Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Z Test PDF
Z Test PDF
Uploaded by
Arun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views5 pagesThe z-test is used to test the null hypothesis that there is no difference between the means of two populations or sets of data. It involves calculating a z-statistic and comparing it to the critical value to determine if the null hypothesis can be rejected. If the p-value is greater than the significance level, usually 0.05, then the null hypothesis that the means are the same cannot be rejected.
Original Description:
Original Title
Z-test.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe z-test is used to test the null hypothesis that there is no difference between the means of two populations or sets of data. It involves calculating a z-statistic and comparing it to the critical value to determine if the null hypothesis can be rejected. If the p-value is greater than the significance level, usually 0.05, then the null hypothesis that the means are the same cannot be rejected.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views5 pagesZ Test PDF
Z Test PDF
Uploaded by
ArunThe z-test is used to test the null hypothesis that there is no difference between the means of two populations or sets of data. It involves calculating a z-statistic and comparing it to the critical value to determine if the null hypothesis can be rejected. If the p-value is greater than the significance level, usually 0.05, then the null hypothesis that the means are the same cannot be rejected.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Z-test
• Use z test to test the null hypothesis
• A two sample z test compares the means of two sets of data to see if
there’s a difference.
• Use the p value from the test to decide whether to support or reject
the null hypothesis.
• For example,
• A manufacturer test some new product to see whether it is superior
to a previous product.
• start by stating the null hypothesis (there’s no difference) and then
state the alternate hypothesis: there is a difference in means.
• Then use z test.
• Use two sample z test if sample size is greater than 30.
• Below 30, use a t-test.
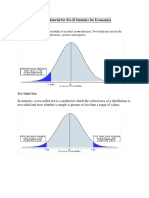
• We will compare the z-Statistic value to the z-Critical two-tail
statistic.
• Use a one-tail test if testing that a value is above or below some level.
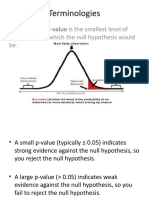
• If the p-value is larger than Alpha (0.05), we cannot reject the null
hypothesis that there is no significant difference in the means of each
sample.
• In this example P(Z <= z) two tail (1) gives us the probability that a
value of the z-Statistic (0) would be observed that is larger in absolute
value than z Critical two-tail (1.96).
• Since the p-value is larger than our Alpha (0.05), we cannot reject the
null hypothesis that there is no significant difference in the means of
each sample.
You might also like
- Hypothesis Testing AssignmentDocument12 pagesHypothesis Testing Assignmentضیاء گل مروتNo ratings yet
- HypothesisDocument10 pagesHypothesismahima singhNo ratings yet
- Hypotheses TestingDocument25 pagesHypotheses TestingEsai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Z-Test of Group 10 (042024)Document34 pagesZ-Test of Group 10 (042024)JUSTINE INDOYONNo ratings yet
- Z TestDocument29 pagesZ TestSujan AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts of Tests of Hypotheses On The Population Mean and Population ProportionDocument33 pagesKey Concepts of Tests of Hypotheses On The Population Mean and Population ProportionElisha Mae BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- C05 +M1+ +S5+ +Summary+DocDocument10 pagesC05 +M1+ +S5+ +Summary+DocAradhna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Central Tendency. Hypothesis TestDocument40 pagesCentral Tendency. Hypothesis TestNihal KocheNo ratings yet
- Predictive Analytics 1Document14 pagesPredictive Analytics 1SULOCHNA KUJURNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 13 - P-Value - Testing - Proportion - Testing Difference Between Two Population MeansDocument10 pagesLecture - 13 - P-Value - Testing - Proportion - Testing Difference Between Two Population MeansNigar QurbanovaNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics 5Document33 pagesBusiness Statistics 5NOOR UL AIN SHAHNo ratings yet
- "T" Test: DR - Shovan Padhy DM1 Yr (Senior Resident) Dept. of CP & T NIMS, HyderabadDocument20 pages"T" Test: DR - Shovan Padhy DM1 Yr (Senior Resident) Dept. of CP & T NIMS, HyderabadPundaleek KalloliNo ratings yet
- Common StatisticsDocument23 pagesCommon StatisticsJeffNo ratings yet
- Parametric TestsDocument57 pagesParametric TestsMukul BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing 3Document19 pagesHypothesis Testing 3ayeshasalman689No ratings yet
- Z and T TestDocument7 pagesZ and T TestshraddhaNo ratings yet
- Z Test PowerPoint April 25 2023Document22 pagesZ Test PowerPoint April 25 2023Martina EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Statistical InferencesDocument10 pagesHypothesis Testing Statistical InferencesReaderNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing 15pagesDocument15 pagesHypothesis Testing 15pagesAravindan RNo ratings yet
- BS Group 4Document36 pagesBS Group 4Aniket KuralkarNo ratings yet
- Statistics SuggestionsDocument74 pagesStatistics SuggestionsDr. Mahbub Alam MahfuzNo ratings yet
- Z-Test and T-TestDocument6 pagesZ-Test and T-Test03217925346No ratings yet
- Testing of HypothesisDocument30 pagesTesting of Hypothesisvikramkaruppannan6807No ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument77 pagesUnit IVChetanNo ratings yet
- Plug-Ins or Add-Ins, Select Data Analysis Toolpak, Click "Go" at The Bottom of TheDocument4 pagesPlug-Ins or Add-Ins, Select Data Analysis Toolpak, Click "Go" at The Bottom of TheAngeline LimNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To T-Tests: Statistical Test Means Hypothesis TestingDocument8 pagesAn Introduction To T-Tests: Statistical Test Means Hypothesis Testingshivani100% (1)
- T Test Function in Statistical SoftwareDocument9 pagesT Test Function in Statistical SoftwareNur Ain HasmaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TesingDocument30 pagesHypothesis Tesingrhythmsuthar123No ratings yet
- CH 11 - Small Sample TestDocument8 pagesCH 11 - Small Sample TesthehehaswalNo ratings yet
- 12 Statistical Analysis T Test RevisedDocument61 pages12 Statistical Analysis T Test RevisedJhoana LangcauonNo ratings yet
- T Test ExpamlesDocument7 pagesT Test ExpamlesSaleh Muhammed BareachNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument23 pagesResearch MethodologynuravNo ratings yet
- MitDocument119 pagesMitalexNo ratings yet
- Non Parametric TestDocument32 pagesNon Parametric TestKammari BharatNo ratings yet
- Paired T-Test: A Project Report OnDocument19 pagesPaired T-Test: A Project Report OnTarun kumarNo ratings yet
- One Sample TDocument3 pagesOne Sample Ttsegish93No ratings yet
- Tagpuno 9.1Document30 pagesTagpuno 9.1rikitagpunoNo ratings yet
- EDA Report - GONZALES EJDocument8 pagesEDA Report - GONZALES EJEJ GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Two Tailed & One TailedDocument5 pagesTwo Tailed & One TailedSefdy ThenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Data Analysis - Part2Document32 pagesLecture 2-Data Analysis - Part2chono090196No ratings yet
- MB0050 Slides Unit 10Document17 pagesMB0050 Slides Unit 10Yogesh Shinde0% (1)
- LESSON 2.1: Z-Test and T-TestDocument4 pagesLESSON 2.1: Z-Test and T-Testimsana minatozakiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Data Analysis - Tests of DifferencesDocument50 pages3 - Data Analysis - Tests of Differencesmnrk 1997No ratings yet
- Statistics in Analytical Chemistry-Part 2: Instructor: Nguyen Thao TrangDocument44 pagesStatistics in Analytical Chemistry-Part 2: Instructor: Nguyen Thao TrangLeo PisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27/chapters 22 & 23: Hypothesis Tests For MeansDocument20 pagesLecture 27/chapters 22 & 23: Hypothesis Tests For MeansSAIRITHISH SNo ratings yet
- 2022 Lecture4 Part1Document31 pages2022 Lecture4 Part1Cynthia ChouNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument78 pagesHypothesis Testingdawit tesfaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing (Statistics)Document23 pagesHypothesis Testing (Statistics)Mich Salvatorē100% (1)
- Study Material For BA-II Statistics For Economics: One Tailed TestDocument9 pagesStudy Material For BA-II Statistics For Economics: One Tailed TestC.s TanyaNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document26 pagesWeek 5Sourav Garodia 221-15-5048No ratings yet
- Elle. HYPOTHESIS TESTINGDocument25 pagesElle. HYPOTHESIS TESTINGJhianne EstacojaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis (T-Test)Document61 pagesStatistical Analysis (T-Test)Symoun BontigaoNo ratings yet
- TAT: Thematic Apperception Test (Story From Picture)Document16 pagesTAT: Thematic Apperception Test (Story From Picture)asif.mba.khanNo ratings yet
- Test of SignificanceDocument22 pagesTest of SignificanceKathiravan GopalanNo ratings yet
- Calculator Use Part14Document1 pageCalculator Use Part14kunichiwaNo ratings yet
- Forms of Test StatisticDocument31 pagesForms of Test StatisticJackielou TrongcosoNo ratings yet
- Biostats 2Document7 pagesBiostats 2baf49411No ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing 1667518636Document16 pagesHypothesis Testing 1667518636saravana s we. wiNo ratings yet
- MathDocument24 pagesMathNicole Mallari MarianoNo ratings yet
- How to Find Inter-Groups Differences Using Spss/Excel/Web Tools in Common Experimental Designs: Book TwoFrom EverandHow to Find Inter-Groups Differences Using Spss/Excel/Web Tools in Common Experimental Designs: Book TwoNo ratings yet