Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AP ES Gist 2018-19 PDF
AP ES Gist 2018-19 PDF
Uploaded by
VijayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AP ES Gist 2018-19 PDF
AP ES Gist 2018-19 PDF
Uploaded by
VijayCopyright:
Available Formats
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Gist of Socio-Economic Survey 2018-19
Geographic, Demographic and Socio-Economic profile of Andhra Pradesh:
Geographical area - 1,62,970 sq km
Area wise - 8th largest state
Located in tropical region
2nd longest coastline in India @ 974 kms
Forest area - 37,707 Sq. Kms (23.54 % the total geographical area) 9th Rank in India
1,62,970 sq km
37,707 Sq. Kms
Population – 10th largest state
2011 Census - 4.10% of the total population of India
Decadal growth of population rose from 18.88 % during 1961-71 to 21.13% during 1981-91
Significant decline was observed in the rate of growth of population and decline is even more
prominent at 9.21% during 2001-11, lower than the All-India’s growth rate of 17.7 %
Density of population – 304 persons per sq.km (2011- 382 persons)
Sex Ratio : 2011 – 997 --- India (2011 - 943) AP is higher in sex ratio
Literacy rate – 2011: 67.35%
Literacy rate of the State is lower than the all India literacy rate at 72.98%
Literacy in Andhra Pradesh increased over 37 % from 29.94 % in 1981 to 67.35 % in 2011
Female literacy rate : 2011 – 59.96%
Urbanisation has been regarded as an important component for growth realization
Percentage of urban population to the total population : 2011 - 29.47%
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 1
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Sand, silt, and clay are the basic types of soils and most of soils are made up of a combination of
these three.
There are various types of soils and the formation of soil is primarily influenced by major
factors such as climate, altitude and composition of bedrock etc.
Disproportion in the distribution of rainfall in the country and excessive heat contribute special
characters to the soils.
Land utilization:
Net sown area – 37.08% (60.43 lakh hectares)
Forest – 22.63 % (36.88 lakh hectares)
Current fallow lands – 8.91% (14.51 lakh hectares)
Land put non-agricultural uses – 12.63% (20.58 lakh hectares)
Barren and uncultivable land – 8.25 % (13.45 lakh hectares)
Fallow land – 7.03%
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 2
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Back to Basics : Net Sown Area and Gross Cropped Area
Net Sown Area is the area sown with crops but is counted only once
Gross Cropped Area (GCA) is the total area sown once, as well as more than once in a particular
year. When the crop is sown on a piece of land for twice, the area is counted twice in GCA
Back to Basics: Current fallow lands
This represents cropped area which is kept fallow (unsown) during the current year
Back to Basics : Forest Area
This includes all land classified either as forest under any legal enactment, or administered as
forest, whether State-owned or private, and whether wooded or maintained as potential forest
land.
The area of crops raised in the forest and grazing lands or areas open for grazing within the
forests remain included under the “forest area”
Back to Basics : Land put non-agricultural uses
This includes all land occupied by buildings, roads and railways or under water, e.g. rivers and
canals, and other land put to uses other than agriculture
Back to Basics : Barren and uncultivable land
This includes all land covered by mountains, deserts, etc. Land which cannot be brought under
cultivation except at an exorbitant cost is classified as unculturable whether such land is in
isolated blocks or within cultivated holdings
Back to Basics: Fallow land
This includes all land which was taken up for cultivation but is temporarily out of cultivation for
a period of not less than one year and not more than five years
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 3
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Macro-Economic Aggregates:
GSDP at current prices for 2018-19 - Rs.9,33,402 Crores [Rs.8,09,548 crores for 2017-18 (First
Revised Estimates) compiled by adding Product taxes and deducting Product subsidies to the
GVA at current basic prices (GVA + Product taxes – Product subsidies = GSDP @ CP)
Central Statistical Office(CSO) has shifted the base year from 2004-05 to 2011-12 and also
revised the methodology
As per the Advance Estimates, the GSDP at constant (2011-12) Prices for the year 2018-19 is
estimated at Rs.6,80,332 crores as against Rs.6,12,793 Crores for 2017-18 (First Revised
Estimates) indicating a growth of 11.02%
India’s GDP - 7%
Sectoral growth rates of GVA of Andhra Pradesh for 2018-19 at constant (2011-12) prices
Agriculture : 10.78% , Industry: 10.24% and Services sector: 11.09%
Per Capita Income (NSDP) of Andhra Pradesh at current prices increased to Rs.1,64,025 from
Rs.1,43,935 in 2017-18 registering a growth of 13.96 %
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 4
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 5
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Back to Basics: GSDP
Back to Basics: GVA
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 6
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Back to Basics: Link between GVA and GSDP
Back to Basics: NSDP
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 7
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Back to Basics: GDP
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 8
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Back to Basics: Sectors of Economy
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 9
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 10
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Public Finance:
Revenue and Expenditure 2017-18:
Own Tax sources - Rs. 49,813 [Rs.58,125 Cr in FY 2018-19 (RE)]
Own Non Tax sources - Rs. 3,814 Cr
Central Transfer - Rs. 51,250 Cr
Total Expenditure by the State excluding ways and means advance - Rs.1,37,486 cr
[Rs.1,48,697 Cr in FY 2018-19 (RE)]
Revenue expenditure - Rs. 1,21,214 Cr [Rs. 1,26,410 Cr in FY 2018-19 (RE)]
Total Debt : Rs. 1,94,862 Cr in 2017-18 [Rs. 2,58,928 Cr in FY 2018-19 (RE)]
Sales Tax accounted for 38% and GST at 35% for 2018-19 RE
Revenue Deficit @ 2017-18 : Rs.16,152 cr
Fiscal Deficit @ 2017-18 : Rs.32,373 cr
Total Expenditure 2018-19: Rs. 1,48,697 Cr
Total Expenditure 2017-18: Rs. 1,37,486 Cr
Revenue Expenditure 2018-19: Rs. 1,26,410 Cr
Revenue Expenditure 2017-18: Rs. 1,21,214 Cr
Total Debt 2017-18: Rs.1,94,862 Cr
Total Debt 2018-19: Rs.2,58,928 Cr
Back to Basics: Expenditure by GOAP
Govt expenditure can be classified in two broad formats: Capital Expenditure and Revenue
Expenditure
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 11
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Capital Expenditure:
This expenditure basically associated with Govt’s asset creation activity.
Example: Building roads, airports, or buying defence equipments etc.
Revenue Expenditure:
This expenditure basically refers to expenditure by Govt to maintain its assets.
Broadly it encompasses expenditure made by govt on salaries for employees, pensions,
maintainance of infrastructure, buying accessories of various equipments which are part of govt
asset , subsidies on education, PDS, loan that has been repaid by govt etc.
Back to Basics : Own Tax Sources
State’s own tax revenue includes taxes such as
Sales Tax
Stamps and Registration
State GST
Professional tax
State Excise
Taxes on motor vehicles
Compensation twds loss of sales tax
Economic variables such as share of agriculture in net state domestic product (NSDP), share of
manufacturing in NSDP, share of non-agricultural sector in NSDP, share of tertiary (services) sector in
NSDP, per capita NSDP, consumer price index, previous year’s deficit/surplus as per cent of previous
year’s total expenditure (revenue account) are taken as the factors affecting the levels of state’s own tax
revenues
Back to Basics : Own Non-Tax Sources
Govt revenue that is either requited or voluntary or both
In the case of voluntary requited payments a further distinction is made between revenue from
assets and revenue from sale of goods and services
Non-tax revenues cover a wide array of government revenue sources, ranging from proceeds
from the sale of communications bandwith, to mineral royalties to interest on loans by govts to
fines and penalties
Non-tax revenues ensure that the sources of revenue to the State exchequer are broad-based
and buoyant
AP’s Own Non-Tax sources include
Mines and minerals
Forests
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 12
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Interest receipts
Education
Medical and Health
Back to Basics: Revenue Deficit
Revenue deficit is a result of a mismatch between expected revenue and expenditure
Revenue deficit arises when government’s actual net receipts are lower than the projected
receipts
On the other hand, if the actual receipts are higher than projected by the government, the
situation is termed as revenue surplus
It should be noted that revenue deficit does not mean the actual loss of revenue.
Let’s understand the same with the help of an example.
If the government spends Rs 100 and earns Rs 125, the net revenue will be Rs 25.
However, if the government has estimated expenditure at Rs 100, and earning at Rs 130,
than its expected revenue would be set at Rs 30. But, since the actual earning is Rs 25, the it
will lead to a revenue deficit of Rs 5 (Expected Revenue Rs 30- Achieved Revenue Rs 25).
Back to Basics: Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit is the difference of government expenditure and government revenue.(assume
that government expenditure is more than revenue).
More fiscal deficit means government has no money, he has to borrow money from central
bank or through some bond/scheme.
If government is borrowing from RBI, in other words RBI has to print more money, so it will
increase the liquidity of money in the market. So people will have more money in their
hand,but we have limited resources. For example, before there was 5 car buyers for 1 car, now
there is 10 car buyer for 1 car. So demand for car will increase and it will increase the price of
car. So price of everything will go up. Ultimately Inflation will go up.
If government is borrowing money from people as bond or some scheme through,
government has to pay high interest after some year. So people will invest their money in
government schemes, so liquidity of the money will come down. Before we have 5 car buyer
for 1 car, now we have 2 car buyer for 1 car, so car price will go down. Price of everything will go
down, people will buy less things. It will slow down the industrial growth and it will be deflation
in the country. It will make economic growth sluggish. And in the situation of the deflation,
Government has to pay high interest to the people.
Third case, government has to borrow money from world bank or from some other country.
Because of that Government has to devalue it’s currency.
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 13
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
As government has no money, government can’t bring any new development scheme. It will become
difficult to tackle any crisis over country.
Prices:
Consumer Price Indices for Industrial Workers:
Increased by 4.20% in state
Increased by 5.63% in All India level
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) serves as an important determinant in formulation of trade, fiscal and
other economic policies by the government
WPI (Base Year 2004-05) for All Commodities increased from 117.3 in Apr 2018 to 119.9 in Mar 2019
Back to Basics: Consumer Price Index
o Consumer Price Index is a measure of change in retail prices of goods and services consumed
by defined population group in a given area with reference to a base year.
o This basket of goods and services represents the level of living or the utility derived by the
consumers at given levels of their income, prices and tastes.
o This index is an important economic indicator and is widely considered as a barometer of
inflation, a tool for monitoring price stability and as a deflator in national accounts.
o Presently the consumer price indices compiled in India are CPI for Industrial workers CPI(IW), CPI
for Agricultural Labourers CPI(AL) and; Rural Labourers CPI(RL) and (Urban) and CPI(Rural).
Back to Basics: Wholesale Price Index
o Wholesale Price Index (WPI) measures the average change in the prices of commodities for
bulk sale at the level of early stage of transactions.
o The index basket of the WPI covers commodities falling under the three major groups namely
Primary Articles, Fuel and Power and Manufactured products.
o WPI basket does not cover services. In India WPI is also known as the headline inflation rate .
o Office of Economic Advisor (OEA), Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of
Commerce and Industry calculates the WPI.
Public Distribution:
Total Fair Price Shops (FPS) – 28,510 as on 31/03/2019
Govt. has enhanced the scale of distribution of Redgram dal through Fair Price Shop
Unpolished rice (Brown Rice) is being distributed to BPL card holders
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 14
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Andhra Pradesh is the first State in the country to implement FP Shops Automation under
“End-to- End Computerization of TPDS Operations”
On 8th June, 2017, Government of Andhra Pradesh declared the State as “Smoke free State"
Allotment of commodities under e-PDS and distribution of commodities through e-PoS cum e-
weighing devices
Fair Price Shops Portability System:
To leverage of technology to the benefit of BPL cardholders, govt has introduced F.P. shops
portability system.
Under this system, the ration cardholder can draw essential commodities from any ePoS
enabled F.P. shop irrespective of having his / her ration card number in Dynamic Key Register of
a particular ePoS enabled F.P. shop.
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 15
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Seasonal Conditions:
South – West Monsoon rainfall
o 2018-19 : 456.6 mm
o Normal rainfall : 556 mm
o Deficit : - 18 %
North-East monsoon
o 2018-19: 124.1 mm
o Normal : 296 mm
o Deficit: - 58 %
Agriculture:
Area under foodgrains
o 2018-19: 40.26 lakh hectares
o 2017-18: 42.06 lakh hectares
o Decrease of 4.27%
Total production of foodgrains
o 2018-19: 151.12 lakh tonnes
o 2017-18: 167.22 lakh tonnes
o Decrease of 9.63%
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 16
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Cropping Intensity
o 2018-19: 1.24
o 2017-18: 1.26
o Marginally declined
Number of holdings
o Increased from 76.21 lakh in 2010-11 to 85.24 lakh in 2015-16
o Huge rise in the number of holdings + decline in the area operated fall in the average size
of the holding from 1.06 hectares in 2010-11 to 0.94 hectares in 2015-16
NEW INITIATIVES:
“YSR RythuBharosa” Scheme:
From October 15th, 2019
Financial assistance to the farmer families + tenant farmers Rs. 12,500/- per year
Extend Interest free loans to all the farmers who avail crop loans during 2019-20
Facilitate “Crop Insurance Premium payment by the government itself instead of farmers for the
entire notified area”
Soil Health Cards
During 2nd cycle of soil health card scheme 6.80 lakh soil samples were collected & analyzed
and 34.62 lakh soil health cards were distributed to the farmers.
Navadhanyalu Seeds
Distributed 7,748 Qtl with a subsidy value of Rs.444.64 Lakhs
Benefitted 0.90 Lakh farmers
Big Tractors
Govt had supplied 11,030 big tractors
Total outlay: 168.05 Cr
Reason To increase the farm power availability
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 17
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
State Agriculture Mission:
Policy advisory body to address the issues of farmers
To have better coordination among the sectors allied to agriculture
Aim To overcome the challenges in delivering quality and timely services to the farming
community and also look into all aspects of production, marketing and pricing of Agriculture and
Horticultural commodities to mitigate the agrarian issues
Horticulture:
Root and tuber crops, ornamental crops, plantation crops like coconut, cashew and cocoa etc
Area - 17.62 Lakh Ha
Production – 327.57 lakhs MT
Area under microirrigation - 2 lakh ha Increased by 8 %
A.P. ranks 2nd in Cashew, Mango and Sweet Orange
A.P. ranks 2nd in Micro Irrigation area coverage
A.P. stands 2nd in the country in silk production
A.P. stands at 1st position in productivity for Chillies, Cocoa, Lime, Oil Palm, Papaya and Tomato
A.P. Ranks 1st in area and production of fruits and spices
Mulberry :
8,560 acres of Mulberry gardens were covered with Drip
Total : 1,04,790 acres
Raw Silk :
Production – 7,476 MTs of Raw Silk (BV+CB)
Growth rate - 10.35%
Yarn Support price scheme
Benefitted 35,069 Silk Handloom Weavers
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 18
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Livestock and Fisheries:
Andhra Pradesh is one of the advanced states for Animal Husbandry sector in the country
Key growth engines : Livestock Milk, Meat and Egg
Milk is the single largest commodity contributing highest economy to the State
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 19
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Rankings of AP
o 1st in Egg production (2036.94 Cr)
o 4th in Meat production (8.03 lakh Metric Tons)
o 4th in Milk production (150.44 Lakh Metric Tons)
Fodder Security Policy:
To provide quality feed and fodder to the Livestock
Feed and fodder of different categories to the farmers / Goshalas will be provided on subsidy
basis
Distributed 45,058 MTs of TMR, 1.32 LMTs of Silage and 62,000 MTs of cattle feed on
concessional prices
Animal induction policy:
31,082 high yielding animals have been inducted from other States in convergence with Welfare
Financing Corporations as a part of poverty alleviation program.
Production of fish/prawn:
o AP ranks 1st in total fish and shrimp production
o Contributes more than 65% of cultured shrimp produced in the country
o AP is contributing 1.61% of global and about 24% of national fish production
o Employment to 14.5 lakh persons
o Contribution to State GSDP : 7.4%
o AP ranks 1st in Aquaculture area and Production
o Power tariff concession provided to 53,500 aquaculture farmers
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 20
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 21
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Forests:
Ranks 9th in India
Forest cover area : 37,707 Sq. Km
Forest cover: 23.54 %
Very Dense Forest : 1,957 Sq. Kms
Moderate Dense Forest : 14,051 Sq. Km
Open Forest : 12,139 Sq. Kms
Scrub Forest : 95.60 Sq. Kms
Wildlife Sanctuaries : 13
National Parks : 3
Total area of National Parks + Wildlife Sanctuaries : 8139.89 Sq. Kms [ 2.53% of the State’s
Forest area and 4.44% of the State’s Geographical area ]
Zoological Parks – 2
Deer Parks – 2
Deer Parks – 2 functioning under the control of private organizations
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 22
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Agriculture Marketing:
Andhra Pradesh state stood 1st place in terms of the total value of trade done on e-NAM.
Market Yard Guntur stands at 1st position with total Trade Value of Rs.6440 Cr
Market Yard Guntur stands at 1st position in terms of online payments made
Market Yard, Duggirala stands at 1st place among all markets in country, in terms of number of
online payments made to farmers with 2,817 No’s of lots for which online payments were made
Industrial Development
1st state in India to take up initiative in bringing A.P. Single Window Clearances system under
e-Biz project of National e-Governance plan of Govt of India
Nearly 6 lakh new persons joining the workforce every year
About 30 lakh jobs are to be created in next five years
Large and Mega industrial projects @ 2018-19:
44
Investment - Rs.16,925.08 crores
Employment - 14130 persons
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises @ 2018-19:
10,068
Investment - Rs.3443.57 Crores
Employment - 93240 persons
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 23
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Chennai Bangalore Industrial Corridor
It is one of the mega Infrastructure projects of Government of India which passes through the
State
3 Nodes have been identified in Phase-I: Krishnapatnam Industrial Node (KPTIN) is a planned
area located in south of Krishnapatnam port as industrial development of around 12,000 ha
Main Objective: Increase the share of manufacturing sector in the GDP of the country and to
create smart sustainable cities which will have worldclass infrastructure, convenient public
transport, power management and an efficient water and waste management system
Vizag Chennai Industrial Corridor
It is a key part of the planned East Economic Corridor and India’s first coastal corridor and the
extent of it is considered from Pydibheemavaram in Srikakulam district to Chennai in Tamilnadu
Nearly 800-kilometer corridor links India with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations
(ASEAN) and East Asian economies that form the bedrock of global manufacturing economy
The corridor traverses 9 districts of the state of Andhra Pradesh
VCIC intends to complement the ongoing efforts of the Government of Andhra Pradesh (GoAP)
to enhance industrial growth and create high quality jobs
Two Nodes, i.e., Visakhapatnam Node and Yerpedu-Srikalahasthi Node were prioritized for
making initial investments
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 24
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Industrial Infrastructure:
GoI sanctioned Mega Food Park at Mallavalli, Krishna District with an estimated cost of Rs.
125.25 crores and the projected Investment is Rs.400 crores
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 25
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Mines and Geology:
Main aim of State Mineral Policy is to serve as a guiding force to translate the State’s mineral
potential into reality with eco-friendly and sustainable mining
Major contributor for the economic growth of the State Minerals
Focus minerals - Bauxite, Heavy minerals, Beach Sand, Limestone, Gold, Diamond, Dolomite,
Oil & Natural gas, Uranium, Garnet, Granite, Titanium, etc.
Purpose - establishment of Cement, Gas based Thermal Plants, Oil Refinery, Cutting & Faceting,
Mining & Refinery, Steel & Sponge, Alumina Smelter and Aluminium Refinery etc., as focus
industry for overall development of the Mining Sector in the State
Mining leases for major minerals: 380
Quarry leases for cut and dressed blocks of granites : 1735
Quarry leases for industrial minerals : 1083
Quarry leases for other Minor Minerals (Construction Minerals) : 4177
State Mineral and Mining sector contributed Rs. 2,147 crore of Mineral Revenue to the
state exchequer during 2017-18
Mineral Revenue during 2018-19 (upto Oct, 2017) : Rs. 2,463 Crore
Percentage growth compared to last year during the same period : 14.71 %
Commerce and Exports:
2017-18 Exports : Rs. 84,640.56 Cr
2018-19 : Rs. 98,983.95 Cr
Major exports - Drugs & Pharmaceuticals, Marine, Agriculture and Agro based products,
Handicrafts, Minerals and Mineral products and Software products
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 26
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Water Resources:
Utilization:
308.703 TMC @ Existing projects
468.688 TMC : Planned utilization under ongoing projects
Irrigation:
Irrigation potential created upto March 2019 : 105.36 lakh acres
New Projects taken up during 2018-19 : 14 [Estimated cost - Rs. 26,942.75 Crs]
12 Projects (11 Projects under Jalayagnam and 1 New Project) are proposed for speedy
completion.
Rainfall:
2018-19 : 34% deficit rainfall
Area under falling category from May-2018 to May-2019 : About 79%
Area more than 8 m. water level in May-2018 : 57%
Area more than 8 m. water level in May-2019 : 66%
Groundwater:
Average groundwater level in May-2019 : 16.19 m
Average groundwater level in May-2018 : 12.80 m
Net fall of 3.39 m from the previous year water level
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 27
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Power:
Installed Capacity : 19,160 MW
Free Agricultural Power Supply @ day time 9 hrs per day
Agricultural Services released @ 2018-19 86,430
Energy met has increased to 63,144 MU @ 2018-19
Per capita consumption of electricity - 1,147 units
Distribution of LED bulbs 2.20 crores
Energy efficient lights @ Gram Panchayats 25.60 lakh
3.23 lakh energy efficient fans and 1.48 lakh numbers of energy efficient tube lights distributed
to households
AP : More than 33% of total LED street lighting in the country in both urban and rural areas
Total LED Street Lights installed : 26.40 lakhs [All India – 78.60 lakhs]
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 28
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Roads:
o Total R&B Road network – 46,237.65 Kms
State Highways - 13500.45 Kms
Major district road and Rural roads – 32,737.20 Kms
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 29
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
o National Highways in AP – 36
o Length of National Highways (36) in AP – 6,859.66 Km [NHAI : 2,267.593 Km + MoRT & HPIU,
Machilipatnam: 461.56 Km]
o Density of National Highways in AP - 13.72 Kms per lakh population (2011)
o Density of National Highways in India – 10.89 km
o For every 1,000 Sq. Kms (AP) - length of 41.46 Kms is available
o For every 1,000 Sq. Kms (India) – 40 km
Transport:
Total vehicles registered – 119.96 lakh vehicles
89% of the vehicles on road are two wheelers
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 30
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
AP stands at 7th position with 8,060 fatalities (5.4% share) [Road Accidents]
Corporation has 4 zones, 12 regions and 128 depots with a total fleet strength of 12,027 buses
and 53263 employees on rolls as on March, 2019
Average vehicle productivity per day of its fleet is 365 kms and the Corporation achieved
99.71% fleet utilisation in 2018-19
Airports:
o Currently there are 6 operational Airports
o Passenger movement at AP Airports enhanced to 5.44 MPPA (FY18-19) at a CAGR of 37% in the
past 5 years
o Air traffic movements recorded during 2018-2019 is 70,000
Seaports:
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 31
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Information Technology:
IT Sector Employment – 30,656 || Investment – 1,030 crores
Electronics Sector Employment – 18,750 || Investment – 1,030 crores
Mee-Seva currently has 460 high impact services 14.44 crore transactions
Under e-Pragathi, more than 12 departments are on-board on this platform with 100+ services,
in the first quarter of Year 2019-20
School Education:
o Total enrollment: 70.41 lakhs
o Annual average dropout rate at I-V classes (Primary Level), I-VIII (Elementary Level) was 0% and
3.94% at IX-X (Secondary Level).
o Necessary measures have been taken to retain children into schools by conducting Rajanna Badi
Bata
o Mid meal scheme 37.22 lakh children
o Digital Class Room equipment is provided in 5000 schools
o Virtual Class Room system integration is completed in 3938 Schools
o Govt has introduced a new scheme called ‘Badikosta’ to provide bicycles to VIII & IX Class girl
students. 3.75 lakh bicycles were distributed to girl students
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 32
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan:
o 352 KGBVs were sanctioned in Educationally Backward mandals in the state and all these
schools were operationalized with an enrolment of 71,495 children
o Andhra Pradesh is the 1st state in the country to introduce digital class rooms in all 352 KGBVs
o KGBVs upgraded to Intermediate level education in 2018-19
o Advanced Digital Class rooms (DCRs) : 2000 Model Primary schools
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 33
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Intermediate Education:
o 457 government junior colleges including 8 govt vocational junior colleges
o 124 private Aided Junior Colleges
Collegiate Education:
Higher Education has been identified as a growth engine in the sunrise state of Andhra Pradesh
and is pushed in a mission approach for sustaining and promoting quality of education and for
providing purposeful education, particularly to students hailing from marginalized sections of
the society
148 Government degree colleges
137 Private aided colleges
Andhra Pradesh State Skill Development Centre (APSSDC): 50 training centres @ Govt Degree
Colleges
25 Key Performance Indicators were designed and colleges were ranked based on indicators
AP Fibre Grid connectivity with 10 mbps 54 Govt. Degree Colleges
‘Solar Equipment’ solution 49 RUSA colleges
Virtual Classrooms @ RUSA funded Colleges
Technical Education:
Government Polytechnics: 84
Aided Polytechnics: 2
Private Polytechnics: 201
Skill Development Centers: 41
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 34
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
PMKVY is initiated to bridge the gap between Industry needs and output from the Educational
Institutions
Family Welfare:
o Sub-centres : 7458
o Primary Health Centers : 1148
o Community Health Centers : 198
o Area Hospitals : 28
o District Hospitals : 14
o Mother and Child Health Centres: 3
o Estimated crude birth rate: 16.2
o Estimated crude death rate: 7.2
o Infant Mortality Rate : 32
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 35
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
o Special New Born Care Units (SNCUs) : 26
o Mini Special New Born Care Units(Tribal) : 21
o Nutrition Rehabilitation Centres : 18
o Newborn Stabilization Units (NBSUs) : 95
o New Born Care Corners (NBCCs) : 789
o Urban Primary Health Centres (UPHCs) : 243
Purpose: to reduce Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) by strengthening neo-natal care services
Dr.YSR Aarogyasri Health Care Trust Services
1,459 Network Hospitals
22.35 Lakh therapies were pre-authorized
13.97 Lakh patients benefitted
117 new procedures added to the existing 942 procedures under Dr. YSR Aarogyasri scheme
AP Vaidhya Vidhana Parishad:
National Programme for Prevention and Control of Fluorosis is being implemented in Guntur,
Prakasam and Nellore districts
At present 8 Cardiac Care Units are functioning
At present 4 Trauma Care Centers are functioning
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 36
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Women Development and Child Welfare:
257 ICDS Projects (200 Rural, 33 Urban & 24 Tribal)
Supplementary Nutrition Programme - prime service rendered under ICDS
For ensuring Quality hot cooked Mid–Day Meal, 1622 Panchayats started growing Nutri
Gardens
Welfare of Disabled:
Pensions: 5.61 lakh Differently Abled persons + 20.84 lakh Senior Citizens
8 Pre-matric and 2 Post-matric hostels
Scholarships to Differently Abled students including Mentally Retarded - 7044
Backward Class Welfare:
At present, there are 773 Govt B.C. hostels, (594 hostels for boys and 179 hostels for girls)
69 BC Residential Schools (56 Residential schools, 11 Upgraded to Jr. Colleges and 2
Independent Jr. Colleges)
Reimbursement of tuition fee for BCs, EBCs & Kapus is one of the main scheme under
Navarathnalu
Social Welfare:
As per the 2011 Census, Scheduled Castes population forms 17.08 % of the total population of
Andhra Pradesh and 79.98% of the Scheduled Caste people live in rural areas
758 hostels are functioning in the state, with an admitted strength of 73,600 in 2018-19
38 Integrated hostel Welfare Complexes are functioning are in the State with an admitted
strength of 8,149
Under Jagjeevan Jyothi Scheme (Free Power) an amount of Rs.108.96 crores was spent
benefitting 13.85 Lakh SC households.
Tribal Welfare:
o The tribal population of Andhra Pradesh according to 2011 Census is 27.39 lakh constituting
about 5.53% of the total population of the State.
o Govt is keen on providing quality residential education to all ST children, safe drinking water to
all ST habitations, providing connectivity to unconnected villages, electrification of unelectrified
ST habitations and Capacity building and Skill upgradation of ST youth
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 37
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
o School Health Programme (Aadivasi Aarogyam) has been implemented in (969) TW Educational
Institutions
o Under health, all 158 PHCs in tribal areas are converted as 24x7 PHCs
Minorities Welfare:
13 Pre-matric Minorities Hostels and 10 Post-matric Hostels functioning aiming the educational
and social development of the poorest of the poor minority students
6 Residential schools in the state aiming the educational and social development in Minority
students with residential amenity
YSR ASARA (SHG Scheme for Minority Women) will be implemented to further strengthen the
system
Housing:
5,84,541 houses in Rural and Urban areas have been taken up for completion
Planning to construct 25 lakh houses in 5 years as a part of “Navaratnalu”, in line with the
government of India’s vision of Housing for all
Rural Supply and Sanitation:
By 2024 every rural person will have access with 70 LPCD within their household premises
Currently, 52 % of habitations are covered with 55 LPCD and 47% of habitations are covered
with 40 LPCD service level, 1% (401) habitations are quality affected
Out of 90 Lakh rural households, about 25 Lakh households are having house connections
Municipal Administration:
110 Urban Local Bodies [14 Municipal Corporations, 71 Municipalities and 25 Nagara
panchayaths]
110 ULBs declared as ODF
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 38
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
MEPMA
o Main objective of MEPMA is to organize poor women into Self Help Groups by covering all
families living in slums and enable them to become self-reliant
o Self Help Groups: 2,16,810
o Total - 22,64,158 members
o Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): 48,65,714 members were enrolled by
covering SHG Members
Rural Development:
Government has announced YSR Pension Kanuka as part of Navarathnalu comprising of various
welfare and developmental activities
Social Security Pensions amount for Old Age Persons, Widows, Toddy Tappers, Weavers,
Single women, Fishermen, ART (PLHIV) Persons,Traditional Cobblers : Rs.2250/- per month
Social Security Pension to Disabled persons : Rs.3,000/- per month
People affected with Chronic Kidney Disease who are undergoing dialysis in both Government
and network hospitals : Rs.10,000/- per month
Reduction of the pension eligibility age from 65 years to 60 years
Under this social safety scheme for poor and vulnerable, authenticated Aadhaar linked pensions
will be provided to 58 lakh beneficiaries with a monthly outlay of over Rs.1374.67 Crores and an
annual outlay of Rs.16,496.04 crores
MGNREGS is being implemented in 12,915 Gram Panchayats in 661 mandals
Under MGNREGA, 1,65,975 Separate Job Cards have been issued
14,985 Shrama Shakti Groups of workers with disabilities are formed in 661 mandals
e-FMS has been established with the objective of implementing an efficient fund transfer
system through online money transfers
MGNREGS converges during 2019-20:
Internal CC Roads : 5000 kms
1 lakh Farm Ponds under Panta Sanjeevini
Anganwadi Buildings : 3000
1 lakh IHHLs (Housing Beneficiaries)
Mini Gokulams : 1300
Animal Hostels : 500
Play Fields : 2000
Village Parks : 661
Burial Grounds : 3000
Laying of 3000 Kms of WBM Roads
BT Roads : 2000 Kms
Horticulture Plantation : 1 lakh acres
Avenue Plantation : 10000 Kms
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 39
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Loan reimbursement and VLR interests are covered under YSR Aasara scheme
The outstanding balances in the SHG women accounts as on 11.04.2019 will be paid to the
SHG women by the Government in four installments
Under Watershed development programme, 3907 watersheds with an area of 19.54 lakh Ha
were completed
Poverty:
Work Force participation Rates (WFPRs) as per Current Weekly Status (CWS):
All India : 32.7%
AP : 41.8%
WFPR @ Rural Areas
All India : 32.6%
AP : 44.4%
WFPR @ Urban Areas
All India : 32.9%
AP : 36.8%
Employment:
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 40
Subscribe to IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel @ Youtube
Skill Development:
Andhra Pradesh State Skill Development Corporation:
99,591 unemployed youth were trained
31,817 got placements
SC training programmes :
11,110 were trained
2,919 got placements
438 Job Melas have been conducted in 2018-19 and facilitating jobs for 38,850 unemployed
youth
Governance:
Government has decided to go all out with Navarathnalu, an integrated scheme with themes
covering agriculture, health, education, housing, welfare sectors
Download High Quality Study Material: www.instamojo.com/nextgenias Page 41
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Management AccountingDocument10 pagesManagement Accountingnikhilgangwani100% (3)
- Charles P. Kindleberger-Economic Growth in France and Britain, 1851-1950-Harvard University Press (1964) PDFDocument392 pagesCharles P. Kindleberger-Economic Growth in France and Britain, 1851-1950-Harvard University Press (1964) PDFMartín AlbertoNo ratings yet
- (Studies in Economic and Social History) R. J. Overy (Auth.) - The Nazi Economic Recovery 1932-1938 (1982, Macmillan Education UK)Document76 pages(Studies in Economic and Social History) R. J. Overy (Auth.) - The Nazi Economic Recovery 1932-1938 (1982, Macmillan Education UK)salman khanNo ratings yet
- Obligations - Questions and Suggested AnswersDocument15 pagesObligations - Questions and Suggested AnswersKatharina CantaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Diversification Enigma CaseDocument3 pagesPortfolio Diversification Enigma CaserahulNo ratings yet
- Outflows and InflowsDocument22 pagesOutflows and InflowsAejay Villaruz Barias67% (3)
- Assistant Director in AP Survey Settlement and Land RecordsDocument4 pagesAssistant Director in AP Survey Settlement and Land RecordsrushikeshNo ratings yet
- District (Posts) OC SC ST BC - A BC - B BC - C BC - D BC - E Others G W G W G W G W G W G W G W G WDocument2 pagesDistrict (Posts) OC SC ST BC - A BC - B BC - C BC - D BC - E Others G W G W G W G W G W G W G W G WrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Civil and Mechnical RKDocument2 pagesCivil and Mechnical RKrushikeshNo ratings yet
- AP C1-DA-Bits NRRDocument34 pagesAP C1-DA-Bits NRRrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Applications For Existing Buildings: PreprintDocument17 pagesRenewable Energy Applications For Existing Buildings: PreprintrushikeshNo ratings yet
- EsDocument468 pagesEsrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Economic Survey 2018-19 Highlights - Part III: Here HereDocument14 pagesEconomic Survey 2018-19 Highlights - Part III: Here HererushikeshNo ratings yet
- Gsma RK PDFDocument1 pageGsma RK PDFrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Sl. No Notification No./ Name of The Recruitment Date of Screening Test Date of (Mains) ExaminationDocument2 pagesSl. No Notification No./ Name of The Recruitment Date of Screening Test Date of (Mains) ExaminationrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Gist of AP Budget 2019-20: Subscribe To IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel at YoutubeDocument18 pagesGist of AP Budget 2019-20: Subscribe To IAS APPSC TSPSC Lectures Channel at YoutuberushikeshNo ratings yet
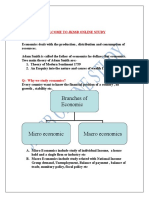
- Branches of Economic: Welcome To JKSSB Online StudyDocument51 pagesBranches of Economic: Welcome To JKSSB Online StudySherry SherNo ratings yet
- Choppies AR 2016Document104 pagesChoppies AR 2016Tefo MoggzNo ratings yet
- Arthur Kitson - The Bankers ConspiracyDocument8 pagesArthur Kitson - The Bankers ConspiracyEdNo ratings yet
- Prosper Chapter6v2 PDFDocument28 pagesProsper Chapter6v2 PDFAdam Taggart100% (2)
- Economics Knowledge Organisers Macroeconomics Year 1Document12 pagesEconomics Knowledge Organisers Macroeconomics Year 1Jhanvi ParekhNo ratings yet
- Hanh Vs CADocument3 pagesHanh Vs CAJotmu SolisNo ratings yet
- Singapore Focus I: Singapore Focus II: China Focus I: China Focus IIDocument47 pagesSingapore Focus I: Singapore Focus II: China Focus I: China Focus IIEdward FoongNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Mnqayi NsDocument74 pagesDissertation Mnqayi Nszuziwe kuwanaNo ratings yet
- Costs and BenefitsDocument40 pagesCosts and BenefitsAbbieNo ratings yet
- Cbaresearch2020-4 Cheungdeonaldo GuerreroDocument14 pagesCbaresearch2020-4 Cheungdeonaldo GuerreroAnghel HamorNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Monetary Policy Goal and TargetsDocument12 pagesConduct of Monetary Policy Goal and TargetsSumra KhanNo ratings yet
- CharlesKindlebergerThe World in Depression, 1929-39Document12 pagesCharlesKindlebergerThe World in Depression, 1929-39Roxana BadeaNo ratings yet
- Modes of Extinguishment of ObligationDocument20 pagesModes of Extinguishment of ObligationJohn Kayle BorjaNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument10 pagesMonetary PolicyAshish MisraNo ratings yet
- Functions of Central BanksDocument4 pagesFunctions of Central BanksAndrea NaquimenNo ratings yet
- Coming Bond Market CollapseDocument15 pagesComing Bond Market CollapseCatalina Vela Garces67% (3)
- Ex Ch21.2A Inflation and DeflationDocument4 pagesEx Ch21.2A Inflation and DeflationBrian WongNo ratings yet
- MycbseguideDocument10 pagesMycbseguideBinoy TrevadiaNo ratings yet
- An Astrological History of Hyper-Inflation: by Robert Gover, USADocument10 pagesAn Astrological History of Hyper-Inflation: by Robert Gover, USASaptarishisAstrology100% (1)
- Business Statistics Project:: TiruchirappalliDocument21 pagesBusiness Statistics Project:: TiruchirappalliGunjan ChandavatNo ratings yet
- Economics QuizDocument13 pagesEconomics QuizBhushan SawantNo ratings yet
- The Global Economy: Socsci 100 The Contemporary World 1Document52 pagesThe Global Economy: Socsci 100 The Contemporary World 1Camille Villena Valmadrid100% (1)
- 3rd Term Lesson Note For Ss2 On EconomicsDocument24 pages3rd Term Lesson Note For Ss2 On Economicslukajoy082No ratings yet
- Grants Interest Rate Observer Summer E IssueDocument24 pagesGrants Interest Rate Observer Summer E IssueCanadianValueNo ratings yet