Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz
Uploaded by
Jonna Mae TurquezaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz
Uploaded by
Jonna Mae TurquezaCopyright:
Available Formats
Premature labor
ü
Hydramnios is a condition that occurs when
Is also called preterm labor too much amniotic fluid builds up during
ü
Labor is premature if it starts more than three weeks pregnancy.
before your due date. ü
It is also called amniotic fluid disorder, or
Risk Factors polyhydramnios
üSmoking
üBeing very overweight or underweight before What Are the Risks of Hydramnios?
pregnancy
üNot getting good prenatal care • Mild hydramnios may not cause any problems.
üDrinking alcohol or using street drugs during Often, extra fluid that appears during the
pregnancy second trimester returns to normal on its own.
üHaving health conditions, such as high blood Mild hydramnios is more common than severe
pressure, preeclampsia, diabetes, blood hydramnios.
clotting disorders, or infections • Hydramnios may occur in normal pregnancies
üBeing pregnant with a baby that has certain with more than one baby (twins, triplets, or
birth defects more).
üBeing pregnant with a baby from in vitro • Severe hydramnios may mean there is a
fertilization problem with the fetus. If you have severe
hydramnios, your health care provider will look
üBeing pregnant with twins or other multiples
for these problems:
üA family or personal history of premature labor
• ü
Birth defects of the brain and spinal column
üGetting pregnant too soon after having a baby
• ü
Blockages in the digestive system
Symptoms
• ü
A genetic problem (a problem with the
chromosomes that is inherited)
ü
Backache, which usually will be in your lower
back. This may be constant or come and go, but
How is Hydramnios Treated?
it won’t ease even if you change positions or do
something else for comfort.
In some cases, the symptoms of hydramnios can be
ü
Contractions every 10 minutes or more often
treated but the cause cannot be treated.
ü
Cramping in your lower abdomen or
• üYour provider may want you to stay in the
menstrual-like cramps. These can feel like gas
hospital.
pains that may come with diarrhea.
• üYour provider may also prescribe medicine to
ü
Fluid leaking from your vagina
prevent a preterm delivery.
ü
Flu-like symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or • üThey might remove some of the extra amniotic
diarrhea. Call your doctor even about mild fluid to relieve your symptoms.
cases. If you can’t tolerate liquids for more than • üNonstress tests can be done to make sure the
8 hours, you must see your doctor. fetus is not in danger (Nonstress tests involve
ü
Increased pressure in your pelvis or vagina listening to the baby's heart rate and
ü
Increased vaginal discharge monitoring contractions for 20 to 30 minutes.)
ü
Vaginal bleeding, including light bleeding
• Your provider may also do tests to find out why
Treatment you have extra fluid. These might include:
• ü
Blood tests to check for diabetes or an
ü
IV fluids infection
ü
Medicine to relax your uterus and stop labor • ü
Amniocentesis (a test that checks amniotic
ü
Medicine to speed up the development of your fluid
baby's lungs
ü
Antibiotics
ü
Being admitted to the hospital
Hydramnios Hydramnios and Delivery
• ü
The doctor can also conduct a pelvic
Hydramnios may cause the mother to go into labor examination and may see the prolapsed cord,
early. or palpate (feel) the cord with his or her
• It is easy for a fetus with a lot of fluid around it fingers.
to flip and turn. This means there is a greater
chance of being in a feet-down position How is an umbilical cord prolapse managed?
(breech) when it is time to deliver. Breech
babies can sometimes be moved into a head- • ü
Because of the risk of lack of oxygen to the
down position, but they often have to be fetus, an umbilical cord prolapse must be dealt
delivered by C-section. with immediately. If the doctor finds a
prolapsed cord, he or she can move the fetus
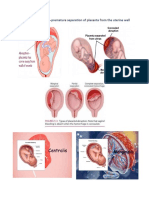
Umbilical Cord Prolapse away from the cord in order to reduce the risk
Umbilical cord prolapse is a complication that occurs of oxygen loss.
prior to or during delivery of the baby. • ü
In some cases, the baby will have to be
• üIn a prolapse, the umbilical cord drops delivered immediately by cesarean section. If
(prolapses) through the open cervix into the the problem with the prolapsed cord can be
vagina ahead of the baby. solved immediately, there may be no
• üThe cord can then become trapped against the permanent injury. However, the longer the
baby's body during delivery. delay, the greater the chance of problems (such
• üUmbilical cord prolapse occurs in as brain damage or death) for the baby.
approximately one in every 300 births.
What are the consequences of umbilical cord
prolapse?
• An umbilical cord prolapse presents a great
danger to the fetus. During the delivery, the
fetus can put stress on the cord. This can result
in a loss of oxygen to the fetus, and may even
result in a stillbirth.
What causes an umbilical cord prolapse?
The most common cause of an umbilical cord prolapse
is a premature rupture of the membranes that contain
the amniotic fluid. Other causes include:
• üPremature delivery of the baby
• üDelivering more than one baby per pregnancy
(twins, triplets, etc.)
• üExcessive amniotic fluid
• üBreech delivery (the baby comes through the
birth canal feet first)
How is an umbilical cord prolapse diagnosed?
The doctor can diagnose a prolapsed umbilical cord in
several ways.
• üDuring delivery, the doctor will use a fetal
heart monitor to measure the baby's heart
rate. If the umbilical cord has prolapsed, the
baby may have bradycardia (a heart rate of less
than 120 beats per minute).
You might also like
- The Child in You - Stefanie StahlDocument222 pagesThe Child in You - Stefanie StahlVi Ha100% (9)
- Kingdom Parenting PDFDocument208 pagesKingdom Parenting PDFAndenet Ashagrie88% (17)
- Placental Abruption PresentationDocument30 pagesPlacental Abruption PresentationNafisat AdepojuNo ratings yet
- Complications of PregnancyDocument24 pagesComplications of PregnancyDeo Olarte100% (1)
- Essential Newborn Care PowerpointDocument35 pagesEssential Newborn Care PowerpointKrystal Tan100% (2)
- Elizabeth G. Querubin BSN 3E1-9 - Group 195 A Ectopic PregnancyDocument16 pagesElizabeth G. Querubin BSN 3E1-9 - Group 195 A Ectopic PregnancyLizeth Querubin97% (38)
- Teenagers Dealing With The Separation of Their Parents - How It Affects Their Academic Performance FINALDocument111 pagesTeenagers Dealing With The Separation of Their Parents - How It Affects Their Academic Performance FINALEd Raven CruzNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Amniotic FluidDocument27 pagesAbnormalities of Amniotic FluidRukmini kakatikar0% (1)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesEctopic PregnancyMary Anne Yap100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta and AbortionDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta and Abortiondanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- Simplicity Parenting Book NotesDocument18 pagesSimplicity Parenting Book NotesSchizo FraiseNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument4 pagesBleeding During PregnancyCarl Andre ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gestational DisordersDocument30 pagesGestational DisordersGwyneth GuintuNo ratings yet
- Pain Bleeding Early PregnancyDocument4 pagesPain Bleeding Early Pregnancyrositaokoye609No ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document69 pagesChapter 212082194No ratings yet
- MCN Report Polyhydramnios 1Document24 pagesMCN Report Polyhydramnios 1Vincent CuyucaNo ratings yet
- AbortionsDocument17 pagesAbortionsDurr E SAJALNo ratings yet
- Aminotic Fluid DisordersDocument34 pagesAminotic Fluid DisordersCheru DugaseNo ratings yet
- Thursday, February 11, 2021 8:04 PM: Chapter 21 Page 1Document29 pagesThursday, February 11, 2021 8:04 PM: Chapter 21 Page 1Christel Ann TianchonNo ratings yet
- First Trimester Bleeding ReportDocument35 pagesFirst Trimester Bleeding ReportAnita PrietoNo ratings yet
- HemorrhagesDocument3 pagesHemorrhagesARAugustoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Four Abortion Life SpanDocument51 pagesLecture Four Abortion Life SpanOmar SanyangNo ratings yet
- A. HEMORRHAGE ABORTIONDocument74 pagesA. HEMORRHAGE ABORTIONMay MayNo ratings yet
- DEFINITION: Abortion Is The Expulsion or Extraction From Its MotherDocument10 pagesDEFINITION: Abortion Is The Expulsion or Extraction From Its MothermOHAN.SNo ratings yet
- AMNIOCENTESISDocument13 pagesAMNIOCENTESISMushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument40 pagesBleeding in Early PregnancyOmar mohamedNo ratings yet
- Emergency Care of Pregnant PatientDocument16 pagesEmergency Care of Pregnant PatientAshraf QotmoshNo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument5 pagesPyloric StenosisfdgrgNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument20 pagesMCN NotesLiamLexus JavierNo ratings yet
- Uterus Larger Than DateDocument68 pagesUterus Larger Than Datesyirah99No ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument56 pagesLabor and DeliveryBernardo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Premature Rupture of The MembranesDocument6 pagesPremature Rupture of The MembranesMaria Donabella OngueNo ratings yet
- Abortion, Hmole, Ectopic PDFDocument9 pagesAbortion, Hmole, Ectopic PDFAyanami PascuaNo ratings yet
- A Woman Who Develops A Complication of PregnancyDocument24 pagesA Woman Who Develops A Complication of PregnancyLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- HydramniosDocument30 pagesHydramniosRahul BaruahNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cerclage: About The Cervix in PregnancyDocument2 pagesCervical Cerclage: About The Cervix in Pregnancyamarendra Wardhana100% (1)
- Premature Rupture of MembraneDocument19 pagesPremature Rupture of MembraneAisyah ShawtyNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaDocument26 pagesPerdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaEmilia NazmaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding From The Genital Tract in Early Pregnancy (Before 28 Weeks)Document76 pagesBleeding From The Genital Tract in Early Pregnancy (Before 28 Weeks)Tiondi francisNo ratings yet
- Pain and Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument4 pagesPain and Bleeding in Early PregnancyROHININo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument4 pagesAbortionlanilyn aquinoNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 High Risk PregnancyDocument11 pagesNCM 109 High Risk PregnancyLea BorceNo ratings yet
- Handout 4Document13 pagesHandout 4ApRil Anne BalanonNo ratings yet
- Maternal Reviewer FinalsDocument36 pagesMaternal Reviewer FinalsHannah QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Management of Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument44 pagesManagement of Bleeding in Early PregnancyOyedele OluwaseunNo ratings yet
- Normal Pregnancy - 094218Document67 pagesNormal Pregnancy - 094218Beatrice habukuwie BaahNo ratings yet
- A Low-Lying Placenta: Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Waste Products Top, Side, Front or Back of The UterusDocument3 pagesA Low-Lying Placenta: Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Waste Products Top, Side, Front or Back of The UterusFREVILYN ABASTANo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregancy: Chena B. CurigDocument35 pagesEctopic Pregancy: Chena B. CurigJaicca Faith Tandih AllasNo ratings yet
- Delgado MCN ActivityDocument16 pagesDelgado MCN ActivityJhayrald GarciaNo ratings yet
- GynaeBoxanswer PDFDocument99 pagesGynaeBoxanswer PDFViktor Charles KDNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid DisordersDocument22 pagesAmniotic Fluid Disordersvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy RevisedDocument44 pagesEctopic Pregnancy RevisedDegefaw BikoyNo ratings yet
- Ruptured Ectopic PresentationDocument21 pagesRuptured Ectopic Presentationlinembambu1992No ratings yet
- 2 Vaginal Discharge ALGORITME PDFDocument1 page2 Vaginal Discharge ALGORITME PDFFikri PutroNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Notes PrelimsDocument14 pagesNCM 104 Notes PrelimsAngel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa - AraDocument6 pagesPlacenta Previa - AraArmi P. AlinaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive HealthDocument72 pagesReproductive HealthLance Andre V. RosalNo ratings yet
- Labor Assisted DeliveriesDocument8 pagesLabor Assisted Deliveriesnena marie evalaroza100% (1)
- Placenta PreviaDocument33 pagesPlacenta PreviamidoNo ratings yet
- #12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesDocument4 pages#12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Abortionme 200907085856Document77 pagesAbortionme 200907085856tengizbaindurishviliNo ratings yet
- Placental AbruptionDocument17 pagesPlacental AbruptionAltynaiNo ratings yet
- CA MaternalDocument156 pagesCA MaternalLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanis MOF Action Indications Contraindication S Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanis MOF Action Indications Contraindication S Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Surgery Can Be A "Cure" For Types 2 DiabetesDocument2 pagesGastrointestinal Surgery Can Be A "Cure" For Types 2 DiabetesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections (Adult and Pediatric Patients)Document4 pagesComplicated Intra-Abdominal Infections (Adult and Pediatric Patients)Jonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Coli, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Bacteroides Fragilis, B. Thetaiotaomicron, and Peptostr Eptococcus SpeciesDocument8 pagesColi, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Bacteroides Fragilis, B. Thetaiotaomicron, and Peptostr Eptococcus SpeciesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Hope Optimism Stress and Social Support in Parents of ChildrenDocument155 pagesHope Optimism Stress and Social Support in Parents of ChildrenIntan HumaerohNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Family Health Nursing Final LastDocument5 pagesModule 3 Family Health Nursing Final LastAmethystNo ratings yet
- Nadeen The Big SisterDocument1 pageNadeen The Big SisterRosyJaforullahNo ratings yet
- Amariah Smith - Personal Statement 1Document2 pagesAmariah Smith - Personal Statement 1api-719526159No ratings yet
- International Islamic University Malaysia: Name: Fatin Farhana Binti Abdul Rahaman MATRIC NUMBER: 0911436 Section: 1Document15 pagesInternational Islamic University Malaysia: Name: Fatin Farhana Binti Abdul Rahaman MATRIC NUMBER: 0911436 Section: 1fatinfarhana21No ratings yet
- Tatay Nanay Stories of Solo Parents Final OutputDocument35 pagesTatay Nanay Stories of Solo Parents Final Outputroseanntripulca2004No ratings yet
- FAFSA Checklist FY23Document2 pagesFAFSA Checklist FY23Lyon HuynhNo ratings yet
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder-How To Spot The Subtle Signs of A Narcissist and Continue To Thrive After An Encounter. (PDFDrive)Document95 pagesNarcissistic Personality Disorder-How To Spot The Subtle Signs of A Narcissist and Continue To Thrive After An Encounter. (PDFDrive)Junior Bushiri MakangaNo ratings yet
- Raidos KeisaiDocument100 pagesRaidos KeisaiJore VisockyteNo ratings yet
- Socio Emotional Development of The Pre SchoolersDocument18 pagesSocio Emotional Development of The Pre SchoolersTintin ArcalasNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Teenage Pregnancy in Heidedal Location, Mangaung DistrictDocument96 pagesFactors Influencing Teenage Pregnancy in Heidedal Location, Mangaung DistrictNoluthando KhumaloNo ratings yet
- 04530-211 04530-219 Model Shown:: Conforms To ASTM F1169 Safety StandardsDocument17 pages04530-211 04530-219 Model Shown:: Conforms To ASTM F1169 Safety StandardsDustin AdairNo ratings yet
- Reading Hansel and GretelDocument3 pagesReading Hansel and Gretelsoniaemilyaputri26No ratings yet
- The Importance of Proteinuria in Preeclampsia and Its Predictive Role in Maternal and Neonatal OutcomesDocument9 pagesThe Importance of Proteinuria in Preeclampsia and Its Predictive Role in Maternal and Neonatal OutcomesimuhammadfahmiNo ratings yet
- RPMC ACEs Questionnaire and Patient HandoutApr2019Document2 pagesRPMC ACEs Questionnaire and Patient HandoutApr2019Tuấn KhangNo ratings yet
- Module 8 MCHNDocument15 pagesModule 8 MCHNEDULLANTES ANA MAENo ratings yet
- 27,30 - The Saudi Building Code (SBC) - PDF - 59-59Document1 page27,30 - The Saudi Building Code (SBC) - PDF - 59-59heshamNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Parental Involvement On Student AchievementDocument81 pagesThe Influence of Parental Involvement On Student AchievementKaterine Mae ForonesNo ratings yet
- AddDocument11 pagesAdddumnezeulNo ratings yet
- Family Tree (Material de Consulta y Estudio)Document37 pagesFamily Tree (Material de Consulta y Estudio)Giorgio StojnicNo ratings yet
- Ob Case StudyDocument3 pagesOb Case StudyDyriane PagsolinganNo ratings yet
- Ndandatho The Village Girl CONTINUATIONDocument215 pagesNdandatho The Village Girl CONTINUATIONNeliswa NenezNo ratings yet
- BREASTFEEDINGDocument3 pagesBREASTFEEDINGMyca PascualNo ratings yet
- CFCS 210 Media Review AssignmentDocument4 pagesCFCS 210 Media Review AssignmentjessicakopNo ratings yet
- Youth Psychology IntroductionDocument26 pagesYouth Psychology IntroductionJANA100% (4)