Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scripting Language: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
joanpadilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
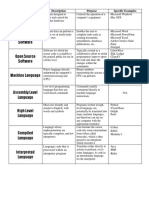
31 views1 pageScripting languages are programming languages used for automating tasks in a specific runtime environment like software applications, web pages, and operating system shells. They are often interpreted rather than compiled for increased performance. Scripting languages allow basic tasks or API calls to be combined into programs. Examples of scripting languages include Bash for Unix systems, JavaScript for web browsers, and Visual Basic for Applications for Microsoft Office. Scripting languages can range from very domain-specific to general-purpose languages used for scripting tasks.
Original Description:
Scripting language
Original Title
Scripting language
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentScripting languages are programming languages used for automating tasks in a specific runtime environment like software applications, web pages, and operating system shells. They are often interpreted rather than compiled for increased performance. Scripting languages allow basic tasks or API calls to be combined into programs. Examples of scripting languages include Bash for Unix systems, JavaScript for web browsers, and Visual Basic for Applications for Microsoft Office. Scripting languages can range from very domain-specific to general-purpose languages used for scripting tasks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pageScripting Language: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
joanpadillaScripting languages are programming languages used for automating tasks in a specific runtime environment like software applications, web pages, and operating system shells. They are often interpreted rather than compiled for increased performance. Scripting languages allow basic tasks or API calls to be combined into programs. Examples of scripting languages include Bash for Unix systems, JavaScript for web browsers, and Visual Basic for Applications for Microsoft Office. Scripting languages can range from very domain-specific to general-purpose languages used for scripting tasks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Scripting language
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigationJump to search
A scripting or script language is a programming language for a special run-time
environment that automates the execution of tasks[1]; the tasks could alternatively be executed
one-by-one by a human operator. Scripting languages are often interpreted, rather
than compiled (as there is decreased performance of when they are compiled, since they are
compiled one line at a time).
Primitives are usually the elementary tasks or API calls[clarification needed], and the language allows them
to be combined into more programs. Environments that can be automated through scripting
include software applications, web pages within a web browser, usage of the shells of operating
systems (OS), embedded systems, as well as numerous games. A scripting language can be
viewed as a domain-specific language for a particular environment; in the case of scripting an
application, it is also known as an extension language. Scripting languages are also sometimes
referred to as very high-level programming languages, as they operate at a high level of
abstraction, or as control languages, particularly for job control languages on mainframes.
The term "scripting language" is also used loosely to refer to dynamic high-level general-purpose
languages, such as Perl,[2] PowerShell, Python, and Tcl[3] with the term "script" often used for
small programs (up to a few thousand lines of code) in such languages, or in domain-specific
languages such as the text-processing languages sed and AWK. Some of these languages were
originally developed for use within a particular environment, and later developed into portable
domain-specific or general-purpose languages. Conversely, many general-purpose languages
have dialects that are used as scripting languages. This article discusses scripting languages in
the narrow sense of languages for a specific environment.
The spectrum of scripting languages ranges from very small and highly domain-specific
languages to general-purpose programming languages used for scripting. Standard examples of
scripting languages for specific environments include: Bash, for the Unix or Unix-like operating
systems; ECMAScript (JavaScript), for web browsers; and Visual Basic for Applications,
for Microsoft Office applications. Lua is a language designed and widely used as an extension
language. Python is a general-purpose language that is also commonly used as an extension
language, while ECMAScript is still primarily a scripting language for web browsers, but is also
used as a general-purpose language. The Emacs Lisp dialect of Lisp (for the Emacs editor) and
the Visual Basic for Applications dialect of Visual Basic are examples of scripting language
dialects of general-purpose languages. Some game systems, notably the Second Life virtual
world and the Trainz franchise of Railroad simulators have been extensively extended in
functionality by scripting extensions (Linden Scripting Language and TrainzScript). In other
games like Wesnoth, the variety of actual games played by players are scripts written by other
users.
You might also like
- 50 Types of Programming Languages and What They DoDocument7 pages50 Types of Programming Languages and What They DoshielaNo ratings yet
- Imperative Programming 1Document169 pagesImperative Programming 1faiyaz pardiwalaNo ratings yet
- Software Applications: Clarification NeededDocument1 pageSoftware Applications: Clarification NeededMark Denniel BantaNo ratings yet
- ScriptingDocument1 pageScriptingAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Scripting Language - WikipediaDocument9 pagesScripting Language - WikipediaGilbertNo ratings yet
- Scripting Language - WikipediaDocument8 pagesScripting Language - WikipediaAndoni Ruiz ErezumaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Integrative Programming and Technologies Part 2Document12 pagesIntroduction To Integrative Programming and Technologies Part 2Arnel NietoNo ratings yet
- Scripting Language - WikipediaDocument12 pagesScripting Language - WikipediaatifchaudhryNo ratings yet
- Scripting Language - WikipediaDocument7 pagesScripting Language - Wikipediaasd1080No ratings yet
- SL Unit IDocument12 pagesSL Unit IPoornaNo ratings yet
- Domain-Specific Language - WikipediaDocument11 pagesDomain-Specific Language - WikipediaGilbertNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Introduction To Scripting Languages: 1.1 Scripts and ProgramsDocument34 pagesUNIT-1 Introduction To Scripting Languages: 1.1 Scripts and Programsakruti raj100% (1)
- Web Scripting LanguagesDocument22 pagesWeb Scripting LanguagesriyazpashaNo ratings yet
- Infot 1 - Chapter 3Document17 pagesInfot 1 - Chapter 3ArianneNo ratings yet
- Programming Languages: 1. PythonDocument12 pagesProgramming Languages: 1. PythonJazmin Shane Buates BellezaNo ratings yet
- Programming LanguageDocument6 pagesProgramming LanguageChidinma Glory EjikeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part I IntroductiontoScriptingDocument54 pagesUnit 1 Part I IntroductiontoScriptinganuradha.reddyNo ratings yet
- Scripting HistoriaDocument1 pageScripting HistoriajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Programming LanguageDocument10 pagesDefinitions: Programming LanguageSyed Fahad ALiNo ratings yet
- SL 1Document16 pagesSL 1kalluru charithaNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamental and Programming: Prepared By: Mary Kris P. Morco Professorial LecturerDocument65 pagesComputer Fundamental and Programming: Prepared By: Mary Kris P. Morco Professorial LecturerXentrix CritzNo ratings yet
- Met A LinguisticDocument10 pagesMet A LinguisticAmulya KodaliNo ratings yet
- TO Computer Programming: Unit 2: Lesson 1Document21 pagesTO Computer Programming: Unit 2: Lesson 1Fritz Ren KeifferNo ratings yet
- Types of Scripting LanguagesDocument8 pagesTypes of Scripting LanguagesMayur LoveNo ratings yet
- C++ Programming Language Language C++ PHP PHP Scripting LanguageDocument2 pagesC++ Programming Language Language C++ PHP PHP Scripting LanguageGenivave Olivar DañoNo ratings yet
- HO W Does Programming Language Work?Document7 pagesHO W Does Programming Language Work?Amal UsmanNo ratings yet
- Types of Programming Languages: Abdullah Alolewi - 361103059 DR - KHALID NazimDocument7 pagesTypes of Programming Languages: Abdullah Alolewi - 361103059 DR - KHALID NazimnazimsattarNo ratings yet
- Programming LanguagesDocument5 pagesProgramming LanguagesSaad KolsawalaNo ratings yet
- Script LanguagesDocument4 pagesScript LanguagesRehman AliNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 1 - Language Design EssayDocument14 pagesASSIGNMENT 1 - Language Design EssayKrishna ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Programming LanguageDocument3 pagesProgramming LanguageShine Cruz RamosNo ratings yet
- List of Programming Languages by TypeDocument26 pagesList of Programming Languages by Typebert_bear1000No ratings yet
- Programming LanguageDocument7 pagesProgramming LanguageDina WondwossenNo ratings yet
- Programming LanguageDocument24 pagesProgramming LanguageKhaldon MetmugNo ratings yet
- 优秀计算机英语资料Document12 pages优秀计算机英语资料laohei889No ratings yet
- Compiler: Translator, ConverterDocument3 pagesCompiler: Translator, Converter2nablsNo ratings yet
- PDF 20220710 205949 0000Document9 pagesPDF 20220710 205949 0000dishajainNo ratings yet
- Programming Languages & Mark-Up LanguagesDocument33 pagesProgramming Languages & Mark-Up LanguagesMohdHelmizanNo ratings yet
- Programming Language - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesProgramming Language - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaelcorinoNo ratings yet
- Seminar WTDocument11 pagesSeminar WTMohammed Razid LathifNo ratings yet
- English III - Video Work - Programming LanguageDocument7 pagesEnglish III - Video Work - Programming LanguageLEIDY FABIOLA SANABRIA VALLEJOSNo ratings yet
- Types and Differences Between Programming LanguagesDocument10 pagesTypes and Differences Between Programming LanguagesrituNo ratings yet
- High LevelDocument3 pagesHigh LevelPromila JangraNo ratings yet
- The Design LanguageDocument10 pagesThe Design LanguageRicardo lemeNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document20 pagesCH 01Ushu GemechuNo ratings yet
- Week 02 Theory Slides-SDocument34 pagesWeek 02 Theory Slides-Simauno55No ratings yet
- A Programming Language Is An Artificial Language Designed To Communicate Instructions To A MachineDocument15 pagesA Programming Language Is An Artificial Language Designed To Communicate Instructions To A MachinehasannahidulNo ratings yet
- PP Innovative Features of Scripting LanguagesDocument20 pagesPP Innovative Features of Scripting Languages014 CSE Devamruth AG100% (1)
- Basic WordsDocument3 pagesBasic Wordsniranjan_meharNo ratings yet
- Cs 390Document1 pageCs 390api-303575969No ratings yet
- Understanding Computer LanguagesDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Computer LanguageszirwaNo ratings yet
- Levels of ProgrammingDocument4 pagesLevels of ProgrammingMitchzel Molo MonteroNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Computer LanguageDocument3 pagesDifferent Types of Computer LanguageMega TronNo ratings yet
- Computer LanguageDocument3 pagesComputer LanguageDebojyoti ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Imperative Programming 2Document195 pagesImperative Programming 2Angelica SaanaayaNo ratings yet
- Languages To Learn: Java: Imperative LanguageDocument2 pagesLanguages To Learn: Java: Imperative LanguageDiljot ArnejaNo ratings yet
- List of Programming LanguagesDocument11 pagesList of Programming LanguagessudipbenNo ratings yet
- NET Framework and Languages: ApplicationDocument10 pagesNET Framework and Languages: ApplicationNagaraju GanapavarapuNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ChartDocument1 pageModule 3 Chartapi-304219156No ratings yet
- PowerShell Practitioner: Understanding The Core Building Blocks of Programming & Scripting through PowerShell, Plus Debunking Popular MisconceptionsFrom EverandPowerShell Practitioner: Understanding The Core Building Blocks of Programming & Scripting through PowerShell, Plus Debunking Popular MisconceptionsNo ratings yet
- Shalwar Kameez: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesShalwar Kameez: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Punjabi SuitDocument2 pagesPunjabi Suitjoanpadilla100% (1)
- Romas de AlganistanDocument2 pagesRomas de AlganistanjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Description: Anarkali SuitDocument1 pageDescription: Anarkali SuitjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Etymology and History: Berlin Ethnographic MuseumDocument3 pagesEtymology and History: Berlin Ethnographic MuseumjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Religiaon PunjabisDocument1 pageReligiaon PunjabisjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Punjabi HinduDocument1 pagePunjabi HindujoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water TripuraDocument1 pageDrinking Water TripurajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Sports: Notable PeopleDocument1 pageSports: Notable PeoplejoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Historia PunjabisDocument2 pagesHistoria PunjabisjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Sikh Era Punjab: Geographic DistributionDocument2 pagesSikh Era Punjab: Geographic DistributionjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Particion PunjabisDocument2 pagesParticion PunjabisjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Sarinda: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesSarinda: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Religion y Cultura TripuraDocument4 pagesReligion y Cultura TripurajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Punjabis: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument4 pagesPunjabis: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- National Highway 8 Sabroom: The Border Post Between Bangladesh and India inDocument1 pageNational Highway 8 Sabroom: The Border Post Between Bangladesh and India injoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Education y Salud TripuraDocument2 pagesEducation y Salud TripurajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Thermal Power Stations ONGC Tripura Power CompanyDocument1 pageElectricity: Thermal Power Stations ONGC Tripura Power CompanyjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Flora y Fauna TripuraDocument1 pageFlora y Fauna TripurajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Medio en Comunicacion TripuraDocument1 pageMedio en Comunicacion TripurajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Etimology Trupura PDFDocument1 pageEtimology Trupura PDFjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Goverment IndiaDocument2 pagesGoverment IndiajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Divisions: List of Districts of TripuraDocument1 pageDivisions: List of Districts of TripurajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Economy: GSDP at Constant Prices (2004 - 05 Base)Document1 pageEconomy: GSDP at Constant Prices (2004 - 05 Base)joanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Tranporte TripuraDocument2 pagesTranporte TripurajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- History: History of Tripura Twipra Kingdom Tripura (Princely State) Kings of Tripura Tripura RebellionDocument2 pagesHistory: History of Tripura Twipra Kingdom Tripura (Princely State) Kings of Tripura Tripura RebellionjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Tripura: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument4 pagesTripura: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Forestry in India Wildlife of IndiaDocument2 pagesBiodiversity: Forestry in India Wildlife of IndiajoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Climate: Edit Tropical Savanna Climate Köppen Climate ClassificationDocument1 pageClimate: Edit Tropical Savanna Climate Köppen Climate ClassificationjoanpadillaNo ratings yet
- Book Review: Cancy Mcarn Issues in Teacher Education, Spring 2009Document4 pagesBook Review: Cancy Mcarn Issues in Teacher Education, Spring 2009juan_carlos0733No ratings yet
- Request Please Only Students Who Are Willing To Join in Haryana in Any District Are Requested To Apply For JobDocument2 pagesRequest Please Only Students Who Are Willing To Join in Haryana in Any District Are Requested To Apply For JobUdayan KarnatakNo ratings yet
- Adherence Tradeoff To Multiple Preventive Therapies and All-Cause Mortality After Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument12 pagesAdherence Tradeoff To Multiple Preventive Therapies and All-Cause Mortality After Acute Myocardial InfarctionRoberto López MataNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. - CSE - R13-Syllabus JntuaDocument132 pagesB. Tech. - CSE - R13-Syllabus JntuaVasim AkramNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Number Systems: Introduction To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Document16 pagesModule 5: Number Systems: Introduction To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Mihai MarinNo ratings yet
- Yusof Ishak Secondary School Humanities Study Tour Ho Chi Minh City, VietnamDocument19 pagesYusof Ishak Secondary School Humanities Study Tour Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnamadamant751No ratings yet
- COLUMNA A. Erosion B. Ecosystem C. Conservation D - .DDocument1 pageCOLUMNA A. Erosion B. Ecosystem C. Conservation D - .DkerinsaNo ratings yet
- SCI Annual Report 2017Document32 pagesSCI Annual Report 2017The Seamen's Church Institute100% (2)
- Personal Tutor: 11 + MATHS Test 6Document10 pagesPersonal Tutor: 11 + MATHS Test 6siddhant4uNo ratings yet
- Everyday Life - B1 - ShoppingDocument7 pagesEveryday Life - B1 - ShoppingAmi BarnesNo ratings yet
- Colony Earth - Part X: The Myriad WorldsDocument7 pagesColony Earth - Part X: The Myriad WorldsV. Susan FergusonNo ratings yet
- O RTIZDocument2 pagesO RTIZKhimberly Xylem OrtizNo ratings yet
- Amazing RaceDocument2 pagesAmazing Racegena sanchez BernardinoNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication: Chapter Nine Khalid HussainDocument49 pagesDNA Structure and Replication: Chapter Nine Khalid HussainKhalid HussainNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 - External Forced Convection - WatermarkDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet 3 - External Forced Convection - WatermarkUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- PL SQL Exercise6Document2 pagesPL SQL Exercise6Nishant AndhaleNo ratings yet
- 2017 Lecture 3 Metal Carbonyls PDFDocument28 pages2017 Lecture 3 Metal Carbonyls PDFMahnoor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Financial AccountingDocument3 pagesSyllabus Financial AccountingHusain ADNo ratings yet
- Site AnalysisDocument4 pagesSite AnalysisS O NALNo ratings yet
- Data Mining With Apriori AlgorithmDocument12 pagesData Mining With Apriori AlgorithmMAYANK JAINNo ratings yet
- Bird Beak Adaptations: PurposeDocument9 pagesBird Beak Adaptations: PurposelilazrbNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive TractDocument14 pagesCongenital Abnormalities of The Female Reproductive TractMary SheshiraNo ratings yet
- Frankenstein ExtractDocument1 pageFrankenstein ExtractAnneNo ratings yet
- Radiant Protection Force Pvt. LTD.,: Col David DevasahayamDocument13 pagesRadiant Protection Force Pvt. LTD.,: Col David Devasahayamabhilash0029No ratings yet
- Differentialequations, Dynamicalsystemsandlinearalgebra Hirsch, Smale2Document186 pagesDifferentialequations, Dynamicalsystemsandlinearalgebra Hirsch, Smale2integrationbyparths671No ratings yet
- Analisis Perencanaan Rekrutmen Aparatur Sipil Negara Kabupaten Mamuju UtaraDocument11 pagesAnalisis Perencanaan Rekrutmen Aparatur Sipil Negara Kabupaten Mamuju UtarafitriNo ratings yet
- SPE-171076-MS The Role of Asphaltenes in Emulsion Formation For Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage (SAGD) and Expanding Solvent - SAGD (ES-SAGD)Document14 pagesSPE-171076-MS The Role of Asphaltenes in Emulsion Formation For Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage (SAGD) and Expanding Solvent - SAGD (ES-SAGD)Daniel FelipeNo ratings yet
- Leading Airline Emirates Boosts Leisure Travel Sales - : Peakwork Case Study: EmiratesDocument3 pagesLeading Airline Emirates Boosts Leisure Travel Sales - : Peakwork Case Study: EmiratesAhmed AbboudNo ratings yet
- Effect of Different Laser Texture Configurations On Improving Surface Wettability and Wear Characteristics of Ti6Al4V Implant MaterialDocument14 pagesEffect of Different Laser Texture Configurations On Improving Surface Wettability and Wear Characteristics of Ti6Al4V Implant Materialnitish kumar100% (1)
- InflibnetDocument3 pagesInflibnetSuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet