Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ic Engine - 2
Ic Engine - 2
Uploaded by
Ricky Sarkar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
IC ENGINE - 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesIc Engine - 2
Ic Engine - 2
Uploaded by
Ricky SarkarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1. Introduction Internal Combustion Engine (2161902)
b)
¢)
i
cylinder head is mounted on the cylinder block. The cylinder head and cylinder block
are provided with water jackets in the case of water cooling or with cooling fins in the
case of air cooling,
Cylinder
‘As the name implies it is a cylindrical vessel or space in which the piston makes a
reciprocating motion. The varying volume created in the cylinder during the operation
of the engine is filled with the working fluid and subjected to different thermodynamic
processes. Ihe cylinder is supported in the cylinder block.
Piston
Itis a cylindrical component fitted into the cylinder forming the moving boundary of
the combustion system. It fits perfectly (snugly) into the cylinder providing a gas-tight
space with the piston rings and the lubricant. It forms the first link in transmitting the
gas forces to the output shaft.
Combustion chamber
The space enclosed in the upper part of the cylin-der, by the cylinder head and the
piston top during the combustion process, is called the combustion chamber. The
combustion of fuel and the consequent release of thermal energy results in the
building up of pressure in this part of the cylinder.
Inlet manifold
The pipe which connects the intake system to the inlet valve of the engine and through
Which air or air-fuel mixture is drawn into the cylinder is called the inlet manifold
Exhaust manifold
The pipe which connects the exhaust system to the exhaust valve of the engine and
through which the products of combustion escape into the atmosphere is called the
exhaust manifold,
Inlet and Exhaust valves
Valves are commonly mushroom shaped pop-pet type. They are provided either on
the cylinder head or on the side of the cylinder for regulating the charge coming into
the cylinder (inlet valve) and for discharging the products of combustion (exhaust
valve) from the cylinder.
Spark Plug
ttis a component to initiate the combustion process in Spark- Ignition (SI) engines and
is usually located on the cylinder head.
Connecting Rod
It interconnects the piston and the crankchaft and trans mits the gas forees from the
piston to the crankshaft. The two ends of the connecting rod are called as small end
and the big end (Fig.1.3). Small end is connected to the piston by gudgeon pin and the
big end is connected to the crankshaft by crankpin.
Crankshaft
It converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into useful rotary motion of the
output shaft. In the crankshaft of a single cylinder engine there are a pair of crank arms
Prepared By: Darshit S. Dadhaniya Department of Mechanical Engineering
Page 14 Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology, Rajkot
Internal Combustion Engine (2161902) L. Introduction
and balance weights. The balance weights are provided for static and dynamic
balancing of the rotating system. The crankshaft is enclosed in a crankcase.
k) Piston rings
= Piston rings, fitted into the slots around the piston, provide a tight seal between the
piston and the cylinder wall thus preventing leakage of combustion gases.
|) Gudgeon pin
= It links the small end of the connecting rod and the piston.
m) Camshaft
= The camshaft (not shown in the figure) and its associated parts control the opening
and closing of the two valves. The associated parts are push rods, rocker arms, valve
springs and tappets. This shaft also provides the drive to the ignition system. The
camshaft is driven by the crankshaft through timing gears.
n) Cams
= These are made as integral parts of the camshaft and are so de-signed to open the
valves at the correct timing and to keep them open for the necessary duration.
©) Flywheel
~The net torque imparted to the crankshaft during one complete cycle of operation of
the engine fluctuates causing a change in the angular velocity of the shaft. In order to
achieve a uniform torque an inertia mass in the form of a wheel is attached to the
‘output shaft and this wheel is callec the flywheel.
p) Carburetor
— Carburetor is used in petrol engine for proper mixing of air and petrol
q) Fuel pump
= Fuel pump is used in diesel engine for increasing pressure and controlling the quantity
of fuel supplied to the injector.
1) Fuel injector
= Fuel injector is used to inject diesel fuel in the form of fine atomized spray under
pressure at the end of compression stroke.
1.2.2 Terminologies used in IC engine
= Cylinder Bore (d): The nominal inner diameter of the working cylinder is called the
cylinder bore and is designated by the letter d and is usually expressed in millimeter
(mm).
= Piston Area (A): The area of a circle of diameter equal to the cylinder bore is called
the piston area and is designated ty the letter A and is usually expressed in square
centimeter (U1?)
= Stroke (UJ Itis the linear distance traveled by the piston when it moves from one
end of the cylinder to the other end. It is equal to twice the radius of the crank. It
is designated by the letter L and is expressed usually in millimeter (mm).
Department of Mechanical Engineering Prepared By: Darshit S. Dadhaniya
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology, Rajkot Page 1.5
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
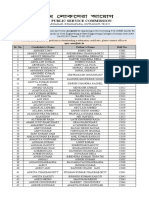
- Sel - Asstt - Prof - Civil Engg - 17oct2019Document11 pagesSel - Asstt - Prof - Civil Engg - 17oct2019Ricky SarkarNo ratings yet
- TT SCHEDULE Yealry 2020 PDFDocument3 pagesTT SCHEDULE Yealry 2020 PDFRicky SarkarNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine - 6Document3 pagesIc Engine - 6Ricky SarkarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PDFDocument98 pagesModule 5 PDFRicky SarkarNo ratings yet
- Ad JR Instr SC Asstt-2017Document2 pagesAd JR Instr SC Asstt-2017Ricky SarkarNo ratings yet
- Applications and Processing of Metals and Alloys: Module-09Document19 pagesApplications and Processing of Metals and Alloys: Module-09Ricky SarkarNo ratings yet
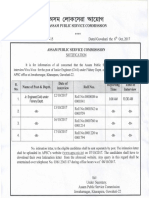
- Notification Urban Dev. Deptt 6 Feb 18Document1 pageNotification Urban Dev. Deptt 6 Feb 18Ricky SarkarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics.31 40Document10 pagesHydraulics.31 40Ricky SarkarNo ratings yet
- Types of Parking Brakes:: Self-Locking: at Certain Critical Value of FC, The Term (B-FC) Becomes Zero, I.e., No ActuationDocument1 pageTypes of Parking Brakes:: Self-Locking: at Certain Critical Value of FC, The Term (B-FC) Becomes Zero, I.e., No ActuationRicky SarkarNo ratings yet
- ASSAM Diploma New SyllabusDocument51 pagesASSAM Diploma New SyllabusRicky SarkarNo ratings yet
- Notification JE (Civil)Document1 pageNotification JE (Civil)Ricky SarkarNo ratings yet