Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Obesity & Weight Loss Therapy: Role of Leptin in Obesity
Uploaded by
MiltonLondoñoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Obesity & Weight Loss Therapy: Role of Leptin in Obesity
Uploaded by
MiltonLondoñoCopyright:
Available Formats
Obesity & Weight Loss Therapy Wasim, J Obes Weight Loss Ther 2015, 5:2
http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2165-7904.1000258
Review Article Open Access
Role of Leptin in Obesity
Muhammad Wasim*
Institute of Biochemistry and Biotechnology, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan
*Corresponding author: Muhammad Wasim, Institute of Biochemistry and Biotechnology, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan, Tel:
923224990977; E-mail: mm.waseemjee@gmail.com
Received date: April 1, 2015; Accepted date: April 21, 2015; Published date: April 30, 2015
Copyright: © 2015 Wasim M. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use,
distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
Obesity has been the problem in the societies of developing and developed world. Some diseases caused by
obesity. To overcome of those diseases it is necessary to control obesity. Most of the articles showed that the Leptin
may be a vital tool to fight against obesity because it is the anti-obesity hormone. By using leptin therapy may be
possible to prevent obesity and diseases like hypertension and diabetes mellitus before their occurrence.
Keywords: Leptin; Hypertension; LEPR (Leptin Receptor); Obesity; of immune cell function. Leptin is structurally related to the long chain
Neuroendocrinobiology helical cytokine family, which includes IL-2, IL-12, and growth
hormone. Main channel of this gene is JAK/STAT [7]. Leptin acts via
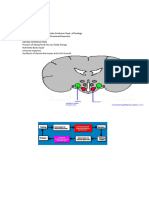
Introduction two groups of arcuate neurons which are located in the hypothalamus
region of the brain. First group expresses Agouti-related peptide and
Leptin is a hormone that comes from Greek word meaning "thin" it Neuropeptide Y (NPY) and second group expresses Pro-Opio-
is also known as "Ob gene" that is located on chromosome number 7. Melano-Cortin (POMC) and Cocaine and Amphetamine-Related
Cytogenetic location is 7q31.31 and consists of three exons and two Transcript (CART) [8].
introns that span 20 kilobases (kb) of DNA. Main role of leptin is to
achieve an energy balance in the body [1]. Leptin binds to receptors in What is Leptin?
brain and performs several actions that may prove that leptin is
important in treating obesity [2]. This hormone is produced by the Leptin is a hormone that was largely unknown to the scientific
adipose tissue, mainly by the white adipose tissue of the human body; community before 1994. Role of leptin is to maintain energy balance
it is comprised of 167 amino acids. The amount of leptin circulating in by regulating food intake and calorie burn rate. As the amount of fat
the body is proportional to the amount of fat of an individual [3]. stored in cells, leptin is secreted into the bloodstream and signals that
Researchers thought that leptin would be the key in controlling make you eat more or less. Actually leptin is a 16-kDa protein. It is
obesity. But research revealed that if greater amount of leptin release secreted by adipocytes and dominantly has major role in the body
then it is less effective in the brain for controlling hunger and food weight regulation by maintaining a balance between food intake and
intake. The result is uncontrolled feeding, leading to greater food expenditure of energy. This gene has several other endocrine
intake and fat storage [4]. It is a 16-kDa circulating hormone that functions. Most important functions are the regulation of immune and
regulates energy homeostasis via hypothalamic neuronal pathways inflammatory responses as well as in angiogenesis and wound healing.
expressing the leptin receptor [1]. The deficiency of leptin or leptin It is observed that leptin is the important hormone that is derived
receptor in humans results in extreme obesity and implicates leptin- from white adipose tissue [9,10]. Leptin discovered more than 10 years
mediated signaling in the regulation of food intake, energy ago, its function is to decrease food intake and increase nerve activity
expenditure, reproductive, thyroid and immune functions [2]. Level of to both thermogenic and non-thermogenic tissue. It was believed that
leptin is positively correlated with fat mass, being increased in obesity leptin is an anti-obesity hormone. Leptin plays major role in the
[4,5]. But some studies suggest that leptin may have a stimulating development of hypertension in obesity [11].
effect on fat oxidation in obese subjects [6]. Leptin is also produced in
fewer amounts in the placenta and probably in the stomach [4]. It is Leptin Regulation
reported that large fat cells produce more leptin than small ones.
Serum leptin concentrations are highly correlated with body fat Many hormones present in the body that upregulate or
content in newborn infants, children and adults [6]. First genetic downregulate the level of leptin. Leptin is upregulated by insulin and
defect of leptin described in 1950s as the spontaneous mutation in cortisol and downregulated by catecholamines. In addition to these
Ob/Ob mice that causes a severe obese phenotype due to overeating factors, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) also serves as a paracrine
and decreased energy expenditure. Leptin gene was named ob and the regulator to increase the secretion of leptin. Leptin also autoregulates
obese mice carrying the mutation were called ob/ob mice. 3 Leptin its own expression by glucose and fatty acids also influence leptin
Receptors (LEPR) are highly expressed in the hypothalamus part of expression [12].
brain which is important in regulating body weight, in T lymphocytes
and vascular endothelial cells. Leptin inhibits food intake by central
action on the hypothalamus. Its functions are quite pleiotropic. It is
implicated in a variety of cellular processes, including the modulation
J Obes Weight Loss Ther Volume 5 • Issue 2 • 1000258
ISSN:2165-7904 JOWT, an open access journal
Citation: Wasim M (2015) Role of Leptin in Obesity. J Obes Weight Loss Ther 5: 258. doi:10.4172/2165-7904.1000258
Page 2 of 3
Regulation of Energy Expenditure, Food Intake and LEPRd, LEPRe and LEPRf. Out of these six, LEPRb is the important
Body Weight by Leptin and longest isoform that has the capacity of strong signaling as
compared to others. Defect in leptin signaling cause severe obesity
Leptin is an important component in the long term regulation of [17]. First missense mutations which were present in the leptin
body weight. Recent studies with obese and non-obese humans receptor (LEPR) were reported. These mutations disrupt LEPR
demonstrated a strong positive correlation of serum leptin signaling. Mutations associated to human obesity were involved in
concentrations with percentage of body fat. It appears that as structural as well as functional relationships within the LEPR [18].
adipocytes increase in size due to accumulation of triglyceride, they
synthesize more and more leptin. Leptin's effects on body weight are Leptin in Obesity
mediated through effects on hypothalamic centers that control feeding
behavior and hunger, body temperature and energy expenditure [13]. Leptin is a neurotransmitter expressed in the brain. This
neurotransmitter signals to the brain mainly in the hypothalamus that
Pathways Involved in Leptin Production when a person stops to eat for maintaining his Body Mass Index. It has
been observed that lab mice have a polymorphism in the leptin gene.
JAK-STAT Pathway has great importance in leptin signaling. Mutations in this gene prevent to manufacture the functional leptin
Studies indicated that in the hypothalamus region, leptin specifically protein. Due to less leptin expression, mice become morbidly obese.
activated STAT3 pathway [14]. Neuropeptide Y promoted feeding Another strain has a mutation or polymorphism in the gene encoding
behavior in the body. Expression of Neuropeptide Y (NPY) will for the Leptin Receptor (LEPR). In this case, signal of the leptin is not
increase during fasting. Absence of the NPY failed to change body received by the brain or the hypothalamus. So due to signal disruption
weight and feeding in normal mice. If any of the components missed or mutations in the leptin receptor, mice become obese
in pathway then less food intake [15]. Pathways of the leptin gene have (www.loop.com/%7Ebkrentzman/obesity/genetics.html). A study
importance in its expression [16]. involves comparison of obese and lean individuals with respect to
leptin level. Experiments included 25 obese and 25 severely lean
Leptin Receptors (LEPR) individuals. Sequence of leptin gene was analyzed by using SSCP,
heteroduplex analysis and automated Sanger sequencing. Result
Activity of leptin is dependent on its binding with its receptor, suggested that in Pakistani population leptin gene may not be a major
known as leptin receptor (LEPR). LEPR belong to gp130 family of cause for obesity and leanness. Until know six mutations have been
cytokine receptor. After the alternative splicing of LEPR, six different reported and these mutations are listed below in Table 1.
isoforms were formed. These isoforms are LEPRa, LEPRb, LEPRc,
Sr. No Mutations Individuals References
1. p.Gly133fsX145 Two Pakistani cousins Montague et al. [2]
2. R105W 4 members from Turkish family Strobel et al. [3]
3. N103K 2 Egyptian children Mazen et al. [4]
4. L72S 14 years old female child Fischer-Posovszky et al. [22]
5. p.Leu161fsX170 1 Obese child from Pakistan Fatima et al. [8]
6. c.104_106delTCA 1 Obese child from Pakistan Fatima et al. [8]
Table 1: Six pathogenic mutations in chronological order.
Diseases Due to Obesity therapy will be very useful for the patients of congenital leptin
deficiency. Leptin has also been used for the treatment of other forms
Some diseases are associated with obesity such as certain types of of energy loss e.g. anorexia nervosa [25]. It was found that immune
cancers, type II diabetes, heart diseases, obstructive sleep apnea and function changed during leptin replacement. Congenital leptin
osteoarthritis [19]. Some factors by which obesity is commonly caused deficiency was evaluated in a 5 year old boy. Boy was evaluated before
include excessive food intake, less physical activity and abnormalities two weeks and after six weeks of leptin therapy. After that treatment,
in genetics as well [20,21]. humoral and cellular immunity was detected by measuring levels of
immunoglobulins and by the analysis of lymphocyte in response to
Leptin Therapy mitogens, respectively [26].
Leptin therapy reversed endocrine as well as metabolic alterations
associated with leptin deficiency [22]. Leptin deficiency was related Neuro-Endocrino-Biological and Obesity
with less numbers of T cells, CD4 and defective T cell proliferation. Scientists reported that obesity and overweight may be associated
These reductions were reversed by leptin therapy [23]. Leptin with cognitive problems. Both obesity and overweight may share
replacement therapy at physiological concentrations after removal of "neuroendocrinobiological roots" in common cerebral areas. In this
high-dosage leptin not worked properly weight regain and study scientist collected 898 samples from school children. Age ranges
hyperphagia was due to deficiency of leptin [24]. Leptin replacement of all the samples were 6 to 13 years. Intellectual level and specific
J Obes Weight Loss Ther Volume 5 • Issue 2 • 1000258
ISSN:2165-7904 JOWT, an open access journal
Citation: Wasim M (2015) Role of Leptin in Obesity. J Obes Weight Loss Ther 5: 258. doi:10.4172/2165-7904.1000258
Page 3 of 3
cognitive profile was done with the help of different experiments. 11. Bravo PE, Morse S, Borne DM, Aguilar EA, Reisin E (2006) Leptin and
Results showed significant difference in intelligence levels in different hypertension in obesity. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2: 163-169.
BMI subgroups calculated by Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children- 12. Fried SK, Ricci MR, Russell CD, Laferrère B (2000) Regulation of leptin
revised (WISC-R). According to regression analysis BMI is the only production in humans. J Nutr 130: 3127S-3131S.
variable that is significantly related to intellectual level. So, to check 13. Hafizuallah AM (2006) Leptin: fights against obesity. Pak J Physiol 2: 1-7
out intellectual level in obese and overweight children a routine 14. Håkansson-Ovesjö ML, Collin M, Meister B (2000) Down-regulated
neurocognitive assessment is recommended [27,28]. STAT3 messenger ribonucleic acid and STAT3 protein in the
hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of the obese leptin-deficient (ob/ob)
mouse. Endocrinology 141: 3946-3955.
Conclusion 15. Shimada M, Tritos NA, Lowell BB, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E (1998) Mice
Obesity has been the problem in the societies of developing and lacking melanin-concentrating hormone are hypophagic and lean.
Nature 396: 670-674.
developed world. Some diseases caused by obesity. To overcome of
those diseases it is necessary to control obesity. Most of the articles 16. Licinio J, Caglayan S, Ozata M, Yildiz BO, Miranda PB, et al. (2003)
Phenotypic effects of leptin replacement on morbid obesity, diabetes
showed that the Leptin may be a vital tool to fight against obesity mellitus, hypogonadism and behavior in leptin-deficient adults. Proc Nat
because it is the anti-obesity hormone. By using leptin therapy may be Acad Sci 101: 4531-4536.
possible to prevent obesity and diseases like hypertension and diabetes 17. Nanjappa V, Raju R, Muthusamy B, Sharma J, Thomas JK, et al. (2011) A
mellitus before their occurrence. comprehensive curated reaction map of leptin signaling pathway. J
Proteomics Bioinform 4: 184-189.
References 18. Kimber W, Peelman F, Prieur X, Wangensteen T, O,Rahilly S, et al.
(2008) Functional characterization of naturally occurring pathogenic
1. Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG (2000) mutations in the human leptin receptor. Endocrinology 149: 6043-6052.
Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404: 661-671. 19. Haslam DW, James WP (2005) Obesity. Lancet 366: 1197-1209.
2. Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP, Soos MA, Rau H, et al. (1997)
20. Kushner FR, Bessesen DH (2007) Treatment of the obese patient
Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early onset obesity (Contemporary Endocrinology). Humana Press.Totowa, NJ 156-175.
in humans. Nature 387: 903–907.
21. Adams JP, Murphy PG (2000) Obesity in anaesthesia and intensive care.
3. Clément K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N, Cabrol S, Pelloux V, et al. (1998) A Br J Anaesth 85: 91-108.
mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary
dysfunction. Nature 392: 398-401. 22. Paz-Filho G, Mastronardi C, Delibasi T, Wong ML, Licinio J (2010)
Congenital leptin deficiency: diagnosis and effects of leptin replacement
4. Ozata M, Ozdemir IC, Licinio J (1999) Human leptin deficiency caused therapy. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 54: 690-697.
by a missense mutation: multiple endocrine defects, decreased
sympathetic tone, and immune system dysfunction indicate new targets 23. Farooqi IS, Matarese G, Lord GM, Keogh JM, Lawrence E, et al. (2002)
Beneficial effects of leptin on obesity, T cell hyporesponsiveness and
for leptin action, greater central than peripheral resistance to the effects
neuroendocrine/metabolic dysfunction of human congenital leptin
of leptin, and spontaneous correction of leptin-mediated defects. Clin
deficiency. J Clin Invest 110: 1093-1103.
Endocrinol Metab 84: 3686–3695.
5. Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, Deng N, Culpepper J, et al. (1995) 24. Montez JM, Soukas A, Asilmaz E, Fayzikhodjaeva G, Fantuzzi G, et al.
(2005) Acute leptin deficiency, leptin resistance, and the physiologic
Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell 83:
response to leptin withdrawal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 2537-2542.
1263-1271.
6. Verdich C, Toubro S, Buemann B, Holst JJ, Bülow J, et al. (2001) Leptin 25. Blüher S, Shah S, Mantzoros CS (2009) Leptin deficiency: clinical
implications and opportunities for therapeutic interventions. J Investig
levels are associated with fat oxidation and dietary-induced weight loss in
Med 57: 784-788.
obesity. Obes Res 9: 452-461.
7. Frühbeck G (2006) Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin. 26. Paz-Filho GJ, Delibasi T, Erol HK, Wong ML, Licinio J (2009) Cellular
immunity before and after leptin replacement therapy. J Pediatr
Biochem J 393: 7-20.
Endocrinol Metab 22: 1069-1074.
8. Fatima W, Shahid A, Imran M, Manzoor J, Hasnain S, et al. (2011) Leptin
deficiency and leptin gene mutations in obese children from Pakistan. Int 27. Parisi P, Verrotti A, Paolino MC, Miano S, Urbano A, et al. (2010)
Cognitive profile, parental education and BMI in children: reflections on
J Pediatr Obes 6: 419-427.
common neuroendrocrinobiological roots. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab
9. Brennan AM, Mantzoros CS (2006) Drug Insight: the role of leptin in 23: 1133-1141.
human physiology and pathophysiology-emerging clinical applications.
Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2: 318-327. 28. Wasim M, Fakhar N (2014) Leptin Gene Mutations in Morbidly Obese
and Severely Lean Individuals from Punjab, Pakistan. J Obes Weight Loss
10. Green ED, Maffei M, Braden VV, Proenca R, DeSilva U, et al. (1995) The Ther 4: 233.
human obese (OB) gene: RNA expression pattern and mapping on the
physical, cytogenetic, and genetic maps of chromosome 7. Genome Res 5:
5-12.
J Obes Weight Loss Ther Volume 5 • Issue 2 • 1000258
ISSN:2165-7904 JOWT, an open access journal
You might also like
- Leptin Wise Diet: 21 Juicing Recipes Understanding Leptin How It Causes Your Body to Burn Fat and Lose Weigh!From EverandLeptin Wise Diet: 21 Juicing Recipes Understanding Leptin How It Causes Your Body to Burn Fat and Lose Weigh!No ratings yet
- Metabolism: The Role of Leptin in Regulating Bone MetabolismDocument9 pagesMetabolism: The Role of Leptin in Regulating Bone MetabolismEgy SunandaNo ratings yet
- Leptin: Regulation and Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandLeptin: Regulation and Clinical ApplicationsSam Dagogo-Jack, MDNo ratings yet
- cphy.c190031Document37 pagescphy.c190031Javier AbalNo ratings yet
- Downsi 6 PDFDocument11 pagesDownsi 6 PDFmutimutimutiNo ratings yet
- Leptin FinalDocument6 pagesLeptin FinalNaveed AkramNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Covid Dan ObesitasDocument15 pagesJurnal Covid Dan ObesitasIcha DestiaNo ratings yet
- Possible Pharmacological Approach Targeting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress To Ameliorate Leptin Resistance in ObesityDocument4 pagesPossible Pharmacological Approach Targeting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress To Ameliorate Leptin Resistance in ObesitySyahrul TubaNo ratings yet
- Mammi 2012 YAAADocument8 pagesMammi 2012 YAAAXochitemiqui YoacihualtNo ratings yet
- Stilbenes May Reduce Obesity by Affecting Adipogenesis, Lipogenesis, Lipolysis & ThermogenesisDocument8 pagesStilbenes May Reduce Obesity by Affecting Adipogenesis, Lipogenesis, Lipolysis & ThermogenesisTony Miguel Saba SabaNo ratings yet
- Leptin Hormone Dramatically Spur Weight LossDocument3 pagesLeptin Hormone Dramatically Spur Weight LossredeveilNo ratings yet
- The Hormonal Control of Food IntakeDocument23 pagesThe Hormonal Control of Food IntakeFarin MauliaNo ratings yet
- LeptinDocument2 pagesLeptinadi chandraNo ratings yet
- Leptin: A Pivotal Regulator of Human Energy HomeostasisDocument5 pagesLeptin: A Pivotal Regulator of Human Energy HomeostasisMara ParamoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Leptin and Ghrelin in The Regulation of Food Intake and Body Weight in Humans: A ReviewDocument14 pagesThe Role of Leptin and Ghrelin in The Regulation of Food Intake and Body Weight in Humans: A ReviewKim Nana UlfaNo ratings yet
- Nutrients 11 02704Document11 pagesNutrients 11 02704RyanNo ratings yet
- Myths and Facts About Leptin and Its Role in EndocrinologyDocument18 pagesMyths and Facts About Leptin and Its Role in EndocrinologyBk FNo ratings yet
- Leptin Resistance and Obesity: Pablo J. Enriori, Anne E. Evans, Puspha Sinnayah, and Michael A. CowleyDocument5 pagesLeptin Resistance and Obesity: Pablo J. Enriori, Anne E. Evans, Puspha Sinnayah, and Michael A. CowleyAlfa RidziNo ratings yet
- Central Leptin Regulation of Obesity and FertilityDocument10 pagesCentral Leptin Regulation of Obesity and FertilityViviana GhenciuNo ratings yet
- Leptin HormoneDocument21 pagesLeptin Hormonemarah almahameed100% (2)
- Set-Point Theory and ObesityDocument6 pagesSet-Point Theory and ObesityDouglas MarinNo ratings yet
- Leptin Hormone and Its Effectiveness in ReproductionDocument6 pagesLeptin Hormone and Its Effectiveness in ReproductionLuisa GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Adiponectin hormone regulates blood sugar and fatty acidsDocument4 pagesAdiponectin hormone regulates blood sugar and fatty acidskukunoNo ratings yet
- Kadar Leptin Saliva Dan Kejadian Karies Gigi Anak ObesitasDocument4 pagesKadar Leptin Saliva Dan Kejadian Karies Gigi Anak ObesitasMaitsa FarrasNo ratings yet
- GRUIARomulus Paper 5-05-2009 Gruia R Buletin 2009Document10 pagesGRUIARomulus Paper 5-05-2009 Gruia R Buletin 2009mihaela_neacsuNo ratings yet
- Role of Leptin in ReproductionDocument10 pagesRole of Leptin in ReproductionCromironNo ratings yet
- Obesity Factors and Control MechanismsDocument10 pagesObesity Factors and Control Mechanismsjunaid011No ratings yet
- Hyperlipidemic Effects of Dietary Saturated Fats Mediated Through PGC-1Document13 pagesHyperlipidemic Effects of Dietary Saturated Fats Mediated Through PGC-1Ilya BerahaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Nutritional SciencesDocument4 pagesRecent Advances in Nutritional SciencesVlad PopaNo ratings yet
- Inter-Organ Cross-Talk in Metabolic Syndrome: Christina Priest and Peter TontonozDocument12 pagesInter-Organ Cross-Talk in Metabolic Syndrome: Christina Priest and Peter TontonozxjorgwxNo ratings yet
- Nature 2000 - Central Nervous System Control of Food IntakeDocument11 pagesNature 2000 - Central Nervous System Control of Food IntakeAlan NiemiesNo ratings yet
- Role of Leptin in Physiology and Emerging Clinical ApplicationsDocument14 pagesRole of Leptin in Physiology and Emerging Clinical Applicationsaida-69No ratings yet
- Lept in 012Document7 pagesLept in 012Carolina De Lima FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0091302203000475 Main PDFDocument29 pages1 s2.0 S0091302203000475 Main PDFLaviniaMenicucciNo ratings yet
- New Concepts in White Adipose Tissue PhysiologyDocument14 pagesNew Concepts in White Adipose Tissue PhysiologyBrilliana JasmineNo ratings yet
- Article-2012-Vaspin in Obesity and Diabetes-Pathophysiological and Clinical SignificanceDocument7 pagesArticle-2012-Vaspin in Obesity and Diabetes-Pathophysiological and Clinical Significancecarlos ArozamenaNo ratings yet
- Dmso 4 141Document14 pagesDmso 4 141doctorbanNo ratings yet
- Differential Effects of Dietary Flavonoids On AdipogenesisDocument21 pagesDifferential Effects of Dietary Flavonoids On AdipogenesisEsNo ratings yet
- Chronic Lipo FatDocument12 pagesChronic Lipo FatDenisse ZayasNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument11 pagesDownloadadri90No ratings yet
- Cellular Warriors at Battle of The BulgeDocument4 pagesCellular Warriors at Battle of The BulgeAndrewChangNo ratings yet
- Eje 257Document15 pagesEje 257Sam SoeteNo ratings yet
- Obesity LeptinDocument41 pagesObesity Leptin2K19/BAE/104 ADITI GARGNo ratings yet
- Scheja & Heeren 2019 The Endocrine Function of Adipose Tissues in Health and Cardiometabolic DiseaseDocument18 pagesScheja & Heeren 2019 The Endocrine Function of Adipose Tissues in Health and Cardiometabolic DiseasevibhutiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EatingDocument39 pagesPhysiology of EatingMeghana N BinuNo ratings yet
- Tugas Fisiologi FinalDocument24 pagesTugas Fisiologi FinalGracemNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance and ObesityDocument6 pagesEnergy Balance and Obesityalihussein100% (4)
- Current and Future Drug Targets in Weight ManagementDocument27 pagesCurrent and Future Drug Targets in Weight ManagementMarcoantonio Rivera FelixNo ratings yet
- Perspective: Leptin's Physiologic Role: Does The Emperor of Energy Balance Have No Clothes?Document3 pagesPerspective: Leptin's Physiologic Role: Does The Emperor of Energy Balance Have No Clothes?ShuiNo ratings yet
- Physiology & Behavior: K Clément, H Mosbah, C Poitou TDocument6 pagesPhysiology & Behavior: K Clément, H Mosbah, C Poitou TvisiniNo ratings yet
- Leptin and Its Essential Role in Health Disease and AgingDocument6 pagesLeptin and Its Essential Role in Health Disease and AgingAndi PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Adipokin 3Document22 pagesAdipokin 3Jajank Japar SNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0196978108001320 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0196978108001320 MainTeodora OnofreiNo ratings yet
- Hepatokines - A Novel Group of Exercise FactorsDocument14 pagesHepatokines - A Novel Group of Exercise FactorsGabriela SolanoNo ratings yet
- Thiazolidinediones - Mechanism of ActionDocument4 pagesThiazolidinediones - Mechanism of ActionOghenetejiri GbakejiNo ratings yet
- Favero2015 PDFDocument10 pagesFavero2015 PDFAruzhan BorankulovaNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Human ObesityDocument14 pagesGenetics of Human Obesitymuralidhar_mettaNo ratings yet
- Leptin and Its Cardiovascular Effects: Focus On AngiogenesisDocument11 pagesLeptin and Its Cardiovascular Effects: Focus On AngiogenesisIgn_SkyfangNo ratings yet
- Cell Communication and Signaling: Leptin and Adiponectin: New Players in The Field of Tumor Cell and Leukocyte MigrationDocument10 pagesCell Communication and Signaling: Leptin and Adiponectin: New Players in The Field of Tumor Cell and Leukocyte Migrationrima noviaNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Immune FunctionVF 19 - 20Document53 pagesObesity and Immune FunctionVF 19 - 20bmvdgxjwh7No ratings yet
- Amelioration of Influenza Virus-Induced Reactive PDFDocument9 pagesAmelioration of Influenza Virus-Induced Reactive PDFMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Properties of Graviola (Annona Muricata) ADocument40 pagesAnticancer Properties of Graviola (Annona Muricata) ADandara AraujoNo ratings yet
- Terapia Fotodinamica UpdateDocument32 pagesTerapia Fotodinamica UpdateMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Preprints202003 0279 v1Document26 pagesPreprints202003 0279 v1harvey moncayo100% (1)
- Acciones Farmacologicas de La PiperinaDocument29 pagesAcciones Farmacologicas de La PiperinaMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Acciones Farmacologicas de La PiperinaDocument29 pagesAcciones Farmacologicas de La PiperinaMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Leptin Resistance A Possible Interface of Inflammation and Metabolism in Obesity-Related Cardiovascular Disease PDFDocument22 pagesLeptin Resistance A Possible Interface of Inflammation and Metabolism in Obesity-Related Cardiovascular Disease PDFMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Serotonin Controlling Feeding and Satiety PDFDocument18 pagesSerotonin Controlling Feeding and Satiety PDFMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Tamiflu PDFDocument28 pagesTamiflu PDFSopheak NGNo ratings yet
- Fasting Induces A Large, Leptin-Dependent Increase in The Intrinsic Action Potential Frequency of Orexigenic Arcuate NucleusDocument5 pagesFasting Induces A Large, Leptin-Dependent Increase in The Intrinsic Action Potential Frequency of Orexigenic Arcuate NucleusMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- A High-Protein Diet Induces Sustained Reductions in Appetite, Ad Libitum Caloric Intake & Body WeightDocument8 pagesA High-Protein Diet Induces Sustained Reductions in Appetite, Ad Libitum Caloric Intake & Body WeightMelissaNo ratings yet
- Early Life Stress Experience May Blunt Hypothalamic Leptin SignallingDocument8 pagesEarly Life Stress Experience May Blunt Hypothalamic Leptin SignallingMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Management of Obesity NewDocument5 pagesPharmacological Management of Obesity Newmilton londoñoNo ratings yet
- Development of A New Colombian Product, Effective For The Treatment of Carious Lesions A Case StudyDocument23 pagesDevelopment of A New Colombian Product, Effective For The Treatment of Carious Lesions A Case StudyMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Advances To The Treatment of ObesityDocument8 pagesPharmacological Advances To The Treatment of Obesitymilton londoñoNo ratings yet
- Beneficios de Un Modelo 5 S en La Industria FarmaceuticaDocument5 pagesBeneficios de Un Modelo 5 S en La Industria FarmaceuticaMiltonLondoñoNo ratings yet
- Leptin and CCKDocument12 pagesLeptin and CCKmilton londoñoNo ratings yet
- Enzyme and Vitamins, BiochemDocument2 pagesEnzyme and Vitamins, BiochemCraigyyNo ratings yet
- Protein-Protein Interaction and System BiologyDocument14 pagesProtein-Protein Interaction and System Biologyamitbhimani100% (2)
- A.1. Competitive InhibitionDocument5 pagesA.1. Competitive InhibitionFlorecita Cabañog100% (1)
- Trends in Drug ResearchDocument186 pagesTrends in Drug ResearchEvsevios HadjicostasNo ratings yet
- Cancer Genetics-Genetic InstabilityDocument60 pagesCancer Genetics-Genetic InstabilityMadhu MithaNo ratings yet
- Genetic SL Test: (100 Marks)Document19 pagesGenetic SL Test: (100 Marks)Ritika GulguliaNo ratings yet
- Letran de Davao, IncDocument3 pagesLetran de Davao, IncPatricia DianeNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesModule 4 - CarbohydratesGallardo Elle chloeNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Application in Bakery IndustryDocument7 pagesEnzyme Application in Bakery IndustryrutwickNo ratings yet
- Basic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureDocument36 pagesBasic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureLutfil HadiNo ratings yet
- AntimetaboliteDocument53 pagesAntimetaboliteRahul LokhandeNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY Gout is disorder of purine metabolismDocument8 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY Gout is disorder of purine metabolismdrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Protein Sequences Ex 091723Document12 pagesProtein Sequences Ex 091723Mai Abdallah El KelanyNo ratings yet
- Milliprep Sample Preparation Kit For MycoplasmaDocument4 pagesMilliprep Sample Preparation Kit For MycoplasmaFiore PinedaNo ratings yet
- Cell MebraneDocument10 pagesCell MebraneChandra SihombingNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules Extension ActivityDocument4 pagesMacromolecules Extension Activityapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Why insulin must be injected and cannot be taken orallyDocument4 pagesWhy insulin must be injected and cannot be taken orallyBethNo ratings yet
- Filetype PDF Complement PathwaysDocument2 pagesFiletype PDF Complement PathwaysScottNo ratings yet
- WBI12 01 MSC 20200123 PDFDocument27 pagesWBI12 01 MSC 20200123 PDFRadhiyaah100% (1)
- Friedman2004 PDFDocument22 pagesFriedman2004 PDFKris SnowNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA QuizDocument3 pagesDNA and RNA QuizDavid GiraldoNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIADocument20 pagesMITOCHONDRIAannisa fauzia rahmahNo ratings yet
- 03 Medication-Related ProblemsDocument13 pages03 Medication-Related ProblemsRoselyn DawongNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Co FactorDocument13 pagesCo FactorMusliza Rashid Noir IpohNo ratings yet
- Branches of ChemistryDocument9 pagesBranches of ChemistryYhan Brotamonte Boneo100% (1)
- What's Next For The AI Protein-Folding RevolutionDocument6 pagesWhat's Next For The AI Protein-Folding RevolutionLuis RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Mammal (Humans)Document3 pagesNutrition in Mammal (Humans)Aaron Dave CanteroNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Properties of Spices, Herbs and Other SourcesDocument589 pagesAntioxidant Properties of Spices, Herbs and Other SourcesAna MariaNo ratings yet
- Biology OPDocument1,478 pagesBiology OPSasha RasinNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)