Professional Documents
Culture Documents
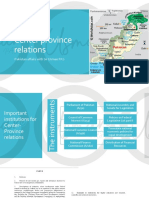
Center Province Relations Under Constitution
Center Province Relations Under Constitution
Uploaded by
Saqib IshaqOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Center Province Relations Under Constitution
Center Province Relations Under Constitution
Uploaded by
Saqib IshaqCopyright:
Available Formats
Center Province Relations under Constitution
PART V
Relations Between Federation and Provinces.
CHAPTER 1. — DISTRIBUTION OF LEGISLATIVE POWERS.
141. Extent of Federal and Provincial laws.
Federation may make laws (including laws extra territorial operation) for the whole or any part of
Pakistan, and a Provincial Assembly may make laws for the Province or any part thereof.
142. Subject-matter of Federal and Provincial laws.
Parliament have exclusive power to make laws in the Federal Legislative List;
A Provincial Assembly shall have power to make laws with respect to any matter not enumerated
in the Federal Legislative List.
143. Inconsistency between Federal and Provincial laws.
If any provision of an Act of a Provincial Assembly is repugnant to any provision of an Act of
Parliament the Act of Parliament, shall prevail
144. Power of Majlis-e-Shoora (Parliament) to legislate for one or more Provinces by consent.
CHAPTER 2. — ADMINISTRATIVE RELATIONS BETWEEN
FEDERATION AND PROVINCES.
145. Power of President to direct Governor to discharge certain functions as his Agent.
Not of article 105
146. Power of Federation to confer powers, etc., on Provinces, in certain cases.
147. Power of the Provinces to entrust functions to the Federation.
148. Obligation of Provinces and Federation.
The executive authority of every Province shall be so exercised as to secure compliance with
Federal laws which apply in that Province.
Page1
duty of the Federation to protect every Province against external aggression and internal
disturbances
149. Directions to Provinces in certain cases.
To the construction and maintenance of means of communication declared in the direction to be
of national or strategic importance.
for the purpose of preventing any grave menace to the peace or tranquility or economic life
150. Full faith and credit for public acts, etc.
151. Inter-Provincial trade.
Inter province - Free trade, commerce and movement
152. Acquisition of land for Federal purposes.
CHAPTER 3. — SPECIAL PROVISIONS
152A. National Security Council.
153. Council of Common Interests.
Pm+4 CM+ 3 members from the Federal Govt nominated by PM
154. Functions and rules of procedure.
Part II of the Federal Legislative List
155. Complaints as to interference with water supplies.
To CCI
156. National Economic Council.
PM+4CMs+4 Member nominated by each CM+4 Members nominated by PM
review the overall economic condition of the country to formulate plans in respect of financial,
commercial, social and economic policies; ensure balanced development and regional
157. Electricity.
158. Priority of requirements of natural gas.
The Province in which a well-head of natural gas is situated shall have precedence over other
parts of Pakistan in meeting the requirements from that well-head
159. Broadcasting and telecasting.
Page2
PART VI
Finance, Property, Contracts and Suits
CHAPTER 1. – FINANCE
Distribution of Revenues between the
Federation and the Provinces.
160. National Finance Commission.
distribution between the Federation and the Provinces of the net proceeds of the taxes
161. Natural gas and hydro-electric power.
the net proceeds of the Federal duty of excise on natural gas and oil to be given to province were
well situated
The net profits earned from the bulk generation of power at a hydro-electric station shall be paid
to the Province in which the hydro-electric station is situated
162. Prior sanction of President required to Bills affecting taxation in which Provinces are interested.
Money bill in NA
163. Provincial taxes in respect of professions, etc.
Miscellaneous Financial Provisions
164. Grants out of Consolidated Fund.
165. Exemption of certain public property from taxation.
165A. Power of Majlis-e-Shoora (Parliament) to impose tax on the income of certain corporations, etc.
CHAPTER 2. — BORROWING AND AUDIT
166. Borrowing by Federal Government.
167. Borrowing by Provincial Government.
Audit and Accounts
168. Auditor-General of Pakistan.
169. Functions and powers of Auditor-General.
170. Power of Auditor-General to give directions as to accounts.
171. Reports of Auditor-General.
CHAPTER 3. — PROPERTY, CONTRACTS,
LIABILITIES AND SUITS
172. Ownerless property. Page3
173. Power to acquire property and to make contracts, etc.
to the grant, sale, disposition or mortgage of any property vested in, and to the purchase or
acquisition of property on behalf of,
174. Suits and proceedings.
by the name of Pakistan and Province by the name of the Province
You might also like
- State Centre State Relation VasanthDocument13 pagesState Centre State Relation VasanthApoorvaChandraNo ratings yet
- MGT111 MidtermSolvedPaper and MCQs Mega FileDocument37 pagesMGT111 MidtermSolvedPaper and MCQs Mega FileSalik Hussain67% (9)
- 2) BCDS Revised Final Draft August 27 2013 PDFDocument157 pages2) BCDS Revised Final Draft August 27 2013 PDFAar Tech CareNo ratings yet
- HyhhDocument9 pagesHyhhMuhammad Javed GabaNo ratings yet
- Eighteenth Amendment NewDocument29 pagesEighteenth Amendment NewRabia JavedNo ratings yet
- 13 - Distribution of Powers Between Federal and Provincial Governments - NotesDocument4 pages13 - Distribution of Powers Between Federal and Provincial Governments - Notesm.tayyab3318No ratings yet
- Pakistan Water Law - 8 Nov 2016Document20 pagesPakistan Water Law - 8 Nov 2016Mashood KhanNo ratings yet
- Centre - State RelationDocument38 pagesCentre - State RelationSiva KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Centre State RelationsDocument13 pagesCentre State RelationsBasil JohnNo ratings yet
- Legislative ProcedureDocument96 pagesLegislative ProcedureAnuroop G AsokanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of 18th AmendmentDocument40 pagesAnalysis of 18th AmendmentRania AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Eighteenth Amendment NewDocument24 pagesEighteenth Amendment Newconfidential fourNo ratings yet
- Psa 622 1. Intro To PsaDocument35 pagesPsa 622 1. Intro To PsaJauzi NajmuddinNo ratings yet
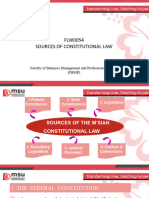
- Sources of Constitutional LawDocument31 pagesSources of Constitutional LawZainal Akmal Ahmad ShukkeriNo ratings yet
- Public Sector Accounting APS 20103 Financial Accounting Systems and ProceduresDocument26 pagesPublic Sector Accounting APS 20103 Financial Accounting Systems and ProceduresAsheequin ZainolNo ratings yet
- 18th AmendmentDocument3 pages18th Amendmentshameeraqsa2No ratings yet
- Current AffairsDocument2 pagesCurrent AffairsAmeer HamzahNo ratings yet
- Centre State RelationsDocument20 pagesCentre State RelationsRanaRanveerNo ratings yet
- Financial Relations Between Centre and State in The Light of ConstitutionDocument11 pagesFinancial Relations Between Centre and State in The Light of Constitutionतेजस्विनी रंजनNo ratings yet
- 18Th Amendment: Here You Are With The Outlines You RequestedDocument4 pages18Th Amendment: Here You Are With The Outlines You RequestedMuhammadNaveedNo ratings yet
- Budget 3Document11 pagesBudget 3तेजस्विनी रंजनNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity (Chapter 15) - Daily Class Notes - Samagra Book Series Batch (Hinglish)Document11 pagesIndian Polity (Chapter 15) - Daily Class Notes - Samagra Book Series Batch (Hinglish)paviliongmatNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ClassDocument14 pagesUnit 3 Classsamy gsNo ratings yet
- Centre - State RelationDocument15 pagesCentre - State RelationGopal AeroNo ratings yet
- 3 FINANCIAL SYSTEMS PROCEDURES Sept 2016-1Document60 pages3 FINANCIAL SYSTEMS PROCEDURES Sept 2016-1eduNo ratings yet
- Inter State RelationsDocument4 pagesInter State RelationsMapuii FanaiNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Pakistan: Relations Between Federation and ProvincesDocument11 pagesConstitution of Pakistan: Relations Between Federation and ProvincesSuhrab Khan JamaliNo ratings yet
- 18th Amendment - A New Social Contract of PakistanDocument3 pages18th Amendment - A New Social Contract of PakistanAmin Khan MarwatNo ratings yet
- Political and Constitutional History of PakistanDocument39 pagesPolitical and Constitutional History of PakistanAreej BaigNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sources of CLDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Sources of CLSylvesterNo ratings yet
- Vajiram RaviDocument18 pagesVajiram Raviaanchalkesharwani54No ratings yet
- Centre State RelationDocument12 pagesCentre State RelationVasanth Subramanyam100% (1)
- The Constitution of The State of SabahDocument54 pagesThe Constitution of The State of SabahmilamoNo ratings yet
- The Role of GovernorDocument5 pagesThe Role of GovernorVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Centre-State Financial Relations-I1: StructureDocument15 pagesUnit 5 Centre-State Financial Relations-I1: StructureAjay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4Document22 pagesUnit - 4Arun ANNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Part-1 Union-State RelationsDocument17 pagesUnit-III Part-1 Union-State RelationsSarthak SabbarwalNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Sources-Jan 19Document49 pagesSession 2 - Sources-Jan 19Chan HF PktianNo ratings yet
- Economic Reforms 33Document4 pagesEconomic Reforms 33Asif Khan ShinwariNo ratings yet
- Mid Topic - India Act 1919Document3 pagesMid Topic - India Act 1919Mohasin Niloy Ahmed 2121497642No ratings yet
- 18th Constitutional AmendmentDocument3 pages18th Constitutional Amendmentrayyan khanNo ratings yet
- Nature of Indian Federalism: Jyoti Assistant Professor Department of Political Science PGGC-11 ChandigarhDocument14 pagesNature of Indian Federalism: Jyoti Assistant Professor Department of Political Science PGGC-11 Chandigarhsamyutha raoNo ratings yet
- Constitution of PakistanDocument11 pagesConstitution of PakistanArslan SajjadNo ratings yet
- National Law University, JodhpurDocument9 pagesNational Law University, JodhpurKRiti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- 2015 S C M R 1739Document35 pages2015 S C M R 1739Ahmad Awais 1No ratings yet
- PF LeynesDocument3 pagesPF LeynesLorenzana, Angela E.No ratings yet
- Consti 1-2Document30 pagesConsti 1-2Jonah BinaraoNo ratings yet
- RTI Manual - As On 29.3.2019Document63 pagesRTI Manual - As On 29.3.2019Aniket NimkarNo ratings yet
- Comparative Federalism: Project OnDocument4 pagesComparative Federalism: Project OnHemantPrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Accountable. He Is One of The Bulwarks of The Democratic System of Government inDocument3 pagesAccountable. He Is One of The Bulwarks of The Democratic System of Government inAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Polity Summary 3 Final Watermark PDF 51 1 68Document5 pagesPolity Summary 3 Final Watermark PDF 51 1 68VIKASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Lu 2 Government Structure and Legal FrameworkDocument2 pagesLu 2 Government Structure and Legal Frameworklydia seliNo ratings yet
- L10 Federalism MC Prelims 2024 Lyst2920Document8 pagesL10 Federalism MC Prelims 2024 Lyst2920jankitkhareNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Union and StatesDocument16 pagesRelationship Between Union and StatesShivani ShreyaNo ratings yet
- The ConstitutionDocument2 pagesThe Constitutiongrace novemberNo ratings yet
- 18 AmendmentDocument5 pages18 AmendmentFahad amin AminNo ratings yet
- 18th Amendment (Summed Up)Document3 pages18th Amendment (Summed Up)Muhammad IshaqNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka Interim Report For Constitutional Reform Principals of DevolutionDocument17 pagesSri Lanka Interim Report For Constitutional Reform Principals of DevolutionThavamNo ratings yet
- FinanceDocument12 pagesFinanceAqeel Imtiyaz 2292No ratings yet
- Polity Summary 3 Final Watermark - PDF 51Document5 pagesPolity Summary 3 Final Watermark - PDF 51pratham mohantyNo ratings yet
- 18th Amendment ROUGHDocument4 pages18th Amendment ROUGHAmina AamerNo ratings yet
- MGT111 (1) Mega FileDocument40 pagesMGT111 (1) Mega FileUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Nature of Centre-Province Relations Under The 1973 ConstitutionDocument1 pageDiscuss The Nature of Centre-Province Relations Under The 1973 Constitutionsahil1sarki2No ratings yet
- ET: What Is The NFC Award, How It Came Into Being and Why Is It Important?Document3 pagesET: What Is The NFC Award, How It Came Into Being and Why Is It Important?Mansoor Ali LaghariNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Eighteenth Amendment and The NFC Awards 250122Document22 pagesRevisiting Eighteenth Amendment and The NFC Awards 250122SdfNo ratings yet
- Federalism in PakistanDocument18 pagesFederalism in Pakistansaimrauf461No ratings yet
- 18th Amendment: Much Ado About Nothing: Syed Akhtar Ali ShahDocument4 pages18th Amendment: Much Ado About Nothing: Syed Akhtar Ali ShahAbdulAzizMehsudNo ratings yet
- The Problems and Issues of Federalism in Pakistan: Muntzra NazirDocument20 pagesThe Problems and Issues of Federalism in Pakistan: Muntzra NazirMuhammad Sohail IrshadNo ratings yet
- Budget Process PakistanDocument68 pagesBudget Process PakistanMomin Qureshi75% (4)
- A Framework For Development of Balochistan Spatial Strategy: Final ReportDocument64 pagesA Framework For Development of Balochistan Spatial Strategy: Final ReportMunir HussainNo ratings yet
- 18 Amendment in Constitution of Pakistan: Evaluation and Way ForwardDocument10 pages18 Amendment in Constitution of Pakistan: Evaluation and Way ForwardFaizan MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Budgetting DSD - LatestDocument72 pagesBudgetting DSD - LatestMuhammad Moeen BhattiNo ratings yet
- NFC Award PDFDocument2 pagesNFC Award PDFMuhammad Usman FayyazNo ratings yet
- Concurrent List: 1973 Constitution and Recent Political DevelopmentsDocument29 pagesConcurrent List: 1973 Constitution and Recent Political Developmentssaad aliNo ratings yet
- CEPI Weekly Bulletin (12-3-22)Document26 pagesCEPI Weekly Bulletin (12-3-22)saleem abroNo ratings yet
- Commemorating 50 Years of The Constitution of Pakistan: Lessons For The Next 50 YearsDocument30 pagesCommemorating 50 Years of The Constitution of Pakistan: Lessons For The Next 50 YearsInstitute of Policy StudiesNo ratings yet
- Ethnicity and National Integration in PakistanDocument11 pagesEthnicity and National Integration in PakistanWaleed TariqNo ratings yet
- National Finance Commission: Prepared By: Javed Ahmed (21705) Faculty: Sir Kashif Imran Dated: 16 June, 2019Document18 pagesNational Finance Commission: Prepared By: Javed Ahmed (21705) Faculty: Sir Kashif Imran Dated: 16 June, 2019Anesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 1716532503-White Paper 2024-25Document118 pages1716532503-White Paper 2024-25Ghulam Mustafa hashmiNo ratings yet
- Szabist - Saad JavedDocument2 pagesSzabist - Saad JavedSaad JavedNo ratings yet
- Public Finance Management - Handbook by Government of SindhDocument172 pagesPublic Finance Management - Handbook by Government of SindhDanish GazdarNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Financing of EducationDocument43 pagesPakistan Financing of EducationKashif SaeedNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Recent NFC AwardDocument24 pagesAnalysis of The Recent NFC Awardfaw03No ratings yet
- NFC Award: Submitted by Mubaraka Quaid JoherDocument10 pagesNFC Award: Submitted by Mubaraka Quaid JoherMubaraka QuaidNo ratings yet
- Historical Evolution of Federalism in PakistanDocument20 pagesHistorical Evolution of Federalism in Pakistanmaria sabirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Public Administration-Mgt111: 1973 Constitution of PakistanDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Public Administration-Mgt111: 1973 Constitution of PakistanAftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Federalism in Pakistan: of Promises and Perils: by Zubair ShahidDocument29 pagesFederalism in Pakistan: of Promises and Perils: by Zubair ShahidAsaad AreebNo ratings yet
- RR 18th AmendmentDocument6 pagesRR 18th AmendmentMaquacR7No ratings yet
- Handouts MPA 401Document28 pagesHandouts MPA 401Muhammad Imran Irshad JalloNo ratings yet