Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M - Mask Adjustment R - Reposition Airway S - Suction Mouth and Nose O - Open Mouth P - Pressure Increase A - Airway Alternative
Uploaded by
Serious LeoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M - Mask Adjustment R - Reposition Airway S - Suction Mouth and Nose O - Open Mouth P - Pressure Increase A - Airway Alternative
Uploaded by
Serious LeoCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Ideal temperature of delivery room.
25-28
2. IMMEDIATE & THOROUGH DRYING Thermoregulation and stimulation
3. Effects of hypothermia infection, coagulation defects, acidosis, delayed
fetal to
newborn circulatory adjustment, hyaline
membrane disease, & brain hemorrhage
4. EARLY SKIN TO SKIN CONTACT Thermoregulation, Provides protection from
infection because of colonization with maternal
skin flora
5. Normal range of temperature of the newborn. 36.5- 37.5
6. PROPERLY TIMED CORD CLAMPING Reduces the risk of anemia in both term & pre-
term babies
Reduces the needs of transfusions & brain
hemorrhage in pre-terms
7. Appropriate period to cord clamping. Preterm – within 1 minute
Term – within 1-3 minutes
8. NON SEPARATION OF NEWBORN FROM Monitor mother & baby every 15 minutes in the
MOTHER FOR EARLY BREASTFEEDING first 1-2 hrs. assess warmth & breathing
9. Postponement of bathing until? >6 hours
10. Proper positioning Facing the breast
Body is close to mother’s body
Whole body is supported
Neck is not flexed nor twisted
11. Proper latching Mouth wide open
Lower lip turned outwards
Baby’s chin touching breast
Suckling is slow, deep with some pauses
12. Component of ventilation corrective steps M - Mask adjustment
R - Reposition airway
S - Suction mouth and nose
O - Open mouth
P - Pressure increase
A - Airway alternative
13. Primary Apnea Decrease in activity, loss of heart rate variability,
and heart rate decelerations
Tactile stimulation is sufficient
14. Secondary Apnea Fall in heart rate and blood pressure
Tactile stimulation is not sufficient and requires
ventilation
15. At what period you may achieve 85-95% O 2? 10 minutes
16. When will you do resuscitation? HR < 60 bpm
17. What to do if coordinated PPV and chest Give Epinephrine
compressions not enough?
18. What limb will you put the pulse ox for Right fingers (preductal)
oxygenation?
19. PPV No adequate spontaneous breathing and at
least 100 bpm of birth
Should be started within 1 minutes
20. CPAP At least <100 bpm
21. Term 21%
22. Pre-term 21-30%
23. 2.5 <1000, <28 weeks
24. 3.0 1000-2000, 28-34 weeks
25. 3.5 2000, 3000, 34-38 weeks
26. Estimated insertion depth of ET? NTL (nasal septum to tragus) +1 cm
27. 1 7
28. 2 8
29. 3 9
30. 4 10
31. Chest compression technique Depth 1/3
90 compressions per minute
Stop when HR is >60
32. Recommended dosage of epinephrine IV/IO: 0.1 to 0.3 ml/kg
ET: 0.5 to 1 ml/kg
If still <60 bpm – repeat doses every 3-5 minutes
33. When to stop resuscitation? persistent absence of a detectable heart rate
(Apgar 0) at 10 minutes is a strong predictor of
mortality
34. Optimal breastfeeding Early initiation of breastfeeding within an
hour after birth
Exclusive breastfeeding for the first six
months after birth
Continued breastfeeding for two years and
beyond with appropriate introduction of
complementary foods at 6 months of age
35. Stimulus for milk production Sucking
36. Lactogenesis I Development of breast
37. Estrogen Ductal growth
38. Progesterone Alveoli/acinar development
39. Prolactin Increases breast tissue in preparation for milk
production
Milk production
Usually takes 30-40 hours after birth before
large volume of milk is produced
40. Oxytocin Milk let-down
41. Advantages of night-time feedings more prolactin is produced at night
Induces relaxation in mothers & promotes sleep
42. Prolactin reflex Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary gland
stimulation prolactin secretion stimulate
acinar cells milk production
43. Let-down reflex Hypothalamus stimulates posterior pituitary
gland
release oxytocin contraction of
myoepithelial cells letdown reflex
44. Major differences of human vs cow’s milk More protein (cow)
More casein (cow)
(+) Beta lactoglobulin (cow)
Whey protein (human)
Alpha lactalbumin (human)
Lactoferrin (human)
Lactose (human)
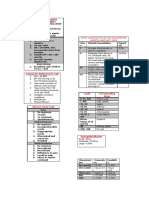
45. Similarities of human vs cow’s milk 20 cal/oz
Composition Human Milk
Water (ml/100ml) 87.1
Caloric Density 20 cal/oz
Protein (g/100 ml) 1.1
Casein (% protein) 40
Whey proteins 60
Alpha lactalbumin 2.6 g/L
Lactoferrin 1.7
Beta lactoglobulin ---
Lactose (g/ 100 ml) 6.8
Fat Balanced unsaturated and
More saturated FA
saturated
Iron Efficient absorption
46. Colostrum 2 – 4 days post delivery
immunologic function
47. Transition milk 7 – 10 days after delivery
48. Mature milk 14 days after delivery
Foremilk
Hindmilk (responsible for satiety, Needed in
order for the child to gain weight)
49. Inverted nipple Hoffman maneuver
50. Breastfeeding pattern need to feed every 1-3 hrs
51. How long breastmilk last at room air? 3-4 hours
52. Breastmilk at refrigerator? 72 hours (or 5-8 days – clean condition)
53. Breastmilk at freezer? 6 months – 12 months
54. Most important factor for preventing early Poor attachment of sore nipples
problems leading to premature weaning
55. Newborn stomach capacity 20-40 ml
56. Permanent avoidance of breastfeeding HIV
You might also like
- Anthropometric MeasurementsDocument3 pagesAnthropometric Measurementssabao kizuiteNo ratings yet
- Stages of LBRDocument3 pagesStages of LBRpjformoso99No ratings yet
- Why Do We Perform Perineal Care?: DurationDocument5 pagesWhy Do We Perform Perineal Care?: DurationA CNo ratings yet
- Maternal Reviewer MidtermmDocument5 pagesMaternal Reviewer Midtermmriveraapriljan22No ratings yet
- GD - L07 - Neonatal AdaptationDocument17 pagesGD - L07 - Neonatal AdaptationGarry SoloanNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument5 pagesNeonatal ResuscitationDoc Prince CaballeroNo ratings yet
- MCN MidtermsDocument4 pagesMCN MidtermsMutya XDNo ratings yet
- MCN Normal LaborDocument37 pagesMCN Normal LaborJharaNo ratings yet
- Transes For CmcaDocument7 pagesTranses For CmcaDenise AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Einc ReviewerDocument4 pagesEinc ReviewerEricson Candelaria0% (1)
- Essential Factors of LaborDocument21 pagesEssential Factors of LaborAjay DNo ratings yet
- NCM-107 4Document10 pagesNCM-107 4FERNANDEZ, RELLY ANDREWNo ratings yet
- Local Media377394424781005866Document29 pagesLocal Media377394424781005866Mae AbabonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For A High Risk NewbornDocument16 pagesNursing Care For A High Risk NewbornAj MacotoNo ratings yet
- Immediate Care of The NewbornDocument4 pagesImmediate Care of The NewbornMichelle GambolNo ratings yet
- The NewbornDocument14 pagesThe NewbornIsabel BangalaoNo ratings yet
- New Born Care: Slide 0: Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesNew Born Care: Slide 0: Learning ObjectivesAmelia ChristmasNo ratings yet
- PED 1.6 Care of NewbornDocument5 pagesPED 1.6 Care of NewbornchristianNo ratings yet
- Principles of Newborn CareDocument11 pagesPrinciples of Newborn CareNarnia NarniaNo ratings yet
- INTRAPARTUM AND NEWBORN CARE (EINC) As Prescribed by The WHO and The Department of HealthDocument1 pageINTRAPARTUM AND NEWBORN CARE (EINC) As Prescribed by The WHO and The Department of HealthSaint Pauls ObgynNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management During Stages of Labor and Delivery UpdatedDocument40 pagesNursing Management During Stages of Labor and Delivery UpdatedCharlmagne LinnamNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Assessment of Newborn, Newborn Adaptation and Normal Growth & DevelopmentDocument4 pagesPhysiologic Assessment of Newborn, Newborn Adaptation and Normal Growth & DevelopmentBernard M. Lapuz FullNo ratings yet
- 15 Signs Stages of LaborDocument84 pages15 Signs Stages of LaborDorothy Jane OrdinarioNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument29 pagesNeonatal Resuscitationapi-385031650% (2)
- NOTES For INTRAPARTAL PERIODDocument9 pagesNOTES For INTRAPARTAL PERIODIRA MONIQUE CABADENNo ratings yet
- Immediate Care of The NewbornDocument4 pagesImmediate Care of The Newbornmelinda100% (1)
- Nursing Management of During Stages of Labor and Delivery UpdatedDocument60 pagesNursing Management of During Stages of Labor and Delivery UpdatedSherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Essential New Born CareDocument2 pagesEssential New Born CareMs. Jia Mae CasimoNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument51 pagesNeonatal ResuscitationAbdulkadir HasanNo ratings yet
- Care of The Newborn: By: Myra DG. Angeles, RN, MANDocument44 pagesCare of The Newborn: By: Myra DG. Angeles, RN, MANMyra De Guzman AngelesNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery CompleteDocument120 pagesLabor and Delivery Completegallegomarjorie16No ratings yet
- Establish Respiration and Maintain Clear AirwayDocument4 pagesEstablish Respiration and Maintain Clear AirwaygvespineliNo ratings yet
- Immediate Newborn Care. BlanksDocument11 pagesImmediate Newborn Care. BlanksMay Princes Torregosa Abucejo100% (1)
- m4 MCN - m4Document140 pagesm4 MCN - m4Kristine KimNo ratings yet
- NRP Basics OPNF 7th EdDocument8 pagesNRP Basics OPNF 7th EdRazil AgilNo ratings yet
- Lesson (5) Neonatal ResuscitationDocument14 pagesLesson (5) Neonatal ResuscitationDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument86 pagesNeonatal ResuscitationMia Fernandez100% (1)
- Newborn ResuscitationDocument6 pagesNewborn ResuscitationMartina MedranoNo ratings yet
- Childbirth: Student HandoutDocument13 pagesChildbirth: Student HandoutDiana AyónNo ratings yet
- Essential New Born CareDocument7 pagesEssential New Born CareAsle ElsaNo ratings yet
- Newborn Priorities in First Days of LifeDocument11 pagesNewborn Priorities in First Days of LifeNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- High Risk NewbornDocument10 pagesHigh Risk NewbornEmmy Flor ValmoriaNo ratings yet
- Waiters Newborn Care PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Newborn Care PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Document100 pagesNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- The NeonatesDocument117 pagesThe NeonatesAirene AalaNo ratings yet
- EINCDocument34 pagesEINCMarc Jamel ROdriguezNo ratings yet
- PENGKAJIAN FISIK BBL (Baru)Document36 pagesPENGKAJIAN FISIK BBL (Baru)Nurfalah SetyawatiNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument19 pagesNeonatal ResuscitationDavina DakapNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument7 pagesNeonatal ResuscitationmilindNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal Period: Methods of Pain ManagementDocument7 pagesIntrapartal Period: Methods of Pain Managementdarkscaler100% (2)
- NCM 107 SL Finals EincDocument7 pagesNCM 107 SL Finals EincAngel DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Immediate Care of The NewbornDocument11 pagesImmediate Care of The NewbornHannahKarizaNo ratings yet
- Pre Term LabourDocument12 pagesPre Term LabourSohail SalarzaiNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor: 4. Dilatation & EffacementDocument7 pagesStages of Labor: 4. Dilatation & EffacementDeejune TorrinoNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY: Pre Labor Infant With Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument4 pagesCASE STUDY: Pre Labor Infant With Respiratory Distress SyndromeE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On IncDocument11 pagesLesson Plan On Incdevangi100% (1)
- MCN NotesDocument20 pagesMCN Noteslyzzythasenci23No ratings yet
- SC D BLOK 22Document40 pagesSC D BLOK 22Anggun Permata Sari SuknaNo ratings yet
- Level of Bilirubin To Cause Jaundice in Older Children and AdultsDocument2 pagesLevel of Bilirubin To Cause Jaundice in Older Children and AdultsSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Tickler Final PDFDocument29 pagesTickler Final PDFSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- West Notes-1 PDFDocument17 pagesWest Notes-1 PDFSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- IM NotesDocument13 pagesIM NotesRoendel BustilloNo ratings yet
- West Notes-1 PDFDocument17 pagesWest Notes-1 PDFSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Disease?: Guaiac-Positive StoolsDocument3 pagesCardiopulmonary Disease?: Guaiac-Positive StoolsSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Agenesis/dysgenesisDocument4 pagesThyroid Gland Agenesis/dysgenesisSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- CBC DidacticsDocument22 pagesCBC DidacticsSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- IM NotesDocument13 pagesIM NotesRoendel BustilloNo ratings yet
- Indications For Weaning: Kilips Classification of Ami With Expected Hospital Mortality RateDocument8 pagesIndications For Weaning: Kilips Classification of Ami With Expected Hospital Mortality RateSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Tickler Final PDFDocument29 pagesTickler Final PDFSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- SGD 8 October 6, 2017: Inputs/Resources Activities Output EffectDocument1 pageSGD 8 October 6, 2017: Inputs/Resources Activities Output EffectSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- CBG Coverage CBG Coverage: Actrapid Sliding ScaleDocument10 pagesCBG Coverage CBG Coverage: Actrapid Sliding ScaleSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- AlprazolamDocument2 pagesAlprazolamFATHICHAHNo ratings yet
- HPI HPI: Personal/Social: Educ'l Level: Occupation: Personal/Social: Educ'l Level: OccupationDocument2 pagesHPI HPI: Personal/Social: Educ'l Level: Occupation: Personal/Social: Educ'l Level: OccupationJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Coping With StressDocument1 pageCoping With StresslindaNo ratings yet
- First SGD - 3rd SessionDocument4 pagesFirst SGD - 3rd SessionSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- (09-06-17) Second SGD - 2nd SessionDocument2 pages(09-06-17) Second SGD - 2nd SessionSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- PPH (Uterine Atony)Document4 pagesPPH (Uterine Atony)Serious LeoNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Preceptorial: Med 2B Group 8Document2 pagesDermatology Preceptorial: Med 2B Group 8Serious LeoNo ratings yet
- AD ManagementDocument2 pagesAD ManagementSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Neural Mechanisms of ItchDocument2 pagesNeural Mechanisms of ItchSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- CPC Case PDFDocument5 pagesCPC Case PDFSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- SGD - HPVDocument3 pagesSGD - HPVSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- SGD - DigestiveDocument4 pagesSGD - DigestiveSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Repro SGDDocument3 pagesRepro SGDSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- SGD - HPVDocument3 pagesSGD - HPVSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- CPC Case PDFDocument5 pagesCPC Case PDFSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument3 pagesAdult Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Use of Prebiotic Supplements To Support Gut Microbiome MaintenanceDocument12 pagesUse of Prebiotic Supplements To Support Gut Microbiome MaintenanceIasa FebrianusNo ratings yet
- Paarambariya MaruthuvamDocument1 pagePaarambariya MaruthuvamAnonymous kCrS4NduNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesRANDY BAOGBOGNo ratings yet
- 106 FinalsDocument27 pages106 FinalsCreciabullecerNo ratings yet
- DR Fardowsa Mohamed Adam Last UpdateDocument71 pagesDR Fardowsa Mohamed Adam Last UpdateAbdulkadir KanaaleNo ratings yet
- Medicine Admitting Conference: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Medicine and SurgeryDocument70 pagesMedicine Admitting Conference: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Medicine and SurgerySTEPHANIE TANNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Anaesthesia - BJA Education - Oxford AcademicDocument14 pagesAlcohol and Anaesthesia - BJA Education - Oxford Academicayesha shaikNo ratings yet
- O C A C, Republic of China (Taiwan) : Items Required For Health Certificate 3 Valid For Three MonthsDocument1 pageO C A C, Republic of China (Taiwan) : Items Required For Health Certificate 3 Valid For Three Months李倬伶No ratings yet
- Zoonoses and Emerging Livestock Systems (ZELS) Supplementary Research Projects 2019-2021Document7 pagesZoonoses and Emerging Livestock Systems (ZELS) Supplementary Research Projects 2019-2021dukegarrikNo ratings yet
- Prevention Treatment of Oral HabitsDocument22 pagesPrevention Treatment of Oral HabitseedmdnndNo ratings yet
- TEACHERS' WORKPLACE - Physical Activity and Sedentary BehaviorDocument194 pagesTEACHERS' WORKPLACE - Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviorhon jia shengNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Blood Sugar Chart Blood Glucose Chart DSMDocument1 pageDiabetes Blood Sugar Chart Blood Glucose Chart DSMBIRD MARKONo ratings yet
- Development and Preliminary Evaluation of PsychomeDocument11 pagesDevelopment and Preliminary Evaluation of Psychomerosa azizahNo ratings yet
- Perez 2007Document8 pagesPerez 2007SNo ratings yet
- Imaging & Other Potential Predictors of Deterioration in COVID-19Document5 pagesImaging & Other Potential Predictors of Deterioration in COVID-19ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument6 pagesReviewer in ScienceReign HonradoNo ratings yet
- Home Economics II PresentationDocument22 pagesHome Economics II PresentationEmmanuel S JamesNo ratings yet
- Kearney 2021 Oi 210216 1617752043.4612Document14 pagesKearney 2021 Oi 210216 1617752043.4612tennisboy92No ratings yet
- Covid-19 Vaccination Microplan Date - (06-05-2021) District: Kanpur NagarDocument4 pagesCovid-19 Vaccination Microplan Date - (06-05-2021) District: Kanpur NagarAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippine Congress AssembledDocument4 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippine Congress AssembledanonNo ratings yet
- Group PresentationDocument26 pagesGroup PresentationA&H Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- LithiumDocument2 pagesLithiumdiet.nurseNo ratings yet
- BUKU Acute Coronary Syndrome Update 2020Document16 pagesBUKU Acute Coronary Syndrome Update 2020Embun Suci LestariNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Usebafraley7100% (1)
- Obstetric Life Support ManualDocument71 pagesObstetric Life Support Manualtf.jorgeNo ratings yet
- Brain: Book ReviewDocument4 pagesBrain: Book ReviewCouncellor AjayNo ratings yet
- 08) Acmtac-Protocol-2019-Revised - 1Document86 pages08) Acmtac-Protocol-2019-Revised - 1Teh NuraqilahNo ratings yet
- Furcation InvolvementDocument39 pagesFurcation InvolvementShaju Jacob PNo ratings yet
- Pfas Letter To Epw 11.15.2021Document10 pagesPfas Letter To Epw 11.15.2021WXMINo ratings yet
- TEJASWINIDocument8 pagesTEJASWINIAyush JamwalNo ratings yet