0% found this document useful (0 votes)
433 views9 pagesExtraction of Plant Materials
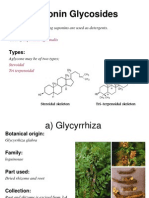
This document summarizes plant extraction methods and properties of some medicinal plants. It describes the plant extraction process, different solvents used, and common extraction techniques like maceration, infusion, digestion, decoction, and percolation. It also outlines key properties of basil, mint, and paan plants, noting their nutritional components and medicinal uses for conditions like indigestion, stress, headaches, and diabetes.
Uploaded by
Praveen Kumar KunamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
433 views9 pagesExtraction of Plant Materials
This document summarizes plant extraction methods and properties of some medicinal plants. It describes the plant extraction process, different solvents used, and common extraction techniques like maceration, infusion, digestion, decoction, and percolation. It also outlines key properties of basil, mint, and paan plants, noting their nutritional components and medicinal uses for conditions like indigestion, stress, headaches, and diabetes.
Uploaded by
Praveen Kumar KunamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd