Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q1-Explain Link State Routing. Ans
Q1-Explain Link State Routing. Ans
Uploaded by
mayankOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q1-Explain Link State Routing. Ans
Q1-Explain Link State Routing. Ans
Uploaded by
mayankCopyright:
Available Formats
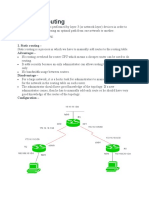
Q1- Explain Link state routing.
Ans - Link state routing is a technique in which each router shares the
knowledge of its neighborhood with every other router in the internetwork.
The three keys to understand the Link State Routing algorithm:
Knowledge about the neighborhood: Instead of sending its routing table, a
router sends the information about its neighborhood only. A router
broadcast its identities and cost of the directly attached links to other
routers.
Flooding: Each router sends the information to every other router on the
internetwork except its neighbors. This process is known as Flooding. Every
router that receives the packet sends the copies to all its neighbors. Finally,
each and every router receives a copy of the same information.
Information sharing: A router sends the information to every other router
only when the change occurs in the information.
The Link state routing algorithm is also known as Dijkstra's algorithm which
is used to find the shortest path from one node to every other node in the
network.
The Dijkstra's algorithm is an iterative, and it has the property that after
kth iteration of the algorithm, the least cost paths are well known for k
destination nodes.
Q2. Difference between Link state routing
and dynamic routing.
Ans – #Link State Routing
Link State Routing is also known as non-adaptive routing
which doesn’t change routing table unless the network administrator
changes or modify them manually. Static routing does not use complex
routing algorithms and It provides high or more security than dynamic
routing.
#Dynamic Routing
Dynamic routing is also known as adaptive routing which
change routing table according to the change in topology. Dynamic routing
uses complex routing algorithms and it does not provide high security like
static routing. When the network change(topology) occurs, it sends the
message to router to ensure that changes then the routes are recalculated
for sending updated routing information.
You might also like
- Unit 4 Network LayerDocument43 pagesUnit 4 Network LayerRahul ChugwaniNo ratings yet
- Types of RoutingDocument34 pagesTypes of RoutingmulukenNo ratings yet
- CNS Mod 3 NLDocument23 pagesCNS Mod 3 NLSamanthNo ratings yet
- Network LayerDocument38 pagesNetwork LayerSoccho cocNo ratings yet
- Routing Algorithms (Distance Vector, Link State) Study Notes - Computer Sc. & EnggDocument6 pagesRouting Algorithms (Distance Vector, Link State) Study Notes - Computer Sc. & Enggkavya associatesNo ratings yet
- 20MIM10073 (Activity1.5)Document7 pages20MIM10073 (Activity1.5)Deepika SheshabutterNo ratings yet
- Understanding Routing What Is Routing?Document17 pagesUnderstanding Routing What Is Routing?Sanjay Kumar MahanaNo ratings yet
- Switching: Comparison of Virtual-Circuit andDocument2 pagesSwitching: Comparison of Virtual-Circuit andkalaNo ratings yet
- NetworkLab 1exDocument14 pagesNetworkLab 1exMadan Prabhu DuraiNo ratings yet
- L7 CN Network Layer FinalDocument8 pagesL7 CN Network Layer FinalJeff jayNo ratings yet
- Routing: Routing Is The Process of Selecting Paths in A Network Along Which To Send Network Traffic. Routing IsDocument8 pagesRouting: Routing Is The Process of Selecting Paths in A Network Along Which To Send Network Traffic. Routing IsMuslim Abdul Ul-AllahNo ratings yet
- Routing For BCADocument35 pagesRouting For BCAPratibhaNo ratings yet
- Network LayerDocument76 pagesNetwork LayerKarthik MNo ratings yet
- Routing BasicsDocument8 pagesRouting BasicsIvelin ValchevNo ratings yet
- Routing, DSDV, DSR, Aodv, ZRP, OdmrDocument17 pagesRouting, DSDV, DSR, Aodv, ZRP, OdmrSelva Kanmani100% (3)
- Unit 3 Dynamic RoutingDocument27 pagesUnit 3 Dynamic RoutingDudzayi KasiyoNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-3Document32 pagesCN Unit-3Narayanapally DeepikaNo ratings yet
- RoutingDocument8 pagesRoutingniravsoni001No ratings yet
- GPSR: Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing For Wireless NetworksDocument49 pagesGPSR: Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing For Wireless Networkslanvo89No ratings yet
- Router RoutingDocument5 pagesRouter RoutingElla Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document14 pagesUnit 8Subeksha PiyaNo ratings yet
- Cosc AssigmentDocument11 pagesCosc AssigmentTsinat TamratNo ratings yet
- Computer Network: Routing ProtocolsDocument46 pagesComputer Network: Routing ProtocolsEmad Samir FarahatNo ratings yet
- Routing Protocol & AlgorithmsDocument45 pagesRouting Protocol & AlgorithmsVikas PsNo ratings yet
- ProtocolsDocument6 pagesProtocolsPŘincê ÂĻĩNo ratings yet
- RoutingDocument22 pagesRoutingisratjahanchandmoniNo ratings yet
- Link State Routing ProtocolDocument11 pagesLink State Routing ProtocolPoonam's favouriteNo ratings yet
- Routing SimulatorDocument69 pagesRouting SimulatorQuestionPapersTube67% (3)
- Q1 - Explain Path Vector Routing. AnsDocument2 pagesQ1 - Explain Path Vector Routing. AnsmayankNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument22 pagesUnit 4 - Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSintu MishraNo ratings yet
- Routing ProtocolsDocument32 pagesRouting ProtocolsPaulNo ratings yet
- CN - UNIT 3 NewDocument30 pagesCN - UNIT 3 NewVarun TyagiNo ratings yet
- NDC Chapter 3Document19 pagesNDC Chapter 3Gedion GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document39 pagesUnit 3anish.t.pNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Routing: Internetworking - Lecture 6Document35 pagesDynamic Routing: Internetworking - Lecture 6GreyHatNo ratings yet
- What Is RoutingDocument13 pagesWhat Is Routingarijitkar0x7No ratings yet
- The Network Layer Is Concerned With GettingDocument103 pagesThe Network Layer Is Concerned With GettingsrinusirisalaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 LabDocument5 pagesLecture 5 LabSerin AskecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.2 Network Layer and Routing - ModifiedDocument72 pagesChapter 4.2 Network Layer and Routing - ModifiedmeheratuNo ratings yet
- What Is Routing AlgorithmDocument12 pagesWhat Is Routing AlgorithmTum BinNo ratings yet
- Routing BasicsDocument28 pagesRouting BasicsMUHAMMAD ABDUL RAHEEMNo ratings yet
- Routing Algorithms PDFDocument41 pagesRouting Algorithms PDFjupitugrigoreNo ratings yet
- GPSRDocument49 pagesGPSRAkhlad NajeemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document30 pagesChapter 4misikir zenebeNo ratings yet
- Introd Uction To IP RoutingDocument14 pagesIntrod Uction To IP Routingapi-292985604No ratings yet
- Routing Protocols: Dalya A.Alrahim AljuboriDocument45 pagesRouting Protocols: Dalya A.Alrahim AljuboriFatima100% (1)
- CNM Chapter5Document18 pagesCNM Chapter5saadmulla1717No ratings yet
- RoutingDocument12 pagesRoutingSuruchi LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Computer Networking - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument20 pagesUnit 4 - Computer Networking - WWW - Rgpvnotes.insusmitaNo ratings yet
- Static RoutingDocument7 pagesStatic RoutingBryan LaTorreNo ratings yet
- Mobile ComputingDocument3 pagesMobile Computingselvam_mcaNo ratings yet
- Routing RIP OSPFDocument5 pagesRouting RIP OSPFnyashamagutsa93No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document19 pagesChapter 6Naveed SultanNo ratings yet
- Basic of RoutingDocument56 pagesBasic of RoutingnjgregNo ratings yet
- Link State RoutingDocument11 pagesLink State RoutingPav TechnicalsNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument6 pagesComputer Networksumair riazNo ratings yet
- W4 - Presentation-Chapter 4 Routing ConceptsDocument21 pagesW4 - Presentation-Chapter 4 Routing ConceptsWendellNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- Mod1 MergedDocument237 pagesMod1 MergedmayankNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document20 pagesLec 8mayankNo ratings yet
- Lec 12Document12 pagesLec 12mayankNo ratings yet
- Lec 18Document12 pagesLec 18mayankNo ratings yet
- Lec 13Document11 pagesLec 13mayankNo ratings yet
- Lec 21Document8 pagesLec 21mayankNo ratings yet
- Lec 7Document10 pagesLec 7mayankNo ratings yet
- Lec 20Document9 pagesLec 20mayankNo ratings yet
- Lec 19Document15 pagesLec 19mayankNo ratings yet
- Mayank Raj - LP - Practice - MostFrequentDigit - 1609843153072Document3 pagesMayank Raj - LP - Practice - MostFrequentDigit - 1609843153072mayankNo ratings yet
- LP - Practice - Nthprime Wipro: Abhishek Upadhyay Finish State: Normal Test Taken On: December 23, 2020 05:45:05 PM IstDocument3 pagesLP - Practice - Nthprime Wipro: Abhishek Upadhyay Finish State: Normal Test Taken On: December 23, 2020 05:45:05 PM IstmayankNo ratings yet
- Mayank Raj - LP - Practice - isExactMultiple - 1609842328169Document3 pagesMayank Raj - LP - Practice - isExactMultiple - 1609842328169mayankNo ratings yet
- ITC Maurya Hotel: LEED O+M: Existing Buildings (v2009)Document1 pageITC Maurya Hotel: LEED O+M: Existing Buildings (v2009)mayankNo ratings yet
- Java Programming (BCSE 3074) Lab File: JULY 2020Document26 pagesJava Programming (BCSE 3074) Lab File: JULY 2020mayankNo ratings yet
- Mayank Raj - LP - Practice - Of5HowManyAreOdd - 1608643659885Document3 pagesMayank Raj - LP - Practice - Of5HowManyAreOdd - 1608643659885mayankNo ratings yet
- Mayank Raj - LP - Practice - Isprime - 1609842023988Document3 pagesMayank Raj - LP - Practice - Isprime - 1609842023988mayankNo ratings yet
- Logical Reasoning (Grouping and Distribution)Document2 pagesLogical Reasoning (Grouping and Distribution)mayank0% (1)
- Mayank Raj - LP - Practice - 2ndLastDigitOfN - 1608643012880Document3 pagesMayank Raj - LP - Practice - 2ndLastDigitOfN - 1608643012880mayankNo ratings yet
- Mayank Raj - LP - Practice - sumOfLastDigitsOf2Numbers - 1608642294898Document3 pagesMayank Raj - LP - Practice - sumOfLastDigitsOf2Numbers - 1608642294898mayankNo ratings yet
- Mayank Raj - LP - Practice - 2ndWordUppercase - 1608644084304Document3 pagesMayank Raj - LP - Practice - 2ndWordUppercase - 1608644084304mayankNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Bidding and Tendering 2Document27 pagesUnit 3 Bidding and Tendering 2mayankNo ratings yet
- Q 1 - What Is BIG O Notation in DAA. Ans-: Worst CaseDocument1 pageQ 1 - What Is BIG O Notation in DAA. Ans-: Worst CasemayankNo ratings yet
- Ans-#Include : 1. Write A C++ Program To Reverse Your Full Name Using StackDocument5 pagesAns-#Include : 1. Write A C++ Program To Reverse Your Full Name Using StackmayankNo ratings yet
- Q. Differentiate Between Random Scan and Raster Scan Display Devices. AnsDocument1 pageQ. Differentiate Between Random Scan and Raster Scan Display Devices. AnsmayankNo ratings yet
- Bresenhem Circle Drawing Algorithm: ProgramDocument4 pagesBresenhem Circle Drawing Algorithm: ProgrammayankNo ratings yet
- Bresenham Algorithm: ProgramDocument3 pagesBresenham Algorithm: ProgrammayankNo ratings yet
- Write A Program in C++ To Delete A Perticular Node From Linked List. AnsDocument9 pagesWrite A Program in C++ To Delete A Perticular Node From Linked List. AnsmayankNo ratings yet
- DDA Line Drawing Algorithm:: ProgramDocument3 pagesDDA Line Drawing Algorithm:: ProgrammayankNo ratings yet