Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Location Advantage Decision Making Workflow
Uploaded by
Marcel Boscanean0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
LocationAdvantageDecisionMakingWorkflow
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageLocation Advantage Decision Making Workflow
Uploaded by
Marcel BoscaneanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
THE LOCATION ADVANTAGE
WORKFLOW
Question Model Analyze Interpret
Formulate the question
Formally frame the issue or need. If location is involved, as it is with most business questions, you can use
geospatial techniques. Your business questions might include asking what an area is like, who lives there,
and where customers or competitors might be located. Which areas or sites might be better for locating a
business? Where are manufacturers, distributors, and retailers? How can you better identify and manage
risks?
Model the solution
Identify the geospatial technique: Which techniques can be used to answer the business question using
location information? You may be able to use visualization, overlay, or routing, or you might measure
distance, perform market segmentation analysis, plan distribution logistics, or find competition.
Gather the required data: What is the data that you will need? Is it tabular data; does it include location?
Where is it stored in the organization: in spreadsheets, or in ERP, BI, SCM, or CRM systems? Will it need
to be collected or purchased? It may already exist in your geospatial application if you use programs like
ArcGIS Online or Business Analyst.
Perform the analysis
Run the model, observe the results, and consider whether the approach could be improved by more or
better data sources, additional parameters, more iterations, or different techniques.
Apply the results
Take action: Apply the findings to the business question. Make decisions based on the organizational
KPIs (key performance indicators).
Integrate results: Create new datasets or modify existing ones, update reports and dashboards, add to
systems and your organizational knowledge base, and synthesize results with non-spatial data.
You might also like
- Win With Advanced Business AnalyticsDocument4 pagesWin With Advanced Business Analyticssumu26No ratings yet
- Aims of SapDocument12 pagesAims of Sapjbadru1973No ratings yet
- Exercise: Site Selection: Choosing The Right LocationDocument29 pagesExercise: Site Selection: Choosing The Right LocationMarcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Transform Your Data Into Actionable InsightsDocument15 pagesTransform Your Data Into Actionable InsightsMonir KhanNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps To A Winning Data Strategy RoadmapDocument4 pages5 Steps To A Winning Data Strategy RoadmapMax GxNo ratings yet
- BA Interview PointsDocument3 pagesBA Interview PointsAmit BNo ratings yet
- Word CloudDocument7 pagesWord CloudaksneternalNo ratings yet
- Guide The Recruiter ToDocument1 pageGuide The Recruiter ToSeshendra VemuriNo ratings yet
- The Execution Premium: Focus Take-AwaysDocument5 pagesThe Execution Premium: Focus Take-AwaysSenny LimNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Site Selection: Choosing The Right LocationDocument29 pagesExercise: Site Selection: Choosing The Right LocationLEONARDO ALBEIRO ORTIZ VILLA0% (1)
- ACTUATE WHITEPAPER PerformanceAnalyticsAssessmentDocument7 pagesACTUATE WHITEPAPER PerformanceAnalyticsAssessmentLetsogile BaloiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Analytics: Dashboards: The Do's and Don'tsDocument12 pagesMarketing Analytics: Dashboards: The Do's and Don'tsPanupadhNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence (BI) Maturity Model: Unit VI BI Maturity, Strategy and Modern Trends in BIDocument59 pagesBusiness Intelligence (BI) Maturity Model: Unit VI BI Maturity, Strategy and Modern Trends in BIDipNo ratings yet
- Strategic Plan For Becoming An Analytics-Driven Organization - Initial DraftDocument16 pagesStrategic Plan For Becoming An Analytics-Driven Organization - Initial Draftnimit kaulNo ratings yet
- Marketing AnalyticsDocument8 pagesMarketing AnalyticskushagraNo ratings yet
- D RoleDocument68 pagesD RoleKarikalan RajendranNo ratings yet
- Sales Operations & ManagementDocument4 pagesSales Operations & ManagementFaraz AlamNo ratings yet
- Checklist MarketingdashboardDocument11 pagesChecklist MarketingdashboardAymanMoftahNo ratings yet
- SAPexperts - An Introduction To SAP Predictive Analytics 2Document59 pagesSAPexperts - An Introduction To SAP Predictive Analytics 2Srikanth SaiNo ratings yet
- SAP Strategy Management Deliver On Corporate Strategy With Enterprise-Wide Alignment PDFDocument30 pagesSAP Strategy Management Deliver On Corporate Strategy With Enterprise-Wide Alignment PDFsteghibelliniNo ratings yet
- Allocation Analyst ResumeDocument5 pagesAllocation Analyst Resumeafjwoovfsmmgff100% (2)
- The Data Science GuideDocument118 pagesThe Data Science GuidetodoherreraNo ratings yet
- Arclyticz Pvt. LTD.: Hubspot Sales HubDocument6 pagesArclyticz Pvt. LTD.: Hubspot Sales HubNikilaa ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Are You Ready To Make It Happen at Mondelēz International? Join Our Mission To Lead The Future of Snacking. Make It MatterDocument4 pagesAre You Ready To Make It Happen at Mondelēz International? Join Our Mission To Lead The Future of Snacking. Make It Matterdiptisawant284No ratings yet
- Business Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionFrom EverandBusiness Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- IBM OM ProjectDocument18 pagesIBM OM ProjectSana SheikhNo ratings yet
- Google Cloud Platform-ArchitectDocument4 pagesGoogle Cloud Platform-ArchitectAnishNo ratings yet
- SAP SapnaDocument5 pagesSAP Sapnaarpangupta007No ratings yet
- 2015 Erp Guide: 14 TruthsDocument8 pages2015 Erp Guide: 14 TruthsJimmy Simón Barboza Baldeon100% (1)
- HardDocument9 pagesHardSourav DeyNo ratings yet
- IPaaS For Data Integration A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandIPaaS For Data Integration A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Business AnalyticsDocument9 pagesBusiness AnalyticsSeven LyxNo ratings yet
- DataOps Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandDataOps Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Profile MadhumitaBhattacharyyaDocument5 pagesProfile MadhumitaBhattacharyyaMadhumita BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Notes BA 300124Document7 pagesNotes BA 300124Naman AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Buma 30083 Fundamentals of Business Analytics Chapter IDocument51 pagesBuma 30083 Fundamentals of Business Analytics Chapter IKing Noli AgootNo ratings yet
- Research On Performance Management Sysytems OF It CompaniesDocument12 pagesResearch On Performance Management Sysytems OF It Companieshardik_kadia2007No ratings yet
- Manage Innovation and Continuous Improvement 1Document31 pagesManage Innovation and Continuous Improvement 1raj ramuk0% (1)
- Lecture 2 - EBusiness ModelsDocument43 pagesLecture 2 - EBusiness ModelsTanjina Parvin TishaNo ratings yet
- Data WarehousingDocument12 pagesData Warehousinguniversity bureauNo ratings yet
- Nama: Rismawaty (Maksi-39/AUD) Ringkasan Chapter 11 Data Visualization and Geographic SystemsDocument1 pageNama: Rismawaty (Maksi-39/AUD) Ringkasan Chapter 11 Data Visualization and Geographic SystemsrismawatyNo ratings yet
- Xaviers Institute of Business Management Studies Sub: Operation ManagementDocument22 pagesXaviers Institute of Business Management Studies Sub: Operation Managementsyed tanseerNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Fahad Mohiuddin Ahmed Mohammad Shahzaib RafiqDocument9 pagesPresented By: Fahad Mohiuddin Ahmed Mohammad Shahzaib RafiqFahad Mohiuddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Cascading Performance MeasuresDocument4 pagesGroup 3 - Cascading Performance MeasuresNeriza PonceNo ratings yet
- Global MarketingDocument19 pagesGlobal MarketingSusharan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Fund. of Business AnalyticsDocument26 pagesModule 2 - Fund. of Business AnalyticsnicaapcinaNo ratings yet
- Business AnalyticsDocument3 pagesBusiness AnalyticsSwati AggarwalNo ratings yet
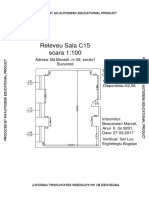
- Releveu Sala C15 Scara 1:100: Adresa: BD - Marasti, NR 59, Sector1 BucurestiDocument1 pageReleveu Sala C15 Scara 1:100: Adresa: BD - Marasti, NR 59, Sector1 BucurestiMarcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Marketing: Understanding Your CustomersDocument35 pagesExercise: Marketing: Understanding Your CustomersMarcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Releveu Sala C15 Scara 1:100: Suprafata Construita 20,03 Suprafata Disponibila 52,56Document1 pageReleveu Sala C15 Scara 1:100: Suprafata Construita 20,03 Suprafata Disponibila 52,56Marcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Understanding Market OpportunityDocument27 pagesExercise: Understanding Market OpportunityMarcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Business, Geography, and The Location AdvantageDocument43 pagesExercise: Business, Geography, and The Location AdvantageMarcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Track Crime Patterns To Aid Law Enforcement PART 1Document17 pagesTrack Crime Patterns To Aid Law Enforcement PART 1Marcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Create A 3D SceneDocument12 pagesCreate A 3D SceneMarcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Section2Exercise1 ExploreBicycleIncidentsUsingOpenData PDFDocument33 pagesSection2Exercise1 ExploreBicycleIncidentsUsingOpenData PDFMarcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Section2Exercise1 ExploreBicycleIncidentsUsingOpenData PDFDocument33 pagesSection2Exercise1 ExploreBicycleIncidentsUsingOpenData PDFMarcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2017-11-27 11.13.39 - 20171204101707Document11 pagesNew Doc 2017-11-27 11.13.39 - 20171204101707Marcel BoscaneanNo ratings yet
- Argumentum Nr. 3 2004-2005 Cap - III PDFDocument29 pagesArgumentum Nr. 3 2004-2005 Cap - III PDFMihaela CreacNo ratings yet