Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handoutssaaccountingheheh
Uploaded by
Mary Elaiza CarinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handoutssaaccountingheheh
Uploaded by
Mary Elaiza CarinCopyright:
Available Formats
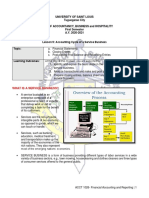
Accounting Process
The Accounting Process is a cycle where a bookkeeper collects, organize, process and close
every financial information that a business engages in. The cycle never stops as each
accounting year is substantial to the latter. Because as long as the business runs, the
owner needs to consistently see the financial health of the company in order for him to
mitigate risks in managing the business. And that’s what the accounting process can provide.
1. Identify the transaction that are recognizable from source documents, like purchase
orders, loan agreements, invoices, etc.
2. Journalizing
A Journal is a book where you record every transaction that the business engages
in.That is why you may hear other people referring to journals as the “Books of
Original Entry”, because it is where you should write down all transactions at the
point when that transaction happened. A journal entry should be always listed in a
double entry manner. Each transaction will be debited and credited. It’s important to
make this step flawless for the reason that this will be the foundation of the whole
accounting accounting cycle.
3. Ledger
Post the entry in the individual accounts in ledgers. Traditionally, the accounts have
been represented as Ts, or so-called T-accounts, with debits on the left and credits
on the right. The account titles are found in the chart of accounts.
The chart of accounts is a listing of all accounts used in the general ledger of an
organization. The chart is used by the accounting software to aggregate information
into an entity's financial statements. The chart is usually sorted in order by account
number, to ease the task of locating specific accounts. The accounts are usually
numeric, but can also be alphabetic or alphanumeric
4. Trial Balance
At the end of the reporting period (usually the end of the month), create a
preliminary trial balance of all the accounts by (a) netting all the debits and
credits in each account to calculate their balances and (b) totaling all the left-side
(i.e., debit) balances and right-side (i.e., credit) balances. The two columns should
be equal.
5. Adjusting Entries are Journalized and Posted
Make additional adjusting entries that are not generated through specific source
documents. For example, depreciation expense is periodically recorded for items like
equipment to account for the use of the asset and the loss of its value over time.
6. Adjusted Trial Balance
Create an adjusted trial balance of the accounts. Once again, the left-side and
right-side entries - i.e. debits and credits - must total to the same amount.
7. Preparation of Financial Statements
Next is the preparation of financial statements (Balance sheet, Income Statement,
Cash Flow Statement and Statement of Changes in Equity). The financial statements
reflects the end results of the business’ efforts within the accounting period.
8. Closing Entries are Journalized and Posted
9. Preparation of Post-Closing Trial Balance
And finally, the last step of the accounting cycle is to create a Post-closing Trial
Balance. This final trial balance contains permanent accounts only; since temporary
accounts are already closed. Never forget to balance your ending debit and credit
accounts.
10.Reversing Entries (Optional)
Reversing entries are made on the first day of an accounting period in order to remove
certain adjusting entries that were made in the previous accounting period. Two
benefits of reversing entries are: the chance of double-counting revenues and/or
expenses will be greatly reduced, and the processing of subsequent documents will be
more efficient. Reversing entries are most often used with accrual type adjusting
entries. (note: adjusting entries that result in increasing an asset or increasing a
liability account may be reversed)
Comprehensive Illustration
Hannah Miranda is a social entrepreneur from Argao. She is into a lot of interesting causes.
Her fine taste is preeminent such that she is considered and authority in planning weddings.
Upon the advice and prodding of her husband, Ryk Sarza, Miranda decided to organize her
wedding consultancy which will be known as SM Wedding Consultancy. Below are the chart of
accounts and the transactions that occurred for the month of May 2018, the first month of
operations.
Chart of Accounts
Acct No. Account
110 Cash
120 Accounts Receivable
130 Supplies
140 Prepaid Rent
150 Prepaid Insurance
160 Service Vehicle
165 Accum. Depreciation- SV
170 Office Eqpt.
175 Accum Depreciation- OE
210 Notes Payable
220 Accounts
230 Salaries Payable
240 Utilities Payable
250 Interest Payable
260 Unearned Referral Revenues
310 Miranda, Capital
320 Miranda, Withdrawals
330 Income Summary
410 Consulting Revenues
420 Referral Revenues
510 Salaries Expense
520 Supplies Expense
530 Rent Expense
540 Insurance Expense
550 Utilities Expense
560 Depreciation Expense-SV
570 Depreciation Expense-OE
580 Miscellaneous Expense
590 Interest Expense
Transactions for the month of May
● May 1
Miranda Invested P250,000 to SM Wedding Consultancy.
Rented Office space and paid two months in advance for P8,000.
● May 2
Miranda issued a promissory note for a P210,000 loan from BPI. The note carries
20% interest per annum and payable, principal and interest, in full in one year.
Hired and office assistant and an account executive each with a P7,800 monthly salary.
Or, each is to receive P300 per day for the 26-day work month. No entry at this point.
They started work immediately
● May 4
Acquired service vehicle for P420,000.
Paid Prudential Guarantee and Assurance Inc. P 14,400 for one year insurance coverage
on the service vehicle
● May 5
Acquired office equipment from Far Square Emporium for P60,000; paying P15,000 cash
and the balance next month.
● May 8
Purchased supplies on credit for P18,000 from People’s Educational Supply.
● May 9
Paid People’s Educational Supply P10,000 of the amount owed
● May 10
Coordinated and finalized simple bridal arrangements for three couples and collected
fees P8,800 per couple.
● May 13
Paid Salaries P6,600. The entity pays salaries every two saturdays.
● May 15
The entity is earning additional revenues by referring consulting clients to friendly
hotels, caterers, printers, and couturiers. Received P10,000 advance fees for the
clients referred.
● May 19
Coordinated and finalized elaborate bridal arrangements for three couples and billed
P12,000 per couple.
● May 25
Miranda withdrew P14,000 for personal expenses.
● May 27
Paid salaries P7,200.
● May 30
Received the ICC-BayanTel telephone bill P1,400.
Received 24,000 from two clients for service billed last May 19.
● May 31
Settled the electricity bill of P3,000 for the month
Required:
1. Prepare journal entries
2. Post journal entries to the Ledger
3. Prepare trial balance
You might also like
- Part 2 Basic Accounting Journalizing LectureDocument11 pagesPart 2 Basic Accounting Journalizing LectureKong Aodian100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Basic AccountingDocument35 pagesChapter 3 Basic AccountingDeanna LuiseNo ratings yet
- Module-7 K12Document82 pagesModule-7 K12Claudette WintersNo ratings yet
- Service Bus - Acctg CycleDocument34 pagesService Bus - Acctg CycleJenniferNo ratings yet
- Accounting CycleDocument9 pagesAccounting CycleRosethel Grace GallardoNo ratings yet
- Journal EntriesDocument2 pagesJournal EntriesMelody Lim DayagNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument14 pagesAccountingKleint Tadem OcialNo ratings yet
- Step 1 - Transactions And/or EventsDocument5 pagesStep 1 - Transactions And/or EventsJEFFREY GALANZA0% (1)
- Accounting CycleDocument33 pagesAccounting CycleKristelle JoyceNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle Upto Trial BalanceDocument60 pagesAccounting Cycle Upto Trial Balanceyenebeb tariku100% (1)
- Final 1st MeetingDocument3 pagesFinal 1st MeetingChristopher CristobalNo ratings yet
- LESSON 10 Business TransactionsDocument8 pagesLESSON 10 Business TransactionsUnamadable UnleomarableNo ratings yet
- Recording TransactionsDocument6 pagesRecording TransactionsGwy PagdilaoNo ratings yet
- What Is Meant by R2R? R2R Plays A Vital Role in The Company, Collecting Data and PostingDocument12 pagesWhat Is Meant by R2R? R2R Plays A Vital Role in The Company, Collecting Data and PostingRAM SUBBAREDDYNo ratings yet
- Business Transactions and Their Analysis As Applied To The Accounting Cycle of A Service Firm (Part 1)Document35 pagesBusiness Transactions and Their Analysis As Applied To The Accounting Cycle of A Service Firm (Part 1)Ponsica Romeo50% (2)
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1: 2. Journal EntriesDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1: 2. Journal EntriesVanessa Lou Torejas67% (3)
- Cma NivasDocument4 pagesCma NivaskasyapNo ratings yet
- Part 3 RecordingDocument65 pagesPart 3 RecordingDONALD GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Mba025 Set1 Set2 520929319Document16 pagesMba025 Set1 Set2 520929319tejas2111No ratings yet
- FABM 2 L2 1st SEM 1st Semester S.Y. 2021 2022Document38 pagesFABM 2 L2 1st SEM 1st Semester S.Y. 2021 2022micx 2104No ratings yet
- 1 The Accounting Equation Accounting Cycle Steps 1 4Document6 pages1 The Accounting Equation Accounting Cycle Steps 1 4Jerric CristobalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Accounting SystemDocument59 pagesIntroduction To Financial Accounting SystemElvanNo ratings yet
- AF Study Material and Practice Questions - Pre Mid TermDocument71 pagesAF Study Material and Practice Questions - Pre Mid TermAkshat Jain100% (1)
- ObjectivesDocument27 pagesObjectivesHazel GumaponNo ratings yet
- Bookeeping Double Entry SystemDocument16 pagesBookeeping Double Entry SystemPhilpNil8000No ratings yet
- BA - L04A - Chart of AccountsDocument8 pagesBA - L04A - Chart of AccountsJessie MelendresNo ratings yet
- Upheavals at A Single Company Pulling DowneDocument5 pagesUpheavals at A Single Company Pulling DowneShesharam ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Bookeeping EntrepDocument71 pagesBookeeping EntrepJanelle Ghia RamosNo ratings yet
- Financial Management AssignmentDocument53 pagesFinancial Management Assignmentmuleta100% (1)
- Accounting and FinanceDocument59 pagesAccounting and FinanceKlodian SulaNo ratings yet
- Books of AccountDocument41 pagesBooks of AccountA cNo ratings yet
- ABM FABM1 AIRs LM Q3 W7 M7.2JounalizingDocument15 pagesABM FABM1 AIRs LM Q3 W7 M7.2JounalizingKarl Vincent DulayNo ratings yet
- Accounting CycleDocument12 pagesAccounting CycleHarjinder Singh100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Chapters 1-4Document32 pagesLecture Notes Chapters 1-4BlueFireOblivionNo ratings yet
- Journal and LedgersDocument3 pagesJournal and LedgersRhea Ramirez55% (11)
- The Basic Business Environment Module 1Document4 pagesThe Basic Business Environment Module 1Wrhed ValentinNo ratings yet
- Abm 1 Midterm Marlowne Brialle T. GalaponDocument9 pagesAbm 1 Midterm Marlowne Brialle T. GalaponCharles Elquime GalaponNo ratings yet
- This Activity Contains 30 QuestionsDocument19 pagesThis Activity Contains 30 QuestionsSylvan Muzumbwe MakondoNo ratings yet
- Posting, Adjusting Entries, Process of Doing A 10-Columnar Worksheets, Closing Entries For Service Type of BusinessDocument18 pagesPosting, Adjusting Entries, Process of Doing A 10-Columnar Worksheets, Closing Entries For Service Type of BusinessRalphjoseph Tuazon100% (1)
- Recording TransactionDocument8 pagesRecording TransactionIan BelmonteNo ratings yet
- PT 1 Transaction AnalysisDocument3 pagesPT 1 Transaction AnalysisJanela Venice SantosNo ratings yet
- Est & Main Accrual Acc Sys L4Document20 pagesEst & Main Accrual Acc Sys L4nahu a dinNo ratings yet
- 6business Transactions and Their Analysis-For Observation4Document38 pages6business Transactions and Their Analysis-For Observation4Marilyn Nelmida TamayoNo ratings yet
- University of Saint Louis Tuguegarao City School of Accountancy, Business and Hospitality First Semester A.Y. 2020-2021Document8 pagesUniversity of Saint Louis Tuguegarao City School of Accountancy, Business and Hospitality First Semester A.Y. 2020-2021Annie RapanutNo ratings yet
- 21MBA0063Document25 pages21MBA0063Kıshöřē JııvăNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 ReviewerDocument16 pagesFabm1 ReviewerNjay SanchezNo ratings yet
- Accounting & Financial AnalysisDocument35 pagesAccounting & Financial AnalysisVishal Ranjan100% (2)
- Presentation by Senthil Kumar BellanDocument21 pagesPresentation by Senthil Kumar BellanSenthil Kumar BellanNo ratings yet
- Finaccl1 120205210417 Phpapp0254Document105 pagesFinaccl1 120205210417 Phpapp0254mukesh697No ratings yet
- Accounting Final RufDocument9 pagesAccounting Final RufSyed HoqueNo ratings yet
- Immersion ReviewerDocument4 pagesImmersion ReviewerAnalyn LafradezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Adjusting The Accounts Service TypeDocument33 pagesLesson 2 Adjusting The Accounts Service TypeSofia Naraine OnilongoNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 Q3 M7 WK7 9 For DigitizedDocument16 pagesFabm1 Q3 M7 WK7 9 For Digitizedquaresmarenzel715No ratings yet
- Accounting Principles - AllDocument104 pagesAccounting Principles - AllAHMED100% (1)
- Accounting As Basis For Managment DecisionDocument18 pagesAccounting As Basis For Managment DecisionRey ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Quarter2Module9 Business ImplementationDocument25 pagesQuarter2Module9 Business ImplementationRexell RedNo ratings yet
- Accounting 111Document6 pagesAccounting 111SOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Question Answer EMBA505Document9 pagesQuestion Answer EMBA505Md. AsaduzzamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 4 NotesLex XuNo ratings yet
- Road Map - GEUTSDocument2 pagesRoad Map - GEUTSMary Elaiza CarinNo ratings yet
- 2017 45th NTRC Annual Report - v1 8 PDFDocument171 pages2017 45th NTRC Annual Report - v1 8 PDFPOC MMPA17No ratings yet
- 2019legislation - RA 11232 REVISED CORPORATION CODE 2019 PDFDocument73 pages2019legislation - RA 11232 REVISED CORPORATION CODE 2019 PDFCris Anonuevo100% (1)
- Chap 018Document37 pagesChap 018Mary Elaiza CarinNo ratings yet
- Notes 03-26-2021Document1 pageNotes 03-26-2021Mary Elaiza CarinNo ratings yet
- 7890136791431Document21 pages7890136791431YahiMicuaVillandaNo ratings yet
- Bir RR 6-2008Document20 pagesBir RR 6-2008Jay CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chattel MortgageDocument4 pagesChattel MortgageJec Luceriaga BiraquitNo ratings yet
- Chap 018Document37 pagesChap 018Mary Elaiza CarinNo ratings yet
- 2306 4149 1 PBDocument17 pages2306 4149 1 PBMary Elaiza CarinNo ratings yet
- Bir RR 6-2008Document20 pagesBir RR 6-2008Jay CastilloNo ratings yet
- IFRS in Your Pocket 2019 PDFDocument116 pagesIFRS in Your Pocket 2019 PDFzahid hameedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1MjhayeNo ratings yet
- Cash RecDocument28 pagesCash RecdazzyahoNo ratings yet
- Revenue Recognition - NPODocument2 pagesRevenue Recognition - NPOHC1990No ratings yet
- Job Order CostingDocument18 pagesJob Order CostingDan RyanNo ratings yet
- Haig Company Maintains A Petty Cash Fund For Small ExpendituresDocument1 pageHaig Company Maintains A Petty Cash Fund For Small ExpendituresAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Single Entity AccountsDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Single Entity Accountsshrish gupta100% (1)
- Questions To Ask When Interviewing An AccountantDocument4 pagesQuestions To Ask When Interviewing An Accountantasset68No ratings yet
- Assign 4 Word - 7edDocument5 pagesAssign 4 Word - 7edValentin Mozheev100% (8)
- CH 11Document43 pagesCH 11Ella ApeloNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Chapter 8Document16 pagesSolutions - Chapter 8Dre ThathipNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Manual Title PageDocument155 pagesInternal Audit Manual Title PageYunita Sari AdhaniNo ratings yet
- Suhaili Personal StatementDocument2 pagesSuhaili Personal StatementSuraya Suhaili Norazmi100% (2)
- An Analysis of The Financial Statements of The Co-Operative Spinning Mills AleppeyDocument12 pagesAn Analysis of The Financial Statements of The Co-Operative Spinning Mills AleppeyShafeekmon AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Karachi Electric Supply Company Limited: Annual ReportDocument72 pagesKarachi Electric Supply Company Limited: Annual ReportGibran LalaniNo ratings yet
- Display Georgian College Academic Transcript UnofficialDocument3 pagesDisplay Georgian College Academic Transcript Unofficialapi-272563560No ratings yet
- Raza ResumeDocument3 pagesRaza Resumeali razaNo ratings yet
- ACC 102 Chapter 6 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesACC 102 Chapter 6 Review QuestionsKaitlyn MakiNo ratings yet
- CashDocument29 pagesCashQuendrick SurbanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Ffa Study Material-DrjDocument19 pagesUnit 1 - Ffa Study Material-DrjTushar Singh SanuNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument5 pagesQuizrinajean catapangNo ratings yet
- Jun18l1fra-C04 QaDocument6 pagesJun18l1fra-C04 QajuanNo ratings yet
- Department of Accounting University of Jaffna-Sri Lanka Programme TitleDocument8 pagesDepartment of Accounting University of Jaffna-Sri Lanka Programme TitleajanthahnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial A40 Kis Aktuaria/Materi TGL 15 A40Document40 pagesTutorial A40 Kis Aktuaria/Materi TGL 15 A40nirmalazintaNo ratings yet
- 03 - Handout - Partnership DissolutionDocument4 pages03 - Handout - Partnership DissolutionJanysse CalderonNo ratings yet
- Investment PropertyDocument10 pagesInvestment PropertyPrudentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Accounting (FAR By: Millan)Document28 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Accounting (FAR By: Millan)Ella MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Understanding To Process CostingDocument43 pagesUnderstanding To Process CostingSarim Saleheen LariNo ratings yet
- LSE AC444 Analysis PDFDocument256 pagesLSE AC444 Analysis PDFHu HeNo ratings yet
- Ice CreamDocument49 pagesIce CreamAnuar LoboNo ratings yet
- 10:06 AM (38 Minutes Ago) To Me: Branch (P&T), BangaloreDocument3 pages10:06 AM (38 Minutes Ago) To Me: Branch (P&T), BangaloreP AND T AUDITNo ratings yet
- CA51024 - Quiz 2 (Solutions)Document6 pagesCA51024 - Quiz 2 (Solutions)The Brain Dump PHNo ratings yet
- Accounting Terms: Instructions: Match The Following Terms To Their Definitions BelowDocument2 pagesAccounting Terms: Instructions: Match The Following Terms To Their Definitions BelowLilik PurwaningsihNo ratings yet