Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Colorectal Cancer Presentation PDF
Colorectal Cancer Presentation PDF
Uploaded by
ismu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views30 pagesOriginal Title
colorectal-cancer-presentation.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views30 pagesColorectal Cancer Presentation PDF
Colorectal Cancer Presentation PDF
Uploaded by
ismuCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
Colorectal Cancer:
Preventable, Beatable,
Treatable
American Cancer Society
Reviewed/Revised May 2018
What we’ll be talking about
▪ How common is colorectal cancer?
▪ What is colorectal cancer?
▪ What causes it?
▪ What are the risk factors?
▪ Can colorectal cancer be prevented?
▪ Tests to find colorectal cancer early
▪ What you can do
▪ More information
Colorectal cancer: How common is it?
▪ 3rd most common cancer in both men and
women in the U.S. (not including skin
cancer).
▪ 2nd leading cause of cancer-related death
in the U.S. for men and women combined.
▪ It’s estimated that more than half of all
cases could be prevented by regular
colonoscopy screening!
What is colorectal cancer?
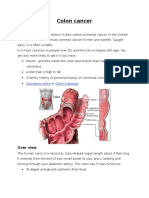
▪ The colon (large bowel
or large intestine)
▪ A muscular tube about 5
feet long
▪ Part of the digestive
system
▪ Absorbs water and salt
from food
▪ Stores waste matter
▪ The rectum is the last 6
inches of the digestive
system.
What is colorectal cancer?
▪ Cancer is the growth of abnormal cells.
▪ Cancer cells can invade and damage
normal tissue.
▪ Colorectal cancer starts in the colon or the
rectum (parts of the digestive system).
▪ ColoRectal Cancer is often abbreviated as
CRC.
Causes of colorectal cancer
▪ We do not know the cause of most
colorectal cancers.
▪ Most likely cause is related to changes in
the genetic material (DNA) in our cells.
▪ Most DNA changes are related to our
lifestyle.
Colorectal cancer risk factors
Risk factors are anything that can increase or
decrease a person’s chance of getting a
disease, such as cancer.
▪ Age
▪ Most CRC occurs in people age 50 and older
▪ Studies show significant increased incidence in
those under age 55 from 2004-2014
▪ Diet
▪ High in red meats (like beef, pork, or lamb)
and processed meats (like hot dogs, bacon, or
cold cuts) raises risk for CRC
▪ High in fruits and vegetables lowers risk
Colorectal cancer risk factors
▪ Physical activity
▪ Less active raises risk
▪ Overweight
▪ Obesity raises risk of having
and dying from CRC
▪ Smoking raises risk
▪ Alcohol use raises risk
▪ Type 2 diabetes raises risk
Colorectal cancer – major risk factors
Some adults have risk factors that make
them much more likely to develop CRC than
others:
▪ Those with inflammatory bowel disease
such as
▪ Ulcerative colitis
▪ Crohn’s disease
▪ Those who have had radiation to the
abdominal or pelvic area to treat a
previous cancer
(Irritable bowel disease is not a risk factor.)
Colorectal cancer – major risk factors
▪ People who have had adenomatous polyps
▪ People who have family members with
adenomatous polyps or FAP, CRC, or
certain inherited syndromes such as Lynch
syndrome (HPNCC)
▪ People who have had CRC in the past (Risk
is even higher if occurred at a younger age)
Talk to your doctor right away if you or
people in your family have any of these
major risk factors.
Risk factors – polyps
A polyp is a growth of tissue in
the lining of an organ.
There are 2 main types of
colorectal polyps:
▪Hyperplastic
Very small chance
they’ll grow into cancer
▪Adenomatous
Most colon and rectal cancers
start as adenomatous polyps
(“adenomas”)
Polyps
Preventing colorectal cancer
▪ Many colorectal cancers could be
prevented with regular screening.
▪ Screening is testing to find a disease in
people who have no symptoms.
▪ Why screen?
▪ To find and remove polyps before they
become cancer
▪ To find CRC early – when it’s small and likely
has not spread, and when treatment can be
more effective
How is CRC screening done?
2 types of tests for CRC screening:
1. Visual exams: Tests that can
find both polyps and
colorectal cancer
2. Stool-based tests: Tests that
mainly find cancer
Visual Exams:
Tests that can find both polyps and cancer
✓ Flexible sigmoidoscopy
✓ Colonoscopy
✓ CT colonography (“virtual colonoscopy”)
▪ These tests look inside the colon to find abnormal areas.
▪ They are done with a lighted tube put in through the
rectum or with special x-ray tests.
▪ If polyps are found they may be removed before they
develop into cancer, so these tests can help prevent cancer.
▪ These tests are preferred for screening (if available) and if a
person is willing to have them.
Colonoscopy
A thin, lighted tube
is put in through
the anus and
rectum and passed
up into the colon to
look for abnormal
areas.
Tissue can be taken
from any areas of
concern and polyps
can be removed.
Colonoscopy
If polyps are found during a colonoscopy
they can be removed with tools used
through the narrow scope. Removing
polyps before they turn into cancer is how
tests like this can prevent cancer.
CT colonography
▪ Air is pumped into the
colon through a flexible
tube
▪ CT scans are then done
▪ Special computer
programs create both
2-dimensional x-ray pictures and a 3-
dimensional "fly-through" view of the
inside of the colon and rectum, which lets
the doctor look for polyps and cancer.
Stool-based Tests:
Tests that mainly find cancer
✓ Fecal immunochemical test (FIT)
✓ Guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT)
✓ Stool DNA tests (sDNA)
▪ All of these test the stool for hidden blood or other
changes that may be signs of cancer.
▪ They are less invasive and easier to do.
▪ They are less likely to find polyps than visual exams.
▪ Colonoscopy will be needed if results are abnormal.
ACS Colorectal Cancer
Screening Guidelines: 2018
▪ At age 45, both men and women at
average risk should begin regular screening
either with a sensitive stool-based test, or
with a visual exam that looks at the colon
and rectum.
▪ People who are in good health and with a
life expectancy of more than 10 years
should continue regular colorectal cancer
screening through the age of 75.
ACS Colorectal Cancer
Screening Guidelines: 2018
Test options for colorectal cancer screening:
▪ Stool-based tests: Tests that mainly find cancer
▪ Highly sensitive fecal immunochemical test (FIT) every
year*, OR
▪ Highly sensitive guaiac-based fecal occult blood test
(gFOBT) every year*, OR
▪ Multi-targeted stool DNA test (MT-sDNA) every 3 years*
(*Abnormal findings will need a colonoscopy as follow-up.)
▪ Visual (structural) exams
▪ Colonoscopy every 10 years, OR
▪ CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy) every 5 years, OR
▪ Flexible sigmoidoscopy (FSIG) every 5 years
ACS Colorectal Cancer
Screening Guidelines: 2018
Adults who are at higher risk for CRC might
need to start screening before age 45, be
screened more often, and/or get specific tests.
Higher risk individuals are those with a family
or personal history of colorectal cancer and
certain types of polyps, other bowel disorders,
or a known hereditary colorectal cancer
syndrome.
So what can you do to prevent
and beat colorectal cancer?
What you can do
▪ Stay at a healthy weight
▪ Be active
✓ At least 150 minutes of
moderate or 75 minutes
of vigorous intensity
activity per week, or an
equivalent combination,
preferably spread
throughout the week
▪ Limit sedentary behavior
What you can do
▪ Eat right
✓ Choose foods and beverages in amounts that
help you get to and stay at a healthy weight
✓ Eat at least 2½ cups of vegetables and fruits
each day
✓ Choose whole grains
✓ Limit red meats (like beef, pork, or lamb) and
processed meats (like hot dogs or luncheon
meats)
▪ Limit alcohol
✓ No more than 2 drinks a day for men and 1 for
women
What you can do
▪ If you are age 45 or older and at average
risk, get tested for colorectal cancer.
▪ Talk with a doctor about which screening
test is best for you.
▪ Talk with a doctor about your medical
history and your family history to find out if
you are at higher risk, need to start testing
earlier, or should have more frequent or
different tests.
What you can do
▪ Screening tests offer the best way to
prevent CRC or find it early. Finding cancer
early gives you a better chance for
successful treatment.
▪ Early CRC usually has no symptoms. Don’t
wait for symptoms to occur.
▪ Again —treatment is most effective when
CRC is found early.
More information
You can get more information on
colorectal cancer on our website,
www.cancer.org/colon, or call
1-800-227-2345 and talk with one of
our cancer information specialists.
Thank you!
©2010 American Cancer Society, Inc. No.0052.19
You might also like
- Moh ExamsDocument12 pagesMoh ExamsPankaj Jindal100% (5)
- HEENT Cheat SheetDocument22 pagesHEENT Cheat SheetKatrina FeriNo ratings yet
- Colorectal: Understanding The Cancer ProcessDocument14 pagesColorectal: Understanding The Cancer ProcessSeli adalah SayaNo ratings yet
- What Is Colorectal Cancer?Document5 pagesWhat Is Colorectal Cancer?Aditya RaoNo ratings yet
- Notes On Liver Colon CancerDocument16 pagesNotes On Liver Colon CancerElleNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer OverviewDocument23 pagesColorectal Cancer OverviewAlina AldeaNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument6 pagesColon CancerUSMP FN ARCHIVOSNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument35 pagesColorectal CancerSHIVAJINo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument6 pagesColon CancerMartin Eduardo Marchena TiradoNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument8 pagesColon Cancersusanna.armentanoNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer ScreeningDocument12 pagesColorectal Cancer ScreeningArniefah RegaroNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer Fact SheetDocument2 pagesColorectal Cancer Fact SheetABY ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Health ScreeningDocument27 pagesHealth ScreeninglilydariniNo ratings yet
- Colon Ca Case Study For Ring BoundDocument66 pagesColon Ca Case Study For Ring BoundMary EnsomoNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDocument40 pagesColorectal Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDian Putri NingsihNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument11 pagesColorectal CancerMithilaa SNo ratings yet
- Philippine Cancer Society Forum:: PolypsDocument2 pagesPhilippine Cancer Society Forum:: PolypsReggie Luna PasonNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: What Are The Symptoms?Document5 pagesSigns and Symptoms: What Are The Symptoms?Waleed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cancer Facts: For WomenDocument6 pagesCancer Facts: For WomenShanntha JoshittaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening and PreventionDocument31 pagesCancer Screening and PreventionShadin SNo ratings yet
- BCSP14 Plain Text April 2021Document8 pagesBCSP14 Plain Text April 2021asrobson1No ratings yet
- Colorectal CAncer InfoDocument2 pagesColorectal CAncer InfoABY ABRAHAM100% (1)
- Ringkasan Colon CancerDocument6 pagesRingkasan Colon CancerPrabha Amandari SutyandiNo ratings yet
- Fecal Occult Blood Test: ColonosDocument3 pagesFecal Occult Blood Test: ColonosMD TIENNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument29 pagesColorectal CancerLeeyanBhadzzVagayNo ratings yet
- Shedding New Light On CancerDocument21 pagesShedding New Light On Cancerthe_revolutionariesNo ratings yet
- Cancer ReportDocument4 pagesCancer Reportdogon123No ratings yet
- About Bowel Cancer - A Quick GuideDocument7 pagesAbout Bowel Cancer - A Quick Guidealvin1445No ratings yet
- English AssegmentDocument7 pagesEnglish AssegmentRenanda PrihastinaNo ratings yet
- Ca RectiDocument7 pagesCa RectiElandNo ratings yet
- Incidence of Cancer and Screening RecommendationsDocument12 pagesIncidence of Cancer and Screening RecommendationsSeba StiánNo ratings yet
- Cancer NursingDocument53 pagesCancer Nursingfairwoods100% (1)
- Colon Cancer: Ulcerative Colitis Crohn's DiseaseDocument11 pagesColon Cancer: Ulcerative Colitis Crohn's DiseasekurniaNo ratings yet
- Nurses As Cancer InsurgentsDocument7 pagesNurses As Cancer InsurgentsNick RealinoNo ratings yet
- Early Detection and Cancer PreventionDocument18 pagesEarly Detection and Cancer PreventionFred YangNo ratings yet
- Cancer DelcolonDocument6 pagesCancer Delcolongabriel vilcaNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument4 pagesCancerTeeVee ThailandNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With Colorectal CancerDocument7 pagesCare of Patients With Colorectal CancerJumar ValdezNo ratings yet
- Renanda & Arju (Cancer Colon)Document15 pagesRenanda & Arju (Cancer Colon)Renanda PrihastinaNo ratings yet
- Colon Cancer Screening and Prevention: Health Screening and PreventionFrom EverandColon Cancer Screening and Prevention: Health Screening and PreventionNo ratings yet
- Neoplasma Liver Iwal-DikompresiDocument30 pagesNeoplasma Liver Iwal-DikompresiSabrina Intan PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Cancer 21Document34 pagesCancer 21preyamvada sNo ratings yet
- Philippine Cancer Control Program - Llamas, Lomod, ParajesDocument39 pagesPhilippine Cancer Control Program - Llamas, Lomod, ParajesSHIELOU LOMODNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer Prevention and Early DetectionDocument33 pagesColorectal Cancer Prevention and Early DetectionNesyah AyuNo ratings yet
- Liver Cancer: Ratheesh R LDocument31 pagesLiver Cancer: Ratheesh R LShehada Marcos BondadNo ratings yet
- CANCER: Know The Warning Signs: Donna V. Puleio, M. D. Upmc-NwDocument48 pagesCANCER: Know The Warning Signs: Donna V. Puleio, M. D. Upmc-NwShield Medical AffairsNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument13 pagesColon CancerMikel Jan PacotNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDocument29 pagesPancreatic Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDokter LinggauNo ratings yet
- New Cellular Aberration Lecture2010Document271 pagesNew Cellular Aberration Lecture2010John Russell MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cancer Prevention PresentationDocument12 pagesCancer Prevention Presentationssnehasingh089No ratings yet
- Liver CancerDocument19 pagesLiver CancerSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- Causes, Risk Factors, and PreventionDocument19 pagesCauses, Risk Factors, and PreventionvictorNo ratings yet
- Testicular Cancer BrochureDocument2 pagesTesticular Cancer BrochuretburkleNo ratings yet
- Screening For Colorectal Cancer: Patient Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument2 pagesScreening For Colorectal Cancer: Patient Frequently Asked QuestionsJulio CardozoNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument5 pagesColon Cancernicwil_wilnicNo ratings yet
- Cancer Research - Jay XieDocument10 pagesCancer Research - Jay XieJay XieNo ratings yet
- Liver Cancer Treatment in Pakistan - NewDocument3 pagesLiver Cancer Treatment in Pakistan - NewMuhammad Shahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Regulation-BreastDocument41 pagesCellular Regulation-BreastMegan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Liver Cancer:: It'S Causes, Preventions, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument25 pagesLiver Cancer:: It'S Causes, Preventions, Symptoms and TreatmentchetankumarbhumireddyNo ratings yet
- Kangker ColorectalDocument16 pagesKangker ColorectalAgit ZNo ratings yet
- Regulatory and Manufacturing Requirements in Compressed Solid Dosage FormsDocument15 pagesRegulatory and Manufacturing Requirements in Compressed Solid Dosage FormsfaikaNo ratings yet
- Microstructure E¡ects On Transport in Reverse MicroemulsionsDocument15 pagesMicrostructure E¡ects On Transport in Reverse MicroemulsionsfaikaNo ratings yet
- Design of Biocompatible Ion SensorsDocument23 pagesDesign of Biocompatible Ion SensorsfaikaNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Formulating Compressed Solids: Iii. Bio vs. Production BatchesDocument16 pagesGuidance On Formulating Compressed Solids: Iii. Bio vs. Production BatchesfaikaNo ratings yet
- Sunscreen-1Document14 pagesSunscreen-1faikaNo ratings yet
- Electroelastic Instabilities in Double Layers and MembranesDocument32 pagesElectroelastic Instabilities in Double Layers and MembranesfaikaNo ratings yet
- The GVDW Theory: A Density Functional Theory of Adsorption, Surface Tension, and ScreeningDocument21 pagesThe GVDW Theory: A Density Functional Theory of Adsorption, Surface Tension, and ScreeningfaikaNo ratings yet
- Interfacial Potentials and CellsDocument22 pagesInterfacial Potentials and CellsfaikaNo ratings yet
- Ion Solvation and ResolvationDocument27 pagesIon Solvation and ResolvationfaikaNo ratings yet
- Adsorption at Polarized Liquid Liquid InterfacesDocument17 pagesAdsorption at Polarized Liquid Liquid InterfacesfaikaNo ratings yet
- PENGARUH KOMBINASI PAKAN BUATAN DAN PAKAN ALAMI CACING SUTERA (Tubifex Tubifex) DENGAN PERSENTASE YANG BERBEDA TERHADAP RETENSI PROTEIN, LEMAK DAN ENERGI PADA IKAN SIDAT (Anguilla Bicolor) PDFDocument6 pagesPENGARUH KOMBINASI PAKAN BUATAN DAN PAKAN ALAMI CACING SUTERA (Tubifex Tubifex) DENGAN PERSENTASE YANG BERBEDA TERHADAP RETENSI PROTEIN, LEMAK DAN ENERGI PADA IKAN SIDAT (Anguilla Bicolor) PDFfaikaNo ratings yet
- Jadwal S2-1Document1 pageJadwal S2-1faikaNo ratings yet
- 9 PDFDocument7 pages9 PDFfaikaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Machine Resistance - 081907Document8 pagesAnesthesia Machine Resistance - 081907zain UL abideenNo ratings yet
- Splenomegaly and HypersplenismDocument59 pagesSplenomegaly and Hypersplenismanas hindawi100% (3)
- Renal Haemodialysis: Adjudication RuleDocument3 pagesRenal Haemodialysis: Adjudication RuleMohammed ZubairNo ratings yet
- LalaDocument31 pagesLalaTeguh PutraNo ratings yet
- Jurnal THT NiaDocument5 pagesJurnal THT NianiajaplaniNo ratings yet
- Leg Edema Assessment and ManagementDocument11 pagesLeg Edema Assessment and Managementastraeax pandaNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument9 pagesAlcoholic Liver DiseasePankaj DixitNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument96 pagesCerebral PalsyRahini PaniNo ratings yet
- Maternal Notes 1Document34 pagesMaternal Notes 1Mica Campoy CabinongNo ratings yet
- RSSM Cibinong - Sistem E-Ticket Makan PasienDocument13 pagesRSSM Cibinong - Sistem E-Ticket Makan PasienAHLI GIZI RSSMCNo ratings yet
- Normal & Abnormal LabourDocument5 pagesNormal & Abnormal Labourra100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term GoalsDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term GoalsdanicaNo ratings yet
- Buster H.yield Facts 2005Document144 pagesBuster H.yield Facts 2005Nisar ShaikNo ratings yet
- Ob Pedia CDDocument13 pagesOb Pedia CDNom Nom100% (1)
- Falls in Elderly PDFDocument35 pagesFalls in Elderly PDFSuraj VermaNo ratings yet
- Introducting The Antibody-42914Document1 pageIntroducting The Antibody-42914Liudmila RusuNo ratings yet
- Free Medical Books On Gastroenterology and Hepatology - Internal Medicine PDFDocument3 pagesFree Medical Books On Gastroenterology and Hepatology - Internal Medicine PDFTammy Stephanie100% (2)
- TRT Targets and Side Effect Management TablesDocument5 pagesTRT Targets and Side Effect Management TablesLucas Ely100% (1)
- SCD Factsheet What Is SCDDocument5 pagesSCD Factsheet What Is SCDAustine OsaweNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance Worksheet AdolfoDocument5 pagesAcid Base Balance Worksheet AdolfoScarlet Guia AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: United StatesDocument11 pagesPathophysiology: United StatesNurullia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- Malaria: Critical Issues - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMalaria: Critical Issues - Lesson Plantangam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Dds Logbook 2012Document81 pagesDds Logbook 2012তৌহিদ তপুNo ratings yet
- DOH Health ProgramsDocument2 pagesDOH Health Programsjeffrey-arocha-6245No ratings yet
- Christine P. SalimbagatDocument2 pagesChristine P. SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- KristendelacruzresumeDocument2 pagesKristendelacruzresumeapi-239213083No ratings yet
- Development of The Body Cavities: EmbryologyDocument9 pagesDevelopment of The Body Cavities: EmbryologyRania FadillaNo ratings yet