Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES
Uploaded by
Raghu Rajan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesANTIHYPERTENSIVES
Uploaded by
Raghu RajanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
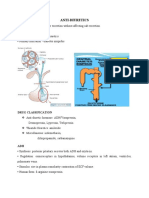
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES
INTRODUCTION
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure).
Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such
as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by
5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce
the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are
many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means.
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES
1. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
2. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists
3. Calcium channel blockers
4. Diuretics
5. Sympatholytics
6. Vasodilators
ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME (ACE) INHIBITORS
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors are a class of medication used primarily for
the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. They work by causing relaxation
of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volume, which leads to lower blood
pressure and decreased oxygen demand from the heart.
You might also like
- Renal PreservationDocument7 pagesRenal PreservationRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Anti-Diuretics: Drug ClassificationDocument4 pagesAnti-Diuretics: Drug ClassificationRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Bladder Irrigation & Ostomy CareDocument15 pagesBladder Irrigation & Ostomy CareRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- CVP MonitoringDocument10 pagesCVP MonitoringRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- 12 Formative EvaluationDocument22 pages12 Formative EvaluationRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- ITEM ANALYSIS. TeachingDocument6 pagesITEM ANALYSIS. TeachingRaghu Rajan100% (5)
- Renal AbscessDocument10 pagesRenal AbscessRaghu Rajan100% (1)
- Ipsg Ward TeachingDocument13 pagesIpsg Ward TeachingRaghu Rajan100% (1)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument9 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies of The KidneyDocument21 pagesCongenital Anomalies of The KidneyRaghu Rajan100% (1)
- Assesment of NewbornDocument74 pagesAssesment of NewbornRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument12 pagesPerformance AppraisalRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its Impact On HealthDocument7 pagesClimate Change and Its Impact On HealthRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Heat WaveDocument40 pagesHeat WaveRaghu Rajan100% (1)
- Westfort College of Nursing Check List For EnemaDocument2 pagesWestfort College of Nursing Check List For EnemaRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- PV ExaminationDocument19 pagesPV ExaminationRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewsDocument10 pagesLiterature ReviewsRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- CaiDocument21 pagesCaiRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Health Care Delivery System in IndiaDocument13 pagesHealth Care Delivery System in IndiaRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Minordisppt 161209154619Document50 pagesMinordisppt 161209154619Raghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument2 pagesEssential Newborn CareRaghu RajanNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)