Professional Documents
Culture Documents
hsg253 Sayfa 03
hsg253 Sayfa 03
Uploaded by
Efari Bahcevan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 page3
Original Title
hsg253_Sayfa_03
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 pagehsg253 Sayfa 03
hsg253 Sayfa 03
Uploaded by
Efari BahcevanYou are on page 1of 1
Health and Satety
Executive
Contents
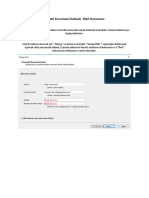
Introduction 5
Scope and target audience 5
Legal considerations 6
Risk reduction and ALARP 6
Overview of isolation hazards. 7
‘Management of isolations 7
Basic principles 7
Design 8
Human factors 10
Roles and responstbilties 12
Training and competence 14
Monitoring, audit and review 15
Setting performance indicators for isolation activities. 17,
Safe systems of work for isolation activities 17
Werk contiol systems. 17
Documentation 17
Controling interactions with other work/systems 18
Controling changes 19.
Key stages of process isolation 27
Hazard identification 22
Risk assessment and selection of isolation scheme 29
Planning and preparation of equipment 37
Installation of the isolation. 32
Draining, venting, purging and flushing 94
Testing and monitoring effectiveness of the fsolation 35
Reinstatement of the plant 58
Isolation situations requiring specific considerations 39
Own isolations. 39
Arrangements for large-scale isolations 47
Extended isolations 42
Appendices 42
1 Legal requirements 42
2 Non-process isolation hazards. 44
8 Checklists for monitoring and roviow 47
4. Valve types and issues 50
5 Isolation methods. 52
6 Example of a solection tool to establish the ‘baseline standard’ for a final
isolation 59
Pipeline bolation requirements 68
Draining, venting, purging and flushing activities 72
Isolations for instrument work 75
8
9
References and further reading 77
Glossary 79
The sa lscaton of plant and equipment Page Sot 8
You might also like
- Visio-GMB Akış Çalışması 2Document1 pageVisio-GMB Akış Çalışması 2Efari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- Ayşe TÜMKAYADocument6 pagesAyşe TÜMKAYAEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- Habibe GülerDocument3 pagesHabibe GülerEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- Sinem AKYÜNCİDocument3 pagesSinem AKYÜNCİEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- Rayme DoğanDocument5 pagesRayme DoğanEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- 03 Calculation Examples of Safety Loops-Türkçe ÖrnekDocument48 pages03 Calculation Examples of Safety Loops-Türkçe ÖrnekEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction - Basics of SIL - Türkçe - Sayfa - 09Document1 page01 Introduction - Basics of SIL - Türkçe - Sayfa - 09Efari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- Kurumsal Mail KurulumuDocument20 pagesKurumsal Mail KurulumuEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- hsg253 Sayfa 01Document1 pagehsg253 Sayfa 01Efari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction - Basics of SIL - Türkçe - Sayfa - 05Document1 page01 Introduction - Basics of SIL - Türkçe - Sayfa - 05Efari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- SYR RP-101 ÖNERİLEN UYGULAMA Güvenlik Raporu HazırlamaDocument23 pagesSYR RP-101 ÖNERİLEN UYGULAMA Güvenlik Raporu HazırlamaEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- BEKRADocument15 pagesBEKRAEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- Alberk QA Muayene KapsamıDocument10 pagesAlberk QA Muayene KapsamıEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- SYR026 IECEx Eğitimi Kayıt FormuDocument3 pagesSYR026 IECEx Eğitimi Kayıt FormuEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet
- ISO 31000 Risk YönetimiDocument3 pagesISO 31000 Risk YönetimiEfari BahcevanNo ratings yet