0% found this document useful (0 votes)
448 views1 pageLocus and Construction: Need To Learn
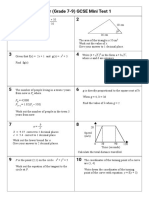
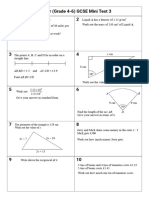
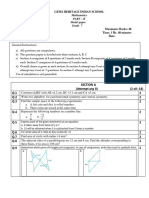
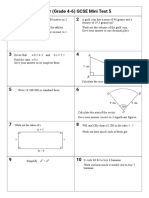
The document discusses the concept of a locus, which is defined as the possible path of a point that satisfies a certain condition. It provides examples of different types of loci, such as a circle representing the locus of points that are a given distance r from a fixed point O, and a perpendicular bisector representing the locus of points that are equidistant from two given points A and B. The document also lists four examples of loci and their geometric constructions to represent points satisfying specific distance conditions from lines, points, or other geometric shapes.
Uploaded by
anwar hossainCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
448 views1 pageLocus and Construction: Need To Learn
The document discusses the concept of a locus, which is defined as the possible path of a point that satisfies a certain condition. It provides examples of different types of loci, such as a circle representing the locus of points that are a given distance r from a fixed point O, and a perpendicular bisector representing the locus of points that are equidistant from two given points A and B. The document also lists four examples of loci and their geometric constructions to represent points satisfying specific distance conditions from lines, points, or other geometric shapes.
Uploaded by
anwar hossainCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd