Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 Atmospheric Motion PartD
Uploaded by
Sanjay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pagesPresentation on Atmospheric Motion PartD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPresentation on Atmospheric Motion PartD
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pages03 Atmospheric Motion PartD
Uploaded by
SanjayPresentation on Atmospheric Motion PartD
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Geostrophic flow is a close Departures from geostrophic
approximation to observed winds balance arise due to:
throughout most of the free – constant changes in the
atmosphere, except near the pressure field
equator where the coriolis force – curvature in the isobars
approaches zero. – vertical wind shear
Significant departure from
geostrophic flow occurs near the
surface due to the effects of
friction.
ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting : lecture 3 13
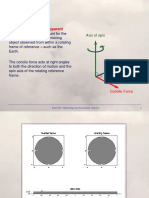
Centripetal Acceleration
Motion around a curved path requires HIGH
an acceleration towards the centre of Fc
curvature: the centripetal
acceleration. V Centripetal
acceleration
LOW
FP
FP
For a low, the coriolis force is less
Centripetal V than the pressure force; for a high it is
acceleration
greater than pressure force. This
Fc results in:
LOW: V < geostrophic
The required centripetal acceleration (subgeostrophic)
is provided by an imbalance between
the pressure and coriolis forces. HIGH: V > geostrophic
(supergeostrophic)
V is here called the gradient wind
ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting : lecture 3 14
Effect of Friction
Geostrophic flow Friction at the surface slows the
away from surface wind. Turbulent mixing extends
effects of friction up to ~100 m to
~1.5 km above surface.
Lower wind speed results in a
smaller coriolis force, hence
reduced turning to right.
Wind vector describes a spiral:
the Ekman Spiral. Surface wind
lies to left of geostrophic wind
• 10-20 over ocean
Ekman Spiral • 25-35 over land
The wind speed a few metres
above the surface is ~70% of
geostrophic wind over the ocean,
even less over land (depending
Vg on surface conditions)
ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting : lecture 3 15
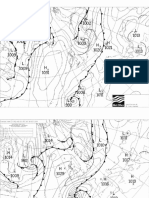
Surface winds cross
isobars at 10-35
ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting : lecture 3 16
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- DK - DK - Planisphere and Star Finder-DK Publishing (2019)Document130 pagesDK - DK - Planisphere and Star Finder-DK Publishing (2019)Philip Emad100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Janice VanCleaves 201 Awesome, Magical, Bizarre, and Incredible ExperimentsDocument81 pagesJanice VanCleaves 201 Awesome, Magical, Bizarre, and Incredible ExperimentsmatijahajekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Humidity Condensation and CloudsDocument13 pagesChapter 04 Humidity Condensation and CloudsnaveedNo ratings yet
- Seasons in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesSeasons in The Philippinesjen mcbrideNo ratings yet
- 03 Atmospheric Motion PartFDocument4 pages03 Atmospheric Motion PartFSanjayNo ratings yet
- 03 Atmospheric Motion PartADocument4 pages03 Atmospheric Motion PartASanjayNo ratings yet
- 03 Atmospheric Motion PartBDocument4 pages03 Atmospheric Motion PartBSanjayNo ratings yet
- 03 Atmospheric Motion PartEDocument4 pages03 Atmospheric Motion PartESanjayNo ratings yet
- 03 Atmospheric Motion PartCDocument4 pages03 Atmospheric Motion PartCSanjayNo ratings yet
- Key Factors And: Barriers To The Adoption of Cold Ironing in EuropeDocument11 pagesKey Factors And: Barriers To The Adoption of Cold Ironing in EuropeSanjayNo ratings yet
- Safety Regulations: International Longshore & Warehouse Union CanadaDocument38 pagesSafety Regulations: International Longshore & Warehouse Union CanadaSanjayNo ratings yet
- Space Management in Smart Room: Mariana FRATU, Aurel FRATUDocument4 pagesSpace Management in Smart Room: Mariana FRATU, Aurel FRATUSanjayNo ratings yet
- Control Room: Drouatscca. Drouatscca. Drouatscca. DrouatsccaDocument2 pagesControl Room: Drouatscca. Drouatscca. Drouatscca. DrouatsccaSanjayNo ratings yet
- U W G A C: Classroom Support Services Design GuideDocument22 pagesU W G A C: Classroom Support Services Design GuideSanjayNo ratings yet
- Indianoil'S Policy: Sustainability & CSRDocument2 pagesIndianoil'S Policy: Sustainability & CSRSanjayNo ratings yet
- Vessel Particulars TI EUROPE IMO No. 9235268Document1 pageVessel Particulars TI EUROPE IMO No. 9235268SanjayNo ratings yet
- Essential Components of A Business PlanDocument1 pageEssential Components of A Business PlanSanjayNo ratings yet
- Six Free Doctors HRDocument1 pageSix Free Doctors HRSanjayNo ratings yet
- Heha Sky ViewDocument45 pagesHeha Sky ViewAprilia SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Celestron CPC 800 X LT 2005Document9 pagesCelestron CPC 800 X LT 2005carrier2100% (3)
- School Book Read Up 33Document8 pagesSchool Book Read Up 33Deep HansNo ratings yet
- Vincent Van Gogh EssayDocument5 pagesVincent Van Gogh Essayapi-402226857No ratings yet
- Public Health Implications of Self-medication Thesis by SlidesgoDocument41 pagesPublic Health Implications of Self-medication Thesis by SlidesgodebajeetdasadhikaridNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting ClimateDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting ClimateNRIZA MAE CACHONo ratings yet
- Solar System Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSolar System Cheat SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 7: The Night Sky - 7.2 Handouts (The Constellation)Document14 pagesScience Chapter 7: The Night Sky - 7.2 Handouts (The Constellation)Kimmy LamNo ratings yet
- Meal Planner Infographics: Here Is Where This Template BeginsDocument33 pagesMeal Planner Infographics: Here Is Where This Template BeginsAl Kayis AlNo ratings yet
- Met 01 LM FinalDocument116 pagesMet 01 LM FinalFrances Jay FerrerNo ratings yet
- Student Copy Session 9 GR 7A ESDocument2 pagesStudent Copy Session 9 GR 7A ESMeme 2020No ratings yet
- Go SkywatchDocument2 pagesGo SkywatchLora BallardNo ratings yet
- Soal Uub Bahasa & Sastra Inggris Kelas X Mipa-IpsDocument7 pagesSoal Uub Bahasa & Sastra Inggris Kelas X Mipa-IpsITA HARDANI0% (1)
- Science 6Document4 pagesScience 6Cristopher MadajeNo ratings yet
- Key Lab Reading & WritingDocument10 pagesKey Lab Reading & WritingSamWellerNo ratings yet
- Advancements On The Solar SystemDocument7 pagesAdvancements On The Solar SystemJohn Kenneth Adorablè EnocNo ratings yet
- Adb SiddarthDocument20 pagesAdb SiddarthSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- MeteorsDocument41 pagesMeteorscharyl jean caga100% (1)
- 26课 西安比北京还热Document41 pages26课 西安比北京还热xqi2708No ratings yet
- Metar - Taf - PirepDocument2 pagesMetar - Taf - PirepSantosh Raj KhanalNo ratings yet
- Presentation DS 1 2021 - 2Document62 pagesPresentation DS 1 2021 - 2udeshi bandadraNo ratings yet
- Programme Ln31 EnglishDocument113 pagesProgramme Ln31 EnglishRafael BonifácioNo ratings yet
- Macro Lighting Options: PhotzyDocument16 pagesMacro Lighting Options: PhotzyEmilNo ratings yet
- Application of Artificial Neural Network To Predict Squall Thunderstorms Using RAWIND DataDocument6 pagesApplication of Artificial Neural Network To Predict Squall Thunderstorms Using RAWIND DatabrigitaNo ratings yet
- February 2019 Sky ChartDocument1 pageFebruary 2019 Sky ChartHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNo ratings yet
- CBSE 8 Science CBSE - Stars and The Solar System, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - Stars and The Solar SystemDocument6 pagesCBSE 8 Science CBSE - Stars and The Solar System, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - Stars and The Solar SystemR.Shruti 1040-12No ratings yet