Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Z-Score
Understanding Z-Score
Uploaded by
Harsha Vardhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views5 pagesOriginal Title
understanding z-score
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views5 pagesUnderstanding Z-Score
Understanding Z-Score
Uploaded by
Harsha VardhanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
772020
Understanding 2-Seores - MathBitsNotebook(A2- COS Math)
Understanding Z-Scores
MathBitsNotebook.com
‘Topical Outline | Algebra 2 Outline | MathBity’ Teacher Resource
Ik
rus
Contact Person: Di
There are many different normal distributions, with each one depending on two parameters: the
population mean, 1, and the population standard deviation, «. Rather than performing
‘computations on each new set of parameters for a variety of normal curves, it is easier to work in
reference to the "simplest case" of the normal curves, called the standard normal distribution.
The process of converting a value from a normal distribution to a value for the standard normal
distribution is called "standardizing" and requires the use of z-scores.
A z-score (or standard score) represents the number of standard deviations
a given value x falls from the mean,
A z-score is a measure of position that indicates the number
of standard deviations a data value lies from the mean, It is
the horizontal scale of a standard normal distribution.
Z-score Calculation:
X-M
o
+ value being examined x
+ population mean yx
+ population standard deviation o|
Z
The z-score is positive if the value lies above the mean, and
negative if it lies below the mean. To calculate a z-score, the
population mean and standard deviation must be known,
To convert a value, x, to a z-score:
* subtract the population mean,
+ then divide by the population standard deviation. @ Round z-scores to two
decimal places.
htps:mathbtsnotebock com/Algobra2/SlalisticsiST2Scores. html 18
772020 Understanding 2-Scores - MathBitsNotebook(A2- COS Math)
Standard Normal
Distribution
“Bell Curve”
01% % 0. 01%
‘Standard
Deviation @ -3 25-2 15-1 O05 QOS ef v1.5 72 925 +3 Maipits
ZScore: -3 25 2 15 1 05 0 405 4 415 42 425 43
Cumulative
Percent:
0.1% 2.3% 15.9% 50% 841% = OT.7% 99.9%
Remember that z-scores tell us how far a value is from the mean, When you "standardize" a
variable, its mean becomes zero and its standard deviation becomes one.
AREA under a Normal Curve:
Areas under all normal curves are related. For example, the area percentage to
the right of 1.5 standard deviations above the mean is identical for all normal
curves. (The term "area" will refer to "area percentage”)
The fact stated above is the reason we can find an area over an interval for any normal curve
by finding the corresponding area under a standard normal curve (with a mean of 0 and a
standard deviation of 1).
We have seen that the Empirical Rule (68% - 95% - 99.7%) subdivides the area under a
normal distribution into sections with widths of one standard deviation. These subdivisions
are fine for determining percentages as long as we are dealing with values that fall at these
exact subdivision locations.
What do we do when the value does not fall at an Empirical Rule subdivision? By using 2-
scores, we have the ability to locate a percentage (or area) under a standard normal
distribution at any location, Z-scores allow for the calculation of area percentages (also called
proportions or probabilities) anywhere along a standard normal distribution curve (and,
consequently along the corresponding normal distribution).
The area percentage (proportion, probability) calculated using a z-score will be a decimal
value between 0 and 1, and will appear in a Z-Score Table. The total area under any normal
htps:mathbtsnotebock com/Algobra2/SlalisticsiST2Scores. html 26
772020
Understanding 2-Seores - MathBitsNotebook(A2- COS Math)
curve is | (or 100%). Since the normal curve is symmetric about the mean, the area on either
sides of the mean is 0.5 (or 50%).
To find a specific area under a normal curve, find the z-score of the data value and use a Z-
Score Table to find the area. A Z-Score Table, is a table that shows the percentage of values
(or area percentage) to the left of a given z-score on a standard normal distribution.
Positive Z-Score Table Negative Z-Score Table
You need both tables!
+ These tables are designed only for the standard normal distribution, which has a mean of
0 and a standard deviation of 1.
+ The lefi most column is how many standard deviations above (or below) the mean to
one decimal place. (The label in the row contains the integer part and the first decimal of
the z-score.)
+ The part of the z-score denoting hundredths is found across the top row of the table.
(The label for columns contains the second decimal of the z-score.)
+ The intersection of the rows and columns gives the probability or area under the normal
curve. Each value in the body of the table is a cumulative area.
|| Z-Score Tables come in different formats, determined by where the
computations were started. Consider these two most popular formats:
1. One form of the table yields probability or area starting at the mean and going to the
right of the mean up to the needed z-score, These tables are usually labeled "cumulative
{rom mean". This table basically works with half of the area under the normal curve, and
the user must take this into consideration and make adjustments when using this table.
This type of table lists positive z-scores only.
2, Another form of the table yields probability or area starting from negative infinity
(the farthest left) and going to the right up to the needed z-score. These tables are usually
labeled "cumulative from the left”. This table works with the entire area under the normal
curve, and requires less adjustments than the first option. This table lists both positive and
negative z-scores, Most beginning statistical textbooks include this Z-Score Table, and
this site will be using this format
Example 1: Find the probability that a variable
has a z-score of less than 0.36
score = 036
Solution: Find the z-score in the table below. The
intersection shows 0.6406. The probability is 64.06%
(or the area percentage of the yellow region is -
0.6406). ~ *
htps:mathbtsnotebock com/Algobra2/SlalisticsiST2Scores. html
a8
772020 Understanding 2-Seores - MathBitsNotebook(A2- COS Math)
Positive z-scores: (Cumulative Areas from the Left)
Z| 9.0 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 0.08 | 0.09
0.0 | 0.5000] 0.5040] 0.5080] 0.5120] 0.5160 |0.199|0.5239| 0.5279] 0.5319] 0.5359)
0.1 10.5398 | 0.5438]0.5478| 0.5517| 0.5557 |0.5596| 0.5636 0.5675] 0.5714] 0.5753)
0.2 |0.5793| 0.5832] 0.5871| 0.5910] 0.5948 |0.5987|
0.6179] 0.6217| 6
044 |0.6554| 0.6591 0.6628] 0.6664] 0.6700
Example 2: A normally distributed population of test scores has a mean of 80 and a
standard deviation of 5.2.
a) Find the percentage of scores that lies below 73.
Start by setting up a sketch of the situation. This will give you a better understanding of where
your values lie and whether your final answer will be reasonable. Remember that the area
under a normal curve is read as an accumulation starting from the left side of the graph,
Normal Distribution for this Example Tahasnocemes ‘Standard Normal Distribution
73-80
32
=-1.34615
f shaded aress are the same!
i a i th RCM rt a of a CEN
efter o i. 009 [008 | 0.07 | 006 | 008 | Bot | 008 [002 | oot | 00 |
-13
0.0823] 0.0838] 0.0853] 0.0869] o.0885{0.0901)o.0918 0.0934] 0.0951 0.0908)
Percentage of scores
below 73 is 9.01%.
[b) Find the percentage of scores that ies between 82 and 86
To find the percentage of the area between two values, such as 82 and 86, find the z-scores for
each value. From the Z-Score Table, find the area to the left of 86 and subtract the area to the
left of 82.
htps:mathbtsnotebock com/Algobra2/SlalisticsiST2Scores. html 46
772020 Understanaing 2-Seores - MathBitsNotebook(A2- COSS Math)
‘Normal Distribution for this Example i uawiaat ise Standard Normal Distitution
7 mean = 80 82: z-score of 0.3846
O=52
rea to left of 86 = 0.8749,
Brea to left of 82 = 0.6480
rea between: 2269=22.69%
WD) asa soa SBE mm
Le
e696 148
¢) Find the percentage of scores that lies above 73.
To find the percentage of the area that lies "above" the
normal curve (which is 1) and subtract the cumulati
ore, take the total area under a
e area to the left of the z-score.
In part a, 73 had a z-score of -1.34615 with a cumulative area to the left of 0.0901 or 9.01%.
The area to the right of this z-score will be 1 - 0.0901 = 0.9099 or 90.99%.
The need for finding percentages (proportions, areas) associated with z-scores
manually, including use of the Z-Score Tables, can be avoided if you know how to use your
graphing calculator. You can see an example of a problem solved using the calculator under
Normal Distributions. For directions on using the graphing calculator (TI-84+ family), see
Nomal fion and the Calculator,
Be careful! You may be asked to determine this information with, and without, the use of a
calculator, so be ready.
NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in pant or whole) from this site to the Internet is copy
‘and is not considered "fair usc" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use"
jght violation
‘Topical Outline | Aleta 2 Outline | MathBitsNotsbook.com | MathBits’ Teacher Resources
‘TemsofUise Contact Person: Donna Rabesis
Copyright 2012-2020 MathBitsNotebook com
All Righis Reserved
htps:mathbtsneteback com/Algobra2/SlatisticsiST2Scores. html 56
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AA SL - Questionbank - Functions - HardDocument11 pagesAA SL - Questionbank - Functions - HardHarsha Vardhan67% (3)
- AA SL - Questionbank - Functions - MediumDocument25 pagesAA SL - Questionbank - Functions - MediumHarsha Vardhan100% (1)
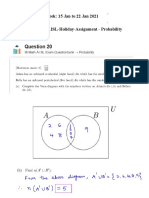
- GR 11 AISL-Holiday-Assignment - ProbabilityDocument11 pagesGR 11 AISL-Holiday-Assignment - ProbabilityHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Solutions Harsha Week 15-22 Jan 2021Document17 pagesSolutions Harsha Week 15-22 Jan 2021Harsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations PDFDocument1 pageQuadratic Equations PDFHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Rythu Bazar PDFDocument5 pagesRythu Bazar PDFHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet