Chronic, only present when HBsAg is present and is an extracellular form of HBcAg)
Hepatitis C is transmitted mainly via which route and is vaccine available?
Blood transfusion/needles
No vaccine available
Hepatitis D is transmitted mainly via which route and is vaccine available?
Requires HBsAg from HBV for replication so it can only infect HBV positive patients
Vaccine available
Hepatitis E is transmitted mainly via which route and is vaccine available?
Fecal-Oral
No
Hyperbilirubinemia in newborns usually
produces no serious consequences
All of the following statements concerning urobilinogen are correct EXCEPT:
urinary levels increased in biliary obstruction
Ehrlich reagent is used in the measurement of:
urobilinogen
In the liver, bilirubin is converted to
bilirubin glucuronide
A breakdown product of bilirubin metabolism that is produced in the colon from the oxidation of urobilinogen by
microorganism is:
urobilin
All of the following methods have been used for the quantitation of serum bilirubin concentrations EXCEPT:
picric acid
Which of the following is characteristic of hemolytic jaundice?
unconjugated serum bilirubin level greater than normal
The product formed from the reduction of bilirubin in the small intestine is:
urobilinogen
The term delta bilirubin refers to
bilirubin tightly bound to albumin
Which reagent is used in the Jendrassik-Grof method to solubilize unconjugated bilirubin?
caffeine
The reference range for total bilirubin in adults is
0.2-1.0 mg/dL
Which of the following statements regarding infection with hepatitis D virus is true?
occurs in patients with hepatitis B
Caffeine is used in bilirubin assays to:
accelerate indirect bilirubin reaction
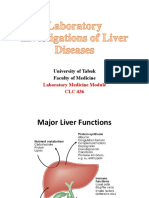
Functions of the liver
Carbohydrate metabolism
Protein metabolism
Lipid metabolism
Conjugation, detoxification and excretion
Vitamin storage
Digestion and formation of bile
Enzymes
Bilirubin metabolism
Hemoglobin is broken down into bilirubin by what?
Reticuloendothelial cells of the spleen, bone marrow, or thymus
Hemoglobin breakdown
1. Hemoglobin
2. Verdohemoglobin
3. Biliverdin + Fe + Globulin
(Biliverdinreductase)
4. Bilirubin + Albumin
5. Bilirubin - Albumin Complex
Hemoglobin conjugation
1. Bilirubin - Albumin Complex
2. Bilirubin
3. Bilirubin + UDP-glucuronic acid
(Glucuronyltransferase)
4. Bilirubin diglucuronide
Where does bilirubin conjugation occur?
Parenchymal cells (Hepatocytes)
What is delta bilirubin?
Bilirubin that is covalently bound to albumin
Conjugated bilirubin is bilirubin that is bound to?
Diglucuronic acid
*Describe bilirubin levels in serum and urine during normal liver function.
Normal in serum
Negative in urine
*Describe urobilinogen levels during normal liver function
Trace amounts
Cause of prehepatic jaundice
Increased hemoglobin breakdown
Describe bilirubin levels in serum during prehepatic jaundice
Increased unconjugated / indirect bilirubin
Describe urobilinogen levels in stool and and urine during prehepatic jaundice
Stool is increased
Urine is increased
Only __________ bilirubin can be excreted into the urine
Conjugated
Target cells are usually found in this condition
Hemolytic anemia
Causes of Hepatic Jaundice
Conjugation failure
Transport failure
Cell damage
Describe bilirubin levels in serum during hepatic jaundice
Increased unconjugated
OR
Increased conjugated
Describe urobilinogen levels of stool & urine during hepatic jaundice
Stool is variable
Urine is increased
Urine bilirubin is found in _________ jaundice
Hepatic
Post hepatic
Causes of Post Hepatic Jaundice
Obstruction of the bile duct
Describe bilirubin levels in serum during post hepatic jaundice
Increased conjugated
Normal - increased unconjugated
Urobilinogen is decreased in both urine and feces during _____________
Post hepatic jaundice
LD is increased during?
Prehepatic jaundice
AST is increased during?
Hepatic jaundice
ALT is increased during?
Hepatic jaundice
GGT is increased during?
Post hepatic jaundice
ALP is increased during?
Post hepatic jaundice
These enzymes are increased during hepatic jaundice
AST
ALT
These enzymes are increased during post hepatic jaundice
GGT
ALP
Why is it that unconjugated bilirubin cannot be excreted in urine?
It is not water soluble
Alpha bilirubin
Unconjugated / indirect
Upgrade to remove ads
Only $1/month
Beta bilirubin
Conjugated / direct
Which type of bilirubin has a high affinity for brain tissue?
Unconjugated
Conjugated bilirubin is soluble in?
Water
Alcohol
Unconjugated bilirubin is soluble in?
Alcohol
Specimen requirements for bilirubin testing
Serum / heparinized plasma
No hemolysis
Protect from the light
In bilirubin assays, hemolysis interferes with what?
Diazo reaction
Diazo reagent
Sulfanilic acid + HCl + Sodium nitrite (NaNO3)
In an Evelyn Malloy reaction, ______________ bilirubin gives an immediate reaction
Conjugated
This type of bilirubin assay can only be used for newborns
Bilirubinometer
Reference range for total bilirubin
0.1 - 1.1 mg/dL
Reference range for direct bilirubin
0.0 - 0.3 mg/dL
Reference range for indirect bilirubin
0.1 - 1.1 mg/dL
Bilirubin diglucuronide + diazonium salt
Azobilirubin
Erhlich's reagent
P - dimethylaminobenzaldehyde
Potential interference for measurement of urobilinogen
Porphobilinogen
Specimen for ammonia assay method
Heparinized plasma on ice
Reference range for ammonia
9 - 33 umols/L
Reyes Syndrome is associated with?
Viral infections
Aspirin use
ALP
Alkaline phosphatase
Increased in post hepatic jaundice
GGT
Gamma GT
Greatly increased in cirrhosis
Wilson's disease
Decreased ceruloplasmin
Increased copper
Kayser - Fleischer rings
Dubin - Johnson syndrome
Defect in the ability of hepatocytes to transport conjugated bilirubin into the bile
Factor VIII deficiency
Most common hereditary cause of increased bilirubin
Gilbert's syndrome
Gilbert's Syndrome
Reduced activity of the enzyme UDP - glucuronyltransferase
Hepatic Jaundice
Biliary Atresia
Rare condition in newborn infants in which the common bile duct between the liver and the small intesting is blocked or
absent
Post hepatic
Crigler - Najjar syndrome
Severely defective UDP - glucuronyltransferase
Hepatic jaundice
Reference range for AST
0 - 30
Reference range for ALT
0 - 37
Reference range for ALP
30 - 90
Liver and Congestive Heart Failure
Failure of the heart to pump blood at the rate required by the metabolizing tissues
Hypoxia is caused by?
Perfusion of blood through the liver is compromised congestive heart failure
Pernicious anemia is a type of which jaundice?
Prehepatic jaundice
Diagnose Kernicterus
Bilirubin > 15mg/dL
OR
>10 mg/dL for more than 2 weeks
Cirrhosis
Architecture of the liver is permanently damaged
Hepatitis
Necrosis & inflammation of hepatocytes
Decreased liver function
_________ is the most liver specific enzyme
ALT
Enzyme levels if the bile duct is obstructed or if the bile canals are inflamed
Increased AST
Increased ALT
Increased LD
Enzyme levels during true hepatic disease
Highly increased ALT
Significantly increased AST
Significantly increased LD
Enzyme levels during obstruction or inflammation of bile ducts
Increased ALP
Increased GGT
Which enzyme would best aid in identifying hepatobiliary disease?
ALP
Which type of cell does the conjugation of bilirubin take place?
Hepatocyte
Which enzyme is responsible for the conjugation of bilirubin?
UDP - glucuronyltransferase
Which form of bilirubin is water soluble and reacts with a diazo reagent without the addition of an accelerator?
Conjugated bilirubin
Which form of hepatitis is caused by a DNA virus?
Hepatitis B
Which enzyme is most useful in establishing the hepatic origin of an elevated ALP?
5'-Nucleotidase
Hepatitis E is likely to cause serious consequences in which portion of the population?
Pregnant women
Worldwide, most primary malignant tumors of the liver are related to?
Alcoholism
The reagent p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde is used to measure what?
Urobilinogen
Which condition would result in primarily conjugated bilirubin?
Dubin - Johnson syndrome
A urinalysis dipstick test was indicated that urobilinogen was absent. What condition does this support?
Biliary obstruction
Target cells are usually found in this condition
Hemolytic anemia
What is bilirubin?
The degradation product of heme. It is produced in the reticuloendothelial cells following breakdown of RBCs.
Which protein transports bilirubin in the blood?
Albumin.
Name the two types of bilirubin.
Direct and indirect. Indirect or unconjugated bilirubin is bilirubin en route to the liver. Once it goes through the liver it is
known as direct bilirubin, conjugated bilirubin or bilirubin diglucuronide.
Explain what happens to bilirubin in the liver.
It is unconjugated with glucoronic acid by the enzyme uridyldiphosphate glucoronyl transferase (UDPG-T). Following
conjugation, direct bilirubin is excreted into the intestine via the bile duct and is reduced by bacteria to urobilinogen.
Urobilinogen is oxidized to urobilinand gives the normal color to stools.
What is the significance of clay colores or light stools?
It is a sign of obstruction of the bile duct. Urobilin is not being produced because bilirubin is not reaching the intestines.
Which substances related to bilirubin metabolism are normally found in the urine?
Only urobilinogen. Bilirubin should not be present in urine.
What urine abnormality is seen with complete obstruction of the biliary tract?
Decreased urobilinogen
Which bilirubin fractions are analyzed in the laboratory?
Total and indirect. The indirect level is calculated by subtracting direct from total.
Compare the solubility of direct and indirect bilirubin.
Direct bilirubin is soluble in water; indirect bilirubin is not. Bot are soluble in alcohol.
Which form of bilirubin can be excreted in the urine?
Only direct bilirubin.
What is a common method for determination of bilirubin levels?
Diazotization with sulfanilic acid. Bilirubin reacts with diazotized sulfanillic acid to produce azobilirubin.
Name several accelerators that are used in the total bilirubin reaction.
Alcohol or caffeine benzoate-acetate can be used to make the indirect bilirubin soluble.
Name a source of error that can decrease the level of bilirubin in a specimen.
Exposure to light. Hemolysis will also cause a decreased level by the Jendrassik-Grof method.
What is the normal range for total bilirubin in an adult?
0.2-1.0 mg/dL. Conjugated (direct) bilirubin is <0.2 mg/dL.
How do normal values for bilirubin in a newborn compare to those in an adult?
Levels are higher in the newborn. The total bilirubin in a 3-5 day old full term infant is 4-6 mg/dL; for a premature infant,
10-12 mg/dL.
What would cause an increase in total bilirubin with a normal concentration of direct bilirubin?
Prehepatic jaundice for example, hemolytic transfusion reaction, hemolytic anemia, or hemolytic disease of the newborn.
What causes physiologic jaundice of the newborn?
Bilirubin metabolism is impaired because the newborn's immature liver doesn't produce the enzyme required for bilirubin
conjugation. Phototherapy is used to reduce the level of bilirubin.
In hemolytic disease of the newborn, which bilirubin fraction is elevated and why?
Indirect due to excessive breakdown of RBCs by maternal antibody.
What is the risk to the newborn from a high level of indirect bilirubin?
Unconjugated bilirubin (indirect) has a high affinity for brain tissue and causes necrosis (kernicterus). WIthout appropriate
treatment, mental retardation, hearing deficits, or cerbral palsy may result.
At what level of bilirubin would an exchange transfusion be indicated in a neonate?
Each institution establishes its own criteria, but an exchange transfusion is usually performed when the unconjugated
bilirubin reaches 20mg/dL.
What method is used to determine neonatal bilirubin?
Direct spectrophotometry at 454nm. This method can't be used for patients over one month of age because of interfering
lipochromes, such as carotenes.
Name two conditions in which direct bilirubin is elevated.
Hepatic and posthepatic jaundice.
What are the typical lab findings in posthepatic jaundice?
Increased total bilirubin, increased direct bilirubin, decreased urine urobilinogen, and clay colored stools.
T
T/F: Bilirubin is produced from the destruction of RBCs
Albumin
Bilirubin is transported from reticuloendothelial cells to the liver by:
Glucuronyl groups
In the liver, bilirubin is conjugated by addition of:
UDP-glucuronyl transferase
Which enzyme is responsible for the conjugation of bilirubin?
Bilirubin tightly bound to albumin
The term δ-bilirubin refers to:
Methene bridges of bilirubin are reduced by intestinal bacteria to form urobilinogens
Part of the normal metabolism of bilirubin
Water soluble
Characteristic of conjugated bilirubin
T
T/F: Urobilinogen is formed in the intestines by bacterial reduction of bilirubin
T
T/F: Bilirubin undergoes rapid photo-oxidation when exposed to daylight
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Which condition is caused by deficient secretion of bilirubin into the bile canaliculi?
Failure of the enterohepatic circulation
In hepatitis, the rise in serum conjugated bilirubin can be caused by:
Ratio of direct to total bilirubin is greater than 1:2
Characteristic of obstructive jaundice
Hemolytic anemia
This would cause an increase in only the unconjugated bilirubin
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Which form of hyperbilirubinemia is caused by an inherited absence of UDP-glucuronyl transferase?
T
T/F: Total bilirubin level is a less sensitive and specific marker of liver disease than the direct level
Jaundice is usually first seen 48—72 hours postpartum in neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
Serum bilirubin levels in the first week following delivery
Lucey-Driscoll syndrome
Which form of jaundice occurs within days of delivery and usually lasts 1-3 weeks, but is not due to normal neonatal
hyperbilirubinemia or hemolytic disease of the newborn?
Falsely low due to inhibition of the diazo reagent by hemoglobin
A lab measures total bilirubin by the Jendrassik-Grof bilirubin method with sample blanking. What would be the effect of
moderate hemolysis on the test result?
Caffeine
Which reagent is used in the Jendrassik-Grof method to solubilize unconjugated bilirubin?
T
T/F: Most colorimetric bilirubin methods are based upon reaction with diazotized sulfanilic acid
T
T/F: Fehling's reagent is added after the diazo reaction to reduce optical interference by hemoglobin
Hgb interference in the second assay
A neonatal bilirubin assay performed at the nursery by bichromatic direct spectrophotometry is 4.0 mg/dL. Four hours
later, a second sample assayed for total bilirubin by the Jendrassik-Grof method gives a result of 3.0 mg/dL. Both samples
are reported to be hemolyzed. What is the most likely explanation of these results?
Using different pH for total and direct assays
In the enzymatic assay of bilirubin, how is measurement of both total and direct bilirubin accomplished?
Multiwavelength reflectance photometry
What is the principle of the transcutaneous bilirubin assay?
You might also like
- AlHawasi - Manual of Clinical PediatricDocument276 pagesAlHawasi - Manual of Clinical PediatricAhmad Just100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan JaundiceDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Jaundicepapadaad86% (35)
- JM 105 SW 120 Ifu 9510905 enDocument124 pagesJM 105 SW 120 Ifu 9510905 enАлекса МирковићNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of JaundiceDocument4 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of JaundiceVirag PatilNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (Sem)Document6 pagesLiver Function Tests (Sem)Francisco NiegasNo ratings yet
- Uvod:: Total BilirubinDocument5 pagesUvod:: Total BilirubingrgicosNo ratings yet
- Liver Panel: EM 6203 Dr. K. AikenheadDocument24 pagesLiver Panel: EM 6203 Dr. K. AikenheadCrystal Lynn Keener SciariniNo ratings yet
- Liver PathologyDocument35 pagesLiver Pathologynhgwdwffp2No ratings yet
- Jaundice 121213125330 Phpapp01Document29 pagesJaundice 121213125330 Phpapp01ARUSHI ARVINDNo ratings yet
- University of Tabuk Faculty of Medicine: Laboratory Medicine Module CLC 436Document26 pagesUniversity of Tabuk Faculty of Medicine: Laboratory Medicine Module CLC 436kholoud220No ratings yet
- Jaundice: Prepared By: Ozhen ArasDocument29 pagesJaundice: Prepared By: Ozhen ArasAzizul HalidNo ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Bilirubin in Liver Function TestsDocument24 pagesClinical Significance of Bilirubin in Liver Function TestsAbdulsalam JumaiNo ratings yet
- 8 BilirubinDocument25 pages8 BilirubinTagreed DerarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 10 BilirubinDocument34 pagesBiochemistry 10 BilirubinKmo mastnNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument29 pagesJaundiceMurali TiarasanNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument90 pagesLiver Functionapi-19641337100% (1)
- BilirubinDocument2 pagesBilirubinZukhruful MuzakkieNo ratings yet
- Causes of Jaundice: Signs and SymptomsDocument9 pagesCauses of Jaundice: Signs and Symptomspragna novaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 LFT BilirubinDocument22 pagesLab 3 LFT Bilirubinpetemaravich333No ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument35 pagesLiver Function TestsMaham RehmanNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument30 pagesLiver FunctionAra ShirikaNo ratings yet
- Labdxtransfinals PDFDocument16 pagesLabdxtransfinals PDFSubhan Souda MangalasseryNo ratings yet
- Chem-Dr - Zainab-Bilirubin-Lab 2Document10 pagesChem-Dr - Zainab-Bilirubin-Lab 2gmpcbpzdysNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Liver Pancreas FCDocument10 pagesEnzymes Liver Pancreas FCLois Lipanovich100% (1)
- 5 - JaundiceDocument16 pages5 - JaundiceHamzehNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument53 pagesJaundiceAbhishiktaAbhiNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: Signs and SymptomsDocument6 pagesJaundice: Signs and Symptomshero111983No ratings yet
- Bilirubin Metabolism: Hd. - Msc. (Biochemistry)Document18 pagesBilirubin Metabolism: Hd. - Msc. (Biochemistry)MuhamadMarufNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With JaundiceDocument33 pagesApproach To A Patient With JaundiceRahul Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Daftar-IsiDocument2 pagesDaftar-Isi'RahmaT' ANdesjer Lcgs CuyyNo ratings yet
- LFTS - Types of JaundiceDocument21 pagesLFTS - Types of JaundiceSumaira JunaidNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Neonatal Jaundice: Dr. Siddeeg Addow Pediatric Resident Khartoum, SudanDocument17 pagesClinical Approach To Neonatal Jaundice: Dr. Siddeeg Addow Pediatric Resident Khartoum, SudanIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Organ Function Test: Assessment of Functions of The OrgansDocument39 pagesOrgan Function Test: Assessment of Functions of The OrgansSri Abinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Jaundice Group 6Document33 pagesObstructive Jaundice Group 6Qurbon AliNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Neonatal Jaundice: Dr. Siddeeg Addow Pediatric Resident Khartoum, SudanDocument17 pagesClinical Approach To Neonatal Jaundice: Dr. Siddeeg Addow Pediatric Resident Khartoum, SudanGiann PersonaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Laboratory Abnormalities in Liver DisordersDocument55 pagesPathophysiology of Laboratory Abnormalities in Liver DisordersYudha fedrian AKNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: Know AsDocument21 pagesJaundice: Know Asnitesh kotianNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument7 pagesNeonatal JaundiceAnas ObiedNo ratings yet
- TESTS FOR LIVER FUNCTION Arneson BookDocument28 pagesTESTS FOR LIVER FUNCTION Arneson Bookzahrotun nisaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests: Presented By-Dr. Arshiya Kaura (JR 1)Document50 pagesLiver Function Tests: Presented By-Dr. Arshiya Kaura (JR 1)vikasNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: Accumulation of Yellow Pigment in The Skin and Other Tissues (Bilirubin)Document65 pagesJaundice: Accumulation of Yellow Pigment in The Skin and Other Tissues (Bilirubin)qreenNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument27 pagesJaundice: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacherryann_calinogNo ratings yet
- Clase 3 HepatogramaDocument9 pagesClase 3 HepatogramajuanpbagurNo ratings yet
- 15 Coned CCRN GastrointestinalDocument21 pages15 Coned CCRN GastrointestinalAkbar TaufikNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests: Dr. ThomasDocument32 pagesLiver Function Tests: Dr. ThomasthomaskodiatteNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TesDocument58 pagesLiver Function TesnoffrizalNo ratings yet
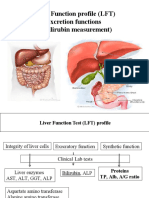
- Liver Function Profile (LFT) Excretion Functions (Bilirubin Measurement)Document22 pagesLiver Function Profile (LFT) Excretion Functions (Bilirubin Measurement)bushra vainceNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument70 pagesLiver Function TestsG Venkatesh100% (5)
- Liver DiseasesDocument10 pagesLiver DiseasesDaniel HikaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test (TSB)Document25 pagesLiver Function Test (TSB)shafyd ramdanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 BilirubbinDocument5 pagesAssignment 3 Bilirubbinhaseeb ShafaatNo ratings yet
- Jaundice - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument11 pagesJaundice - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfCONSTANTIUS AUGUSTONo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument14 pagesJaundiceAnuradha NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- Name of Test:-Serum Bilirubin Test: Tests For Liver FunctionDocument4 pagesName of Test:-Serum Bilirubin Test: Tests For Liver FunctionHiba EmadNo ratings yet
- Aquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45Document8 pagesAquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45JulieNo ratings yet
- HyperbilirubinemiaDocument48 pagesHyperbilirubinemiaEdrik Luke Pialago100% (2)
- Liver Function Tests and How To Relate ThemDocument82 pagesLiver Function Tests and How To Relate ThemG VenkateshNo ratings yet
- BilirubinDocument21 pagesBilirubinlaucegosaNo ratings yet
- Jaundice NotesDocument8 pagesJaundice NotesDanielle Jann Manio ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM Jaundice FinalDocument54 pagesBIOCHEM Jaundice FinalJohnRobynDiezNo ratings yet
- Causes: Neonatal Jaundice or Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia, or Neonatal Icterus (From The GreekDocument7 pagesCauses: Neonatal Jaundice or Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia, or Neonatal Icterus (From The GreekIzzah100% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Jaundice, (Hyperbilirubinemia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandJaundice, (Hyperbilirubinemia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Appendix A Transmittal Letter To The Dean of College of Allied MedicalsciencesDocument5 pagesAppendix A Transmittal Letter To The Dean of College of Allied MedicalsciencesMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- CiullabbDocument71 pagesCiullabbMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Abo Blood Group SystemDocument10 pagesAbo Blood Group SystemMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- SKULLDocument1 pageSKULLMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- HarrisDocument35 pagesHarrisMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- CiullahemaDocument60 pagesCiullahemaMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- WritemepleasetodayDocument40 pagesWritemepleasetodayMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- CiullaisDocument23 pagesCiullaisMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- CiullaparaDocument10 pagesCiullaparaMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- HarrmicroDocument16 pagesHarrmicroMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Excretory SystemMariel Abatayo0% (1)
- HarrhemaDocument62 pagesHarrhemaMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- HarrchemDocument126 pagesHarrchemMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry IDocument8 pagesClinical Chemistry IMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Name of InternDocument3 pagesName of InternMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Be Wary of Tricks and TrapsDocument29 pagesBe Wary of Tricks and TrapsMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- PlasmaDocument5 pagesPlasmaMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Pharmaceutical AgentsDocument5 pagesDrugs and Pharmaceutical AgentsMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- SimsDocument4 pagesSimsMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Did You Get ItDocument13 pagesDid You Get ItMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermssDocument8 pagesDefinition of TermssMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Hematology MicroscopeDocument1 pageHematology MicroscopeMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Rotation 5 - Clinical MicrosDocument2 pagesRotation 5 - Clinical MicrosMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Handbook: With Key Word Index (5th Ed.) - Hudson (Cleveland), OH: Lexi-CompDocument1 pageHandbook: With Key Word Index (5th Ed.) - Hudson (Cleveland), OH: Lexi-CompMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Exchange TransfusionDocument13 pagesExchange TransfusionSaba WaheedNo ratings yet
- Clinical Management GuidelineDocument246 pagesClinical Management GuidelineKyaw Htet KhaingNo ratings yet
- Krok 2 Paper 4Document6 pagesKrok 2 Paper 4berdaderagaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Phototherapy With Alumunium Foil Reflectors On Neonatal HyperbilirubinemiaDocument5 pagesEffect of Phototherapy With Alumunium Foil Reflectors On Neonatal HyperbilirubinemiaBunga Tri AmandaNo ratings yet
- Journal Critiquing Article Reviewed:: Submitted To: Prof. Cynthia A. Umila, RN, MAN Submitted By: Yvette Claire L. BorresDocument6 pagesJournal Critiquing Article Reviewed:: Submitted To: Prof. Cynthia A. Umila, RN, MAN Submitted By: Yvette Claire L. BorresYVETTE CLAIRE BORRESNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice CmeDocument39 pagesNeonatal Jaundice CmeGideon K. Mutai100% (1)
- Jaundice PDFDocument44 pagesJaundice PDFBouzed26 SadekNo ratings yet
- Post Operative Care in The WardDocument9 pagesPost Operative Care in The WardCaamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Recent - Neonatal JaundiceDocument30 pagesRecent - Neonatal JaundiceBibek DasNo ratings yet
- (Bilirubin-Albumin) Binding and Neonatal JaundiceDocument6 pages(Bilirubin-Albumin) Binding and Neonatal JaundiceErwin SmithNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Neonatal Jaundice at A TertiaryDocument4 pagesPrevalence of Neonatal Jaundice at A TertiaryJulia StantonNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: Presenter: DR Rakesh Dey DM Resident Dept of NeonatologyDocument70 pagesNeonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: Presenter: DR Rakesh Dey DM Resident Dept of Neonatologyrakesh deyNo ratings yet
- Depth 2 Concept, Goals, Assessment, Principles ofDocument134 pagesDepth 2 Concept, Goals, Assessment, Principles ofAswathy Aswathy100% (1)
- BMJ-Neonatal Jaundice PDFDocument54 pagesBMJ-Neonatal Jaundice PDFkhacthuanprovipNo ratings yet
- Normal NewbornDocument127 pagesNormal Newbornjanetwillams100% (3)
- Mock - 1 Paper - 2 Test Questions PDFDocument38 pagesMock - 1 Paper - 2 Test Questions PDFAjay GokulNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice Lecture,,By DR Kassahun GirmaDocument25 pagesNeonatal Jaundice Lecture,,By DR Kassahun GirmaKassahun Girma GelawNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: Dr. Nahed Al-NaggerDocument25 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: Dr. Nahed Al-NaggerElok Pratiwi100% (2)
- Case Presentation: Neonate With JaundiceDocument56 pagesCase Presentation: Neonate With JaundiceKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- Neonataljaundice 140128015601 Phpapp02Document39 pagesNeonataljaundice 140128015601 Phpapp02Tina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Managing Breast Milk JaundiceDocument7 pagesUnderstanding and Managing Breast Milk JaundiceJulian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Case Report - HiperbilirubinemiaDocument52 pagesCase Report - HiperbilirubinemiaJenni SaragihNo ratings yet
- Kode Icd-10 Maternal Dan NeonatalDocument64 pagesKode Icd-10 Maternal Dan NeonatalEndah TriNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: Prevention, Assessment and Management 2Document20 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: Prevention, Assessment and Management 2kyawswakyawswaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: A Review and Guidelines For Its Management in Resource Limited CountriesDocument29 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: A Review and Guidelines For Its Management in Resource Limited CountriesJovian LutfiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Phototherapy On Serum Calcium Level in Neonatal JaundiceDocument5 pagesEffect of Phototherapy On Serum Calcium Level in Neonatal JaundiceRahmah WantiNo ratings yet
- (Pedia 3a) Neonat BDocument21 pages(Pedia 3a) Neonat BZai Ra DianaNo ratings yet