Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Porter Competitive Strategy
Porter Competitive Strategy
Uploaded by
amiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Porter Competitive Strategy
Porter Competitive Strategy
Uploaded by
amiCopyright:
Available Formats
MICHAEL PORTER’S COMPETITIVE STRATEGIES
Competitive strategy raises the following questions:
Should we compete on the basis of lower cost (and thus price), or should we differentiate our products or services on some basis other than
cost, such as quality or service?
Should we compete head to head with our major competitors for the biggest but most sought-after share of the market, or should we focus on a
niche in which we can satisfy a less sought-after but also profitable segment of the market?
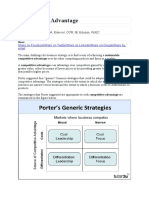
Three “generic” competitive strategies for outperforming other corporations in a particular industry:
Lower Cost Strategy
- ability of a company or a business unit to design, produce and market a comparable product more efficiently than its competitors
Differentiation Strategy
- ability of a company to provide unique and superior value to the buyer in terms of product quality, special features or after-sale
service
Focus
- ability of a company to provide unique and superior value to a particular buyer group, segment of a market line or geographic
market
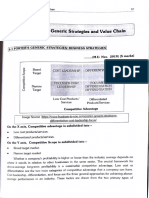
Porter proposed that a firm’s competitive advantage in an industry is determined by its competitive scope—that is, the breadth of the
company’s or business unit’s target market.
-----BROAD MASS MARKET TARGET-----
Cost leadership
lower-cost competitive strategy that aims at the broad mass market and requires “aggressive construction of efficient-
scale facilities, vigorous pursuit of cost reductions from experience, tight cost and overhead control, avoidance of marginal customer
accounts, and cost minimization”
Because of its lower costs, the cost leader is able to charge a lower price for its products than its competitors and still make a
satisfactory profit.
Provides a defense against rivals
Provides a barrier to entry
Generates increased market share
Differentiation
is aimed at the broad mass market and involves the creation of a product or service that is perceived throughout the
industry as unique.
can be associated with design, brand image, technology, features, dealer network or customer service
Brand loyalty Lowers customers sensitivity to price
Increases buyer loyalty
Can generate higher profits
----MARKET NICHE (NAROOW MARKET) ----
Cost focus
low-cost competitive strategy that focuses on a particular buyer group or geographic market and attempts to serve only
this niche to the exclusion of others
Differentiation focus
concentrates on a particular buyer group, product line segment or geographic market to serve the needs of a narrow
strategic market more effectively than its competitors
RISKS IN COMPETITIVE STRATEGIES
A company following a differentiation strategy must ensure that the higher price it charges for its higher quality is not too far above
the price of the competition, otherwise customers will not see the extra quality as worth the extra cost- this is Cost Proximity
Risk of: Cost Leadership, Differentiation, Focus
ISSUES IN COMPETITIVE STRATEGIES
Stuck in the middle
when a company has no competitive advantage and is doomed to below-average performance
Successful entrepreneurial ventures follow focus strategies.
They differentiate their product or service from those of others by focusing on customer wants in a segment of the market, thereby achieving a
dominant share of that part of the market.
You might also like
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionFrom EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- PINTURA CORPORATION - THE LENA LAUNCH - by Group 4Document8 pagesPINTURA CORPORATION - THE LENA LAUNCH - by Group 4Rini RafiNo ratings yet
- PartnershipDocument7 pagesPartnershipami50% (2)
- ECON01G - Lec4 - Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument4 pagesECON01G - Lec4 - Elasticity of Demand and Supplyami100% (1)
- Rural MarketingDocument337 pagesRural MarketingAnirban MandalNo ratings yet
- Feasibility New Mobiles ShopDocument6 pagesFeasibility New Mobiles ShopAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Part 5Document7 pagesStrategic Management Part 5aansh rajNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Competitive AdvantageDocument3 pagesStrategic Management Competitive AdvantageUpendra RaoNo ratings yet
- GRP5 GCSDocument42 pagesGRP5 GCSThilak AlvaNo ratings yet
- Strategic PositioningDocument13 pagesStrategic PositioningleesadzebondeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Global Business-Level Strategies - Choosing Competitive Strategies in A Single IndustryDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Global Business-Level Strategies - Choosing Competitive Strategies in A Single IndustryBảo ChâuuNo ratings yet
- Building Competitive Advantage Through Business-Level StrategyDocument33 pagesBuilding Competitive Advantage Through Business-Level StrategyRizwan Sait100% (2)
- Business Strategy N ModelsDocument1 pageBusiness Strategy N ModelsLasitha NawarathnaNo ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage: Print Page Share On Facebook Share On Twitter Share On Linkedin Share On Google Share by EmailDocument3 pagesCompetitive Advantage: Print Page Share On Facebook Share On Twitter Share On Linkedin Share On Google Share by EmailAarthi MuthusamiNo ratings yet
- Strategy FormulationDocument49 pagesStrategy FormulationAra BellaNo ratings yet
- Competitive AdvantageDocument3 pagesCompetitive AdvantageAnonymous X8hNvFAyzNo ratings yet
- Business Level Strategies UnitDocument23 pagesBusiness Level Strategies Unitwruttika jadhavNo ratings yet
- Cost Leadership and DifferentiationDocument44 pagesCost Leadership and DifferentiationkevrysantosaNo ratings yet
- Leadership, Differentiation, and Focus. These Strategies Are Applied at TheDocument4 pagesLeadership, Differentiation, and Focus. These Strategies Are Applied at TheromirathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document21 pagesChapter 5oduniyiabimNo ratings yet
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocument4 pagesPorter's Generic StrategiesJayanta RakshitNo ratings yet
- Business Management 3B Exam NotesDocument39 pagesBusiness Management 3B Exam NotesTashaNo ratings yet
- On Competitive StrategiesDocument33 pagesOn Competitive Strategiesmmjmmj100% (1)
- Competative StrategiesDocument9 pagesCompetative StrategiessaiNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Strategic ManagementDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Strategic ManagementRezwan SharifNo ratings yet
- Business Level StrategyDocument28 pagesBusiness Level Strategydjayaram144No ratings yet
- Module 5 - Strategic ManagementDocument28 pagesModule 5 - Strategic ManagementPrime Johnson FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocument8 pagesPorter's Generic StrategiesRohit GoilkarNo ratings yet
- 11 1204 Porter StrategyDocument13 pages11 1204 Porter Strategyanna rambuNo ratings yet
- Business StrategyDocument25 pagesBusiness StrategySarthak BansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Business Strategy: Differentiation, Cost Leadership, and Blue OceansDocument4 pagesChapter 6: Business Strategy: Differentiation, Cost Leadership, and Blue OceansJANo ratings yet
- Addendum To LJ Strategicmgtnotes2012Document21 pagesAddendum To LJ Strategicmgtnotes2012harisshaikh7070No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5ERICKA MAE NATONo ratings yet
- Stratma MaDocument17 pagesStratma MaMae TndnNo ratings yet
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocument17 pagesPorter's Generic StrategiesSharandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage With Respect ToDocument17 pagesCompetitive Advantage With Respect ToSourabh ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Michael PorterDocument5 pagesMichael PorterJyot SnaNo ratings yet
- Businesslevelstrategies 150913142511 Lva1 App6892Document31 pagesBusinesslevelstrategies 150913142511 Lva1 App6892Md. Rashed Kamal 221-45-042No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Global Business-Level Strategies - Choosing Competitive Strategies in A Single IndustryDocument17 pagesChapter 4 - Global Business-Level Strategies - Choosing Competitive Strategies in A Single IndustryHà Nhi LêNo ratings yet
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocument7 pagesPorter's Generic StrategiesBasant SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Business Level StrategyDocument30 pagesLesson 7 - Business Level StrategysurangauorNo ratings yet
- CSGM Mid Term NotesDocument26 pagesCSGM Mid Term NotesAdithyaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Ass1Document8 pagesStrategic Management Ass1Milford Kudakwashe MoyanaNo ratings yet
- SU190264W Strategic Management Ass1Document8 pagesSU190264W Strategic Management Ass1Milford Kudakwashe MoyanaNo ratings yet
- GSB Mba TM Iv Strategic Management: Unit III - Business StrategyDocument44 pagesGSB Mba TM Iv Strategic Management: Unit III - Business StrategyPurnima SoNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?Document24 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?MahiraNo ratings yet
- First: Generic Strategies Generic Competitive Strategies:: Product DifferentiationDocument8 pagesFirst: Generic Strategies Generic Competitive Strategies:: Product DifferentiationYousab KaldasNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic StrategiesDocument29 pagesThe Five Generic StrategiesmahiNo ratings yet
- 1ps-Business Level StrategyDocument2 pages1ps-Business Level StrategyI Nyoman Sujana GiriNo ratings yet
- V. Five Generic Competitive Strategies Cost Efficient Management and Revamping of The Value ChainDocument5 pagesV. Five Generic Competitive Strategies Cost Efficient Management and Revamping of The Value Chaingwyneth aquinoNo ratings yet
- Generic StrategyDocument55 pagesGeneric Strategynadgirviraj100% (2)
- Lima Strategi GenerikDocument12 pagesLima Strategi GenerikLIANo ratings yet
- Neric Strategies v1Document49 pagesNeric Strategies v1GabrieleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Strat Formulation Long Term Goals PP Slides 2024Document22 pagesChapter 6 Strat Formulation Long Term Goals PP Slides 2024gailastrid16No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Dealing With The CompetitionDocument7 pagesChapter 8: Dealing With The CompetitionMandy00011123322No ratings yet
- Bab 8 MPSDocument27 pagesBab 8 MPSKuro AshiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Assignment 3Document14 pagesStrategic Management Assignment 3Djimajor Robert TettehNo ratings yet
- SM 6Document22 pagesSM 6Ayesha TariqNo ratings yet
- Porters Generic StrategiesDocument16 pagesPorters Generic StrategiesManoj kumar MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 STRATEGIC FORMULATIONDocument5 pagesChapter 5 STRATEGIC FORMULATIONJohn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Strategy FormulationDocument14 pagesModule 3 - Strategy FormulationRonald Reagan AlonzoNo ratings yet
- 1207 - Chapter 4Document3 pages1207 - Chapter 4Matthew CivelloNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?Document21 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?RajatNo ratings yet
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)From EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)No ratings yet
- Value-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1From EverandValue-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1No ratings yet
- Advantage & Disadvantage and Team Decision MakingDocument4 pagesAdvantage & Disadvantage and Team Decision MakingamiNo ratings yet
- Corporate StrategyDocument2 pagesCorporate StrategyamiNo ratings yet
- Architecture Music Drame DanceDocument5 pagesArchitecture Music Drame Danceami0% (1)
- Fundamentals of Income Taxation: Focus Notes On TaxationDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Income Taxation: Focus Notes On TaxationamiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - ParCorDocument13 pagesReviewer - ParCoramiNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Schemes, Accounting Periods, Methods, and ReportingDocument30 pagesIncome Tax Schemes, Accounting Periods, Methods, and ReportingamiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Income Taxation: Focus Notes On TaxationDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Income Taxation: Focus Notes On TaxationamiNo ratings yet
- MARN01B - Lec1 - MarketingDocument1 pageMARN01B - Lec1 - MarketingamiNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting P3Document4 pagesFinancial Accounting P3amiNo ratings yet
- Scanned With CamscannerDocument4 pagesScanned With CamscanneramiNo ratings yet
- ECON01G - Lec6 - Market StructuresDocument5 pagesECON01G - Lec6 - Market StructuresamiNo ratings yet
- ECON01G - Lec3 - Demand and SupplyDocument3 pagesECON01G - Lec3 - Demand and SupplyamiNo ratings yet
- Financial Mangement Slides Lecture 1Document56 pagesFinancial Mangement Slides Lecture 1Aqash AliNo ratings yet
- Making AgreemenDocument4 pagesMaking AgreemenEvan VarianNo ratings yet
- Lapanday Foods Corporation v. CIRDocument9 pagesLapanday Foods Corporation v. CIRHazel SegoviaNo ratings yet
- CLD New AssignmentDocument23 pagesCLD New Assignmentshubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Prit PPT ProjectDocument16 pagesPrit PPT ProjectpriteshNo ratings yet
- The Syngenta Challenge 2012 CaseDocument8 pagesThe Syngenta Challenge 2012 CaseAbhinav VarunNo ratings yet
- CISCOTable of ContentsDocument7 pagesCISCOTable of ContentsBayrem AmriNo ratings yet
- 205 Marketing ResearchDocument13 pages205 Marketing ResearchShiv MethekarNo ratings yet
- Problem Management OTC November 2014Document28 pagesProblem Management OTC November 2014DeepakNo ratings yet
- Cost McqsDocument10 pagesCost McqsAnum ChNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Financial Management Principles and Applications 7th Edition PDF ScribdDocument42 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Financial Management Principles and Applications 7th Edition PDF Scribdcheryl.morgan378100% (43)
- Reading 35 Exchange-Traded Funds - Mechanics and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesReading 35 Exchange-Traded Funds - Mechanics and Applicationstristan.riolsNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Module 1 Basic and DefinitionsDocument3 pagesE-Commerce Module 1 Basic and DefinitionsJenifer Borja BacayoNo ratings yet
- CVP Tutorial SheetDocument4 pagesCVP Tutorial SheetDaneille Baker0% (1)
- Kajaria Ceramics - IC - HSIE-202101232125474239802Document22 pagesKajaria Ceramics - IC - HSIE-202101232125474239802bharat ratnaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Brand ManagementDocument31 pagesStrategic Brand ManagementÄädï ShëïkhNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets: Quarter 2 - MELC 13Document8 pagesActivity Sheets: Quarter 2 - MELC 13dominic dalton caling100% (2)
- Rural Market SegmentationDocument16 pagesRural Market SegmentationAnonymous d3CGBMz100% (1)
- Rocket Brand SolutionsDocument17 pagesRocket Brand SolutionsSujeet PathareNo ratings yet
- Variance QuestionsDocument3 pagesVariance QuestionsHadeed HafeezNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and Markets: Subject Code: EL15FN505Document63 pagesFinancial Institutions and Markets: Subject Code: EL15FN505Anusha RajNo ratings yet
- Coke's International Marketing StrategyDocument5 pagesCoke's International Marketing StrategySyed Hassan Raza67% (6)
- Affiliate Marketing Review 2020Document2 pagesAffiliate Marketing Review 2020Sule ManNo ratings yet
- Rural MarketingDocument3 pagesRural Marketingdebnath_banNo ratings yet
- The Nordic Way 2012Document27 pagesThe Nordic Way 2012Guillaume KasperskiNo ratings yet
- Anti-Corruption in Public Procurement inDocument32 pagesAnti-Corruption in Public Procurement inYustina Lita Sari100% (1)
- BBED4103 E-CommerceDocument8 pagesBBED4103 E-CommerceHoàng Yến NhiNo ratings yet