Professional Documents
Culture Documents
14657
Uploaded by
shiva kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesnotes for secondary school exam
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnotes for secondary school exam
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pages14657
Uploaded by
shiva kumarnotes for secondary school exam
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Chemical Kinetics
© derive a relationship between half life and rate constant for first order reaction;
© solve numericals on the relationships:
© explain collision theory of reaction rates.
© explain the effect of temperature on reaction rate, and
explain Arrhenius equation and activation energy.
14:1 RATE OK A CHEMICAL, REACTION
When the reactants are mixed to perform a reaction, there are no products present
initially. As time passes, the concentration of the products increases and that of
the reactants decreases. The rate of any chemical reaction can be expressed as
the rate of the change in concentration of a reactant (or a product).
‘Change in concentration
‘Time taken
Rate of a chemical reaction = of a reactant or a product
_ mollitre™!
~~ second
Let us consider the following chemical reaction :
2NO(g) + Br(g) ——> 2NOBr(g)
The rate for this reaction can be determined by measuring the increase in the
molar concentration of NOBr at different time intervals.
Let us see how we can express the rate of this reaction. You know that molar
concentration of a substance is expressed by enclosing the formula of the substance
in square bracket.
For example, [NOBr] represents the molar concentration of NOBr.
Let us suppose that [NOBr], is the molar concentration at time r, and [NOBr], is
the molar concentration at time t,.
Then, change in molar concentration = [NOBr], ~ [NOBr], = A{NOBr]
At
Here, A means change in the respective quantity.
A{NOBr]
a
Time required for the change =
Therefore, the rate of formation of NOBr =
This expression gives the rate of reaction in terms of NOBr.
If the decrease in the molar concentration of NO or Br, is measured we can write
the rate of the reaction with respect to NO as
_ ~AINO]
“At
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net .
Scanned with CamScanner
Chemical Kinetics
-ABBry]
At
Thus, the rate of a reaction can be expressed either in terms of reactants or
products, We find in the reaction mentioned above that two moles of NO react
with one mole of Br,. Therefore, the change in concentration of NO in a given
time Ar will be double than that for Br,. Thus, in order to make the rates with
respect to different reactants or products equal, the rate expression is divided by
the storichrometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation.
and wart. Br, as =
For example, in the equation,
2NO(g) + Br(g) —> 2NOBr(g)
‘The rate of reaction with respect to reactants and products is expressed as,
1 ALNOBr}] __ 1 A(NOBr] _ -ALBr]
rate of reaction ae 2 a ae
The rate of a reaction depends on the concentration of reactants. As the reaction
proceeds the reactants get consumed and their concentration decreases with time.
Therefore, the rate of reaction does not remain constant during the entire reaction,
Alconcentration]
‘The rate of a reaction given as wr
gives an average rate.
ACNOBr]
ar
a reaction is the rate of reaction at any particular instant of time, we express
instantaneous rate by making Ar very small
For example, gives the average rate of reaction, Instantaneous rate of
lim [NOBr] _ d[NOBr]
M30 Ar > od
When concentration of any of the reactants or products is plotted against time,
the graph obtained is as given below :
Product
&
4
5
° Reactant
Time —>
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net .
Scanned with CamScanner
Chemical Kinetics
For the reaction,
2N,0,(g) —> 2NO,(g) + O,(g)
Average rate of reaction
1 AIN,O5] AINO,] _ Al2]
At At
vl
eg
wie
i 1 dINzO¢]_ 1 d{NO,]_ d{O,]
and instantaneous rate = 2 aA 2 a a
The rate of a chemical reaction is affected by the following factors :
1. The concentration of reactants ; Generally the rate of a reaction increases
as the concentration of the reactants is increased,
2. ‘Temperature — A reaction is faster when the reaction temperature is
increased,
3. Presence of a catalyst — A catalyst alters the reaction rate without being
consumed by the reaction,
For example :
i) Reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water is extremely slow. It
occurs very fast in the presence of platinum as catalyst.
‘You would study these effects in more detail in the following sections of this
lesson.
Example 14.1 : Express the average and instantaneous rate of the following
reaction
N,(g) + 3H,(g) ——> 2NH,(g)
in terms of (i) rate of formation of NH,,
Gi) rate of disappearance N,, and
Gi) rate of disappearance of H,.
Write the different expressions for the rate of reactions.
Solution : The expression for the three rates are :
A(NH
Average rate of formation of NH, awa
AIN,]
Ar
Average rate of disappearance of N,
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net .
Scanned with CamScanner
Chemical Kinetics
tH.
Average rate of disappearance of H, = fel
‘d{NH.
Instantaneous rate of formation of NH, = “3!
. UN}
Instantaneous rate of disappearance of N, =“)
. lH]
Instantaneous rate of disappearance of H, = “a2!
To equate the three rates, divide each rate by the coefficient of the corresponding
‘substances in the balanced equation,
AIN,] __ 1 ATH]
M73 At
[H.
Average rate =
1. Which of the following units could be used to express the rate of reaction
between magnesium and hydrochloric acid?
(a) cms
(pb) cm? mins!
(oc) om? st
(d) mol dm? min“!
2, For the following reaction,
2NO,(g) + F,(g) —> 2NO,F(g)
Write the expression for the average, rate of reaction in terms of :
(a) rate of formation of NO.F
(b)._ rate of disappearance of NO»
(c)_ rate of disappearance of F;
(d)_ equivalent rate of formation of product and disappearance of reactants.
3. Express the instantaneous rates of formation of product and disappearance
of reactants for the above reaction,
4, Explain why the reaction CO(g) + NO,(g) > CO,(g) + NO(g) occurs more
slowly when the volume of the system is increased.
Office.: 606 , 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1,
Ph.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968
www.newtonclasses.net .
Scanned with CamScanner
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Part-I: UNIT 1 (Organic Chemistry)Document8 pagesPart-I: UNIT 1 (Organic Chemistry)shiva kumarNo ratings yet
- CRF Nitk BrochureDocument54 pagesCRF Nitk Brochureshiva kumarNo ratings yet
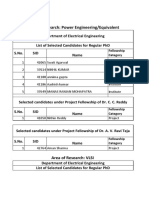
- Area of Research: Power Engineering/EquivalentDocument2 pagesArea of Research: Power Engineering/Equivalentshiva kumarNo ratings yet
- List of Provisionaly Selected Candidates For Regular PHD Department of ChemistryDocument2 pagesList of Provisionaly Selected Candidates For Regular PHD Department of Chemistryshiva kumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering List of Selected Candidates For Regular PHDDocument1 pageDepartment of Mechanical Engineering List of Selected Candidates For Regular PHDshiva kumarNo ratings yet
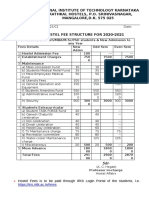
- National Institute of Technology Karnataka Surathkal Hostels, P.O. Srinivasnagar, MANGALORE, D.K. 575 025Document2 pagesNational Institute of Technology Karnataka Surathkal Hostels, P.O. Srinivasnagar, MANGALORE, D.K. 575 025shiva kumarNo ratings yet
- NMR QuestionsDocument2 pagesNMR Questionsshiva kumar100% (1)
- JD Monthly Magazine For IAS and KAS JUNE-2020 PDFDocument60 pagesJD Monthly Magazine For IAS and KAS JUNE-2020 PDFshiva kumarNo ratings yet
- Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and CoordiDocument1 pageInfrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordishiva kumarNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)