Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lobal Warming Is The Long-Term Rise in The Average
Uploaded by
ramiduyasan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views6 pagesOriginal Title
global warming.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views6 pagesLobal Warming Is The Long-Term Rise in The Average
Uploaded by
ramiduyasanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
global warming is the long-term rise in the average
temperature of the Earth's climate system. the
terms global warming and climate change are often used
interchangeably,[5] but climate change includes
both global warming and its effects, such as changes in
precipitation and impacts that differ by region. [6] There
were prehistoric periods of global warming,[7] but
observed changes since the mid-20th century have been
much greater than those seen in previous records covering
decades to thousands of years.[ It is extremely likely that
human influence has been the dominant cause of the
observed warming since the mid-20th centuryemission
of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane,
and nitrous oxide. Climate model projections summarized
in the report indicated that during the 21st century the
global surface temperature is likely to rise a further 0.3 to
1.7 °C (0.5 to 3.1 °F) in a moderate scenario, or as much as
2.6 to 4.8 °C (4.7 to 8.6 °F) in an extreme scenario,
depending on the rate of future greenhouse gas
emissions and on climate feedback effects. The effects of
global warming include rising sea levels, regional changes
in precipitation, more frequent extreme weather events
such as heat waves, and expansion of deserts.[14] Surface
temperature increases are greatest in the Arctic, which has
contributed to the retreat of glaciers, permafrost, and sea
ice. Overall, higher temperatures bring more rain and
snowfall, but for some
regions droughts and wildfires increase instead.
[15] Climate change threatens to diminish crop yields,
harming food security, and rising sea levels may flood
coastal infrastructure and force the abandonment of many
coastal cities.[16][17] Environmental impacts include
the extinction or relocation of many species as
their ecosystems change, most immediately the
environments of coral reefs,[18] mountains, and
the Arctic.[19] Due to the persistence of CO2 in the
atmosphere and the inertia of the climate system, climatic
changes and their effects will continue for millennia even if
carbon emissions are stoppedeffects of the Industrial
Revolution, so there was little net warming between the
18th century and the mid-19th century,[27][28] when
thermometer records began to provide global coverage.
[29] The IPCC has adopted the baseline reference period
1850–1900 as an approximation of pre-industrial global
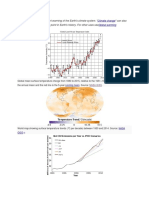
mean surface temperature.[27].[20] 2009–2018 decade
was 0.93 ± 0.07 °C warmer than the pre-industrial baseline
(1850–1900).[30] Currently, surface temperatures are
rising by about 0.2 °C per decade.[31] Since 1950, the
number of cold days and nights have decreased, and the
number of warm days and night have increased. the most
common measure of global warming is the increase in the
near-surface atmospheric temperature, over 90% of the
additional energy stored in the climate system over the
last 50 years has warmed ocean water.[34] The remainder
of the additional energy has melted ice and warmed
Further examples include sea level rise,[38] widespread
melting of snow and land ice,[39] increased heat content
of the oceans,[40] increased humidity,[41] and the
earlier timing of spring events,[42] such as
the flowering of Global warming refers to global averages, with the amount of
warming varying by region. Since the pre-industrial period, global
average land temperatures have increased almost
twice as fast as global average temperatures. [44] This
is due to the larger heat capacity of oceans and
because oceans lose more heat by evaporation.
[45] Patterns of warming are independent of the
locations of greenhouse gas emissions because the
gases persist long enough to diffuse across the
planet; however, localized black carbon deposits on
snow and ice do contribute to Arctic warming.[46]plants.
[43]the continents and the atmosphere
[
You might also like
- Global WarmingDocument282 pagesGlobal WarmingKpime DesmondNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - WikipediaDocument75 pagesClimate Change - WikipediaWajahat AliNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Observed Temperature ChangesDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming: Observed Temperature ChangesJared AllenNo ratings yet
- Global Warming in Change of Climate: TemperatureDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming in Change of Climate: TemperaturePraveen ChintuNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Causes, Effects & SolutionsDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming: Causes, Effects & SolutionsbaljitNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Global Warming Is The Increase in The Average Temperature of Earth's NearDocument20 pagesGlobal Warming: Global Warming Is The Increase in The Average Temperature of Earth's NearJatinChadhaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument410 pagesClimate ChangeJomel Paolo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Increase in TheDocument40 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Increase in TheFahmy RamdhanyNo ratings yet
- GW: Global warming basics & evidence for warmingDocument22 pagesGW: Global warming basics & evidence for warmingJustin Robert RoqueNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument43 pagesGlobal WarmingAsheer Uddin KhiljiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Forum Utk ESTDocument12 pagesGlobal Warming Forum Utk ESTakmal08No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument16 pagesGlobal WarmingDhana SekarNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Global Warming Refers To The Rising Average Temperature of Earth's Atmosphere andDocument18 pagesGlobal Warming: Global Warming Refers To The Rising Average Temperature of Earth's Atmosphere andSyed FurqanNo ratings yet
- Observed Temperature Changes: Global Warming Is The Rising Average Temperature ofDocument15 pagesObserved Temperature Changes: Global Warming Is The Rising Average Temperature ofBrian Luke SalimNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal WarmingbdezyNo ratings yet
- Navigation Search Climate Change Global Warming (Disambiguation)Document10 pagesNavigation Search Climate Change Global Warming (Disambiguation)firaforaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesGlobal Warming: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAbhishek BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate Change: A SummaryDocument11 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate Change: A SummaryUmang MotaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Causes and EffectsDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming Causes and EffectsVamsikrishna PanugantiNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal WarmingKylliíanNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument21 pagesGlobal WarmingnanaoNo ratings yet
- Global Warming - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument24 pagesGlobal Warming - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAbdullaKakkadKarumbilNo ratings yet
- Observed Temperature ChangesDocument10 pagesObserved Temperature Changesveena GOYALNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Increase in TheDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Increase in TheshailusolankiNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument18 pagesGlobal WarmingAlekhyaNimmalapudiNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument38 pagesGlobal WarmingManonmani PudhuezuthuNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal WarmingDipika KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Global Warming1Document5 pagesGlobal Warming1Jasvinder Singh100% (1)
- Global Warming: FA2 Project 1.shubham Tiwari 2.chanchal Bisen 3.aayush Saxena 4.yash Upadhyay 5.prakhar BinwarDocument17 pagesGlobal Warming: FA2 Project 1.shubham Tiwari 2.chanchal Bisen 3.aayush Saxena 4.yash Upadhyay 5.prakhar BinwarShubham Vijay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Causes and EffectsDocument14 pagesGlobal Warming Causes and EffectsSanju MathewNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument67 pagesClimate ChangeKarl GustavNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Increase in TheDocument40 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Increase in Thepoojari_neetaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument17 pagesGlobal WarmingSreekumar C PillaiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Radiative ForcingDocument5 pagesGlobal Warming: Radiative Forcingapi-26228968No ratings yet
- Enviro SearchDocument106 pagesEnviro SearchLorenzo C. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Jump To: Navigation, SearchDocument27 pagesGlobal Warming: Jump To: Navigation, SearchmarisporttNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Global Mean Surface Temperature Anomaly Relative To 1961-1990Document16 pagesGlobal Warming: Global Mean Surface Temperature Anomaly Relative To 1961-1990Harsh BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Navigation SearchDocument16 pagesGlobal Warming: Navigation SearchIffi JamilNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal Warmingsam_m4bNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument2 pagesGlobal WarmingAndrew Lee MakatarunganNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Global Warming Is The Rise in The Average Temperature of Earth's Atmosphere and Oceans SinceDocument3 pagesGlobal Warming: Global Warming Is The Rise in The Average Temperature of Earth's Atmosphere and Oceans Sincesanthu550No ratings yet
- Global Warming ExplainedDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming ExplainedAnkur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Climate Change: Effects On WeatherDocument3 pagesDefinition of Climate Change: Effects On Weatherafieq de fingqaerNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument1 pageGlobal Warmingamalav4No ratings yet
- Wikpedia Global Warming Is The Current Rise inDocument5 pagesWikpedia Global Warming Is The Current Rise inRendel AbrasiaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Increase in TheDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Increase in TheMayank MeherNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Causes and EffectsDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming: Causes and EffectsJessie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Causes, Effects and SolutionsDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming: Causes, Effects and SolutionsyudhishtherNo ratings yet
- Global Warming ArtikelDocument9 pagesGlobal Warming ArtikelRochman HadiNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument22 pagesGlobal WarmingPrerna Portel SilwalNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate ChangeShashi Kant SinghNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Increase in The Average Temperature of The Earth'sDocument12 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Increase in The Average Temperature of The Earth'sSanjeev BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Global warming causes and effects explainedDocument2 pagesGlobal warming causes and effects explained123rajnikantNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument1 pageGlobal WarmingNatan Ribeiro CostaNo ratings yet
- Climate Askdmq231Document67 pagesClimate Askdmq231demi theistNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Initial Causes of Temperature Changes (External Forcings)Document7 pagesGlobal Warming: Initial Causes of Temperature Changes (External Forcings)marvvinNo ratings yet
- Article of Global Warming: Submitted By: Mikko Gabrielle OrprecioDocument7 pagesArticle of Global Warming: Submitted By: Mikko Gabrielle OrprecioMark Kevin OngNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Term Used To Describe A Gradual Increase in The Average Temperature of The EarthDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Term Used To Describe A Gradual Increase in The Average Temperature of The EarthMarxel S. AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Q&A Explains Natural and Human FactorsDocument8 pagesClimate Change Q&A Explains Natural and Human FactorsLealyn CadaydayNo ratings yet
- Statement Prediction: Prior ReadingDocument3 pagesStatement Prediction: Prior ReadingramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Animal GroupsDocument1 pageAnimal GroupsramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- What Global WarmingDocument4 pagesWhat Global WarmingramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- War Scene Animation: by Team 3Document17 pagesWar Scene Animation: by Team 3ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Annual Return of A Company (Other Than A Company Limited by Guarantee)Document5 pagesAnnual Return of A Company (Other Than A Company Limited by Guarantee)ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Prize Giving Count Sports Meet Count Stournaments Count Nesda Count Grand CountDocument2 pagesPrize Giving Count Sports Meet Count Stournaments Count Nesda Count Grand CountramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- What Global WarmingDocument4 pagesWhat Global WarmingramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (Activity) Subject: History Grade: 7 Name: Roll: DateDocument1 pageWorksheet (Activity) Subject: History Grade: 7 Name: Roll: DateramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 Language and CommunicationDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 Language and CommunicationramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (Activity) Subject: History Grade: 7 Name: Roll: DateDocument1 pageWorksheet (Activity) Subject: History Grade: 7 Name: Roll: DateramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Farming (12.04.20)Document1 pageWorksheet On Farming (12.04.20)ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 2 - United Nations PDFDocument1 pageFormative Assessment 2 - United Nations PDFramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet Ch 8-10Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet Ch 8-10ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- How To Earn $10,000 While Learning To Code - Rob Percival PDFDocument52 pagesHow To Earn $10,000 While Learning To Code - Rob Percival PDFAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet-1 Chapter 8,9,10Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet-1 Chapter 8,9,10ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Two-Set Venn Diagram PDFDocument2 pagesTwo-Set Venn Diagram PDFramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet-1 Chapter 8,9,10Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet-1 Chapter 8,9,10ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Ramidu Yasan - FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT L2Document1 pageRamidu Yasan - FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT L2ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Ramidu Yasan - FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT L2Document1 pageRamidu Yasan - FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT L2ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Ramidu Yasan - FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT L2Document1 pageRamidu Yasan - FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT L2ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Ramidu Yasan - FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT L2Document1 pageRamidu Yasan - FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT L2ramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Two-Set Venn Diagram PDFDocument2 pagesTwo-Set Venn Diagram PDFramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Can We Prevent DeasiesDocument5 pagesCan We Prevent DeasiesramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Libraries of The WorldDocument7 pagesLibraries of The WorldramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- DraculaDocument1 pageDracularamiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument6 pagesGlobal WarmingramiduyasanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: By: Gabrielle Barrett, Tivonia Daley, Kayla Lawson and Dominque ValentineDocument18 pagesClimate Change: By: Gabrielle Barrett, Tivonia Daley, Kayla Lawson and Dominque ValentineTonique GordonNo ratings yet
- International Environmental Agreements PresentationDocument30 pagesInternational Environmental Agreements Presentationkuldeep sainiNo ratings yet
- cLIMATE CHANGEDocument4 pagescLIMATE CHANGEVannak VislowNo ratings yet
- Net Zero StandardDocument65 pagesNet Zero StandardNicole FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Join The Green Revolution and Stop PollutionDocument14 pagesJoin The Green Revolution and Stop PollutionHAMZA IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Lets Talk About Climate Change Fun Activities Games - 710Document2 pagesLets Talk About Climate Change Fun Activities Games - 710Kristen MuñozNo ratings yet
- Our Changing PlanetDocument1 pageOur Changing PlanetConstantin OpreaNo ratings yet
- Selfa SuwandiDocument6 pagesSelfa SuwandiWandi CendanaNo ratings yet
- Karnataka State Action Plan On Climate ChangeDocument224 pagesKarnataka State Action Plan On Climate ChangePika PshawNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Global Climate Change WebquestDocument1 pageRubric For Global Climate Change Webquestapi-304600541No ratings yet
- Practice Exercises CAEDocument2 pagesPractice Exercises CAENiya PreldjichNo ratings yet
- 12 11 25 Sermon. Christ The KingDocument4 pages12 11 25 Sermon. Christ The Kingschreamonn5515No ratings yet
- Cause Effect EssayDocument2 pagesCause Effect Essaymac léinnNo ratings yet
- Global Warming & Ocean CurrentsDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming & Ocean Currentsapi-3702002No ratings yet
- Taking Stock: A Global Assessment of Net Zero TargetsDocument30 pagesTaking Stock: A Global Assessment of Net Zero TargetsComunicarSe-ArchivoNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper 1 PDFDocument3 pagesReaction Paper 1 PDFJawehNo ratings yet
- Can Climate Change Really End the WorldDocument2 pagesCan Climate Change Really End the WorldDavid Christopher InciongNo ratings yet
- Perceptions of Masbate Students on EVs' Role in Cutting EmissionsDocument15 pagesPerceptions of Masbate Students on EVs' Role in Cutting EmissionsJohn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument1 pageClimate ChangeVincent William RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Examine The Effect of Climate Change On Communities and Natural SystemsDocument2 pagesExamine The Effect of Climate Change On Communities and Natural SystemsEmilie ENo ratings yet
- Webquest - Carbon FootprintDocument4 pagesWebquest - Carbon Footprintapi-250255512No ratings yet
- C Rsia: Implementation PlanDocument8 pagesC Rsia: Implementation PlanRekib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Potential and Relationship With Greenhouse GasesDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming Potential and Relationship With Greenhouse GasesHammad AshrafNo ratings yet
- SA SkitDocument3 pagesSA SkitJitender YadavNo ratings yet
- MacrofinalDocument12 pagesMacrofinalapi-486409803No ratings yet
- Love and Protect Thy Nature For Thy BETTER Future: Cause of Global WarmingDocument2 pagesLove and Protect Thy Nature For Thy BETTER Future: Cause of Global Warmingalyssa valdezNo ratings yet
- False Alarm: How Climate Change Panic Costs Us Trillions, Hurts The Poor, and Fails To Fix The Planet - Björn LomborgDocument5 pagesFalse Alarm: How Climate Change Panic Costs Us Trillions, Hurts The Poor, and Fails To Fix The Planet - Björn Lomborglixunoxy0% (1)
- Five-Paragraph EssayDocument2 pagesFive-Paragraph EssayceriasakiNo ratings yet
- Ocean plankton drive oxygen productionDocument1 pageOcean plankton drive oxygen productionDayu Btarismari 12No ratings yet
- Manalili Please Print LabyuDocument2 pagesManalili Please Print LabyuTal MigallonNo ratings yet