Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Forms and Uses of the Present Perfect, Past Perfect, and Past Progressive Tenses
Uploaded by
Bulan Water DistrictOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Forms and Uses of the Present Perfect, Past Perfect, and Past Progressive Tenses
Uploaded by
Bulan Water DistrictCopyright:
Available Formats
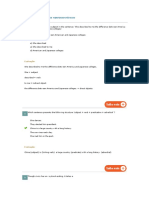
The PRESENT PERFECT TENSE is formed with a present tense form of "to have" plus the past participle of
the verb (which can be either regular or irregular in form). This tense indicates either that an action was
completed (finished or "perfected") at some point in the past or that the action extends to the present:
ACTIONS STARTED IN THE PAST AND CONTINUING IN THE PRESENT
They haven't lived here for years.
She has worked in the bank for five years.
We have had the same car for ten years.
Have you played the piano since you were a child?
WHEN THE TIME PERIOD REFERRED TO HAS NOT FINISHED
I have worked hard this week.
It has rained a lot this year.
We haven't seen her today.
ACTIONS REPEATED IN AN UNSPECIFIED PERIOD BETWEEN THE PAST AND NOW.
They have seen that film six times
It has happened several times already.
She has visited them frequently.
We have eaten at that restaurant many times.
ACTIONS COMPLETED IN THE VERY RECENT PAST (+JUST)
Have you just finished work?
I have just eaten.
We have just seen her.
Has he just left?
WHEN THE PRECISE TIME OF THE ACTION IS NOT IMPORTANT OR NOT KNOWN
Someone has eaten my soup!
Have you seen 'Gone with the Wind'?
She's studied Japanese, Russian, and English.
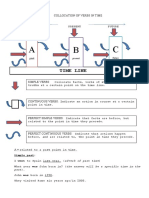
The past perfect refers to a time earlier than before now. It is used to make it clear that one event
happened before another in the past. It does not matter which event is mentioned first - the tense
makes it clear which one happened first.
Event A Event B
John had gone out when I arrived in the office.
Event A Event B
I had saved my document before the computer crashed.
Event B Event A
When they arrived we had already started cooking.
Event B Event A
He was very tired because he hadn't slept well.
PAST PERFECT + JUST
'Just' is used with the past perfect to refer to an event that was only a short time earlier than before now,
e.g.
The train had just left when I arrived at the station.
She had just left the room when the police arrived.
I had just put the washing out when it started to rain.
The PAST PROGRESSIVE TENSE indicates continuing action, something that was happening, going on, at some
point in the past. This tense is formed with the helping "to be" verb, in the past tense, plus the present participle of
the verb (with an -ing ending):
I was riding my bike all day yesterday.
Joel was being a terrible role model for his younger brother.
The past progressive indicates a limited duration of time and is thus a convenient way to indicate that something
took place (in the simple past) while something else was happening:
Carlos lost his watch while he was running.
The past progressive can express incomplete action.
I was sleeping on the couch when Bertie smashed through the door.
Singular Plural
I was walking we were walking
you were walking you were walking
he/she/it was walking they were walking
Singular Plural
I was sleeping we were sleeping
you were sleeping you were sleeping
he/she/it was sleeping they were sleeping
Singular Plural
I was being we were being
you were being you were being
he/she/it was being they were being
The present progressive tense is used for an on-going action in the present.
Examples of the Present Progressive Tense
Caroline is looking for the latest brochure.
Dan and Billy are fishing off the pier.
You can also have a negative version:
Caroline is not looking for the latest brochure.
Dan and Billy are not fishing off the pier.
And the question version:
Is Caroline looking for the latest brochure?
Are Dan and Billy fishing off the pier?
The present progressive tense can also be used to describe an activity which is going to happen in the
future (especially for planned activities). For example:
We are moving to New Zealand in the summer.
The train is arriving in 2 minutes.
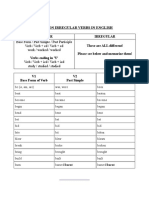
V1 V2 V3
BASE FORM OF VERB PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE
be (is, am,are) was, were been
beat beat beaten
become became become
begin began begun
bend bent bent
bet bet bet
bid bid bid
bite bit bitten
blow blew blown
break broke broken
bring brought brought
build built built
burn burned/burnt burned/burnt
buy bought bought
catch caught caught
choose chose chosen
come came come
cost cost cost
cut cut cut
dig dug dug
dive dove dived
V1 V2 V3
BASE FORM OF VERB PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE
do did done
draw drew drawn
dream dreamed/dreamt dreamed/dreamt
drive drove driven
drink drank drunk
eat ate eaten
fall fell fallen
feel felt felt
fight fought fought
find found found
fly flew flown
forget forgot forgotten
forgive forgave forgiven
freeze froze frozen
get got gotten
give gave given
go went gone
grow grew grown
hang hung hung
have had had
hear heard heard
V1 V2 V3
BASE FORM OF VERB PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE
hide hid hidden
hit hit hit
hold held held
hurt hurt hurt
keep kept kept
know knew known
lay laid laid
lead led led
leave left left
lend lent lent
let let let
lie lay lain
lose lost lost
make made made
mean meant meant
meet met met
pay paid paid
put put put
read read read
ride rode ridden
ring rang rung
V1 V2 V3
BASE FORM OF VERB PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE
rise rose risen
run ran run
say said said
see saw seen
sell sold sold
send sent sent
show showed shown
shut shut shut
sing sang sung
sit sat sat
sleep slept slept
speak spoke spoken
spend spent spent
stand stood stood
swim swam swum
take took taken
teach taught taught
tear tore torn
tell told told
think thought thought
throw threw thrown
V1 V2 V3
BASE FORM OF VERB PAST SIMPLE PAST PARTICIPLE
understand understood understood
wake woke woken
wear wore worn
win won won
write wrote written
You might also like
- Common Irregular Verbs in English: V1 Base Form of Verb V2 Past Simple V3 Past ParticipleDocument4 pagesCommon Irregular Verbs in English: V1 Base Form of Verb V2 Past Simple V3 Past ParticipleSaba ShaukatNo ratings yet
- English - TensesDocument11 pagesEnglish - TensesVlad VargauNo ratings yet
- Informal French Expressions and their English EquivalentsFrom EverandInformal French Expressions and their English EquivalentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- VERBOS IRREGULARES CUEVAdocxDocument4 pagesVERBOS IRREGULARES CUEVAdocxJonel CuevaNo ratings yet
- BI - Modul Potensi Cemerlang Amanjaya SPM 2017Document128 pagesBI - Modul Potensi Cemerlang Amanjaya SPM 2017Aazril71No ratings yet
- VERBOS IRREGULARES CUEVAdocxDocument4 pagesVERBOS IRREGULARES CUEVAdocxJonel CuevaNo ratings yet
- Disney Manga: Beauty and the Beast - The Beast's TaleFrom EverandDisney Manga: Beauty and the Beast - The Beast's TaleRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (29)
- BI - Modul Potensi Cemerlang Amanjaya SPM 2017Document128 pagesBI - Modul Potensi Cemerlang Amanjaya SPM 2017sylent goh100% (2)
- Our Courses Schools FAQ's Prices Blog Contact Us: EnglishDocument15 pagesOur Courses Schools FAQ's Prices Blog Contact Us: EnglishImtiyazNo ratings yet
- Common Irregular Verbs in English Memorization GuideDocument5 pagesCommon Irregular Verbs in English Memorization GuidechichetasNo ratings yet
- English Irregular Verbs ListDocument5 pagesEnglish Irregular Verbs ListmauricioxrmNo ratings yet
- Verbs: Home Parts of Speech Sentence Structure Punctuation Usage ExercisesDocument8 pagesVerbs: Home Parts of Speech Sentence Structure Punctuation Usage ExercisesIza ZuzazaNo ratings yet
- English Irregular VerbsDocument5 pagesEnglish Irregular VerbsJorge del CarpioNo ratings yet
- Presentation +Past+SimpleDocument23 pagesPresentation +Past+SimpleRotari DiankaNo ratings yet
- English Irregular Verbs ListDocument5 pagesEnglish Irregular Verbs ListpeterNo ratings yet
- Tense Split View and Grammar PointsDocument5 pagesTense Split View and Grammar PointstinNo ratings yet
- COMMON IRREGULAR VERBS IN ENGLISHDocument4 pagesCOMMON IRREGULAR VERBS IN ENGLISHLoredanaNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs: Brought To You by The Purdue University Online Writing LabDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs: Brought To You by The Purdue University Online Writing LabNedyalko NedyalkovNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs: Base Form of Verb Past Tense Past ParticipleDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs: Base Form of Verb Past Tense Past ParticipleJohn EltNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs: Base Form of Verb Past Tense Past ParticipleDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs: Base Form of Verb Past Tense Past Participleg tsNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs: Base Form of Verb Past Tense Past ParticipleDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs: Base Form of Verb Past Tense Past ParticipleFernando2350No ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs: Base Form of Verb Past Tense Past ParticipleDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs: Base Form of Verb Past Tense Past ParticipleHANNAH GARDOSENo ratings yet
- 164 .Irregularverblist 2 PDFDocument5 pages164 .Irregularverblist 2 PDFSilvia PekelmanNo ratings yet
- Tense FormationDocument3 pagesTense FormationJelena JosijevićNo ratings yet
- English Irregular Verbs ListDocument2 pagesEnglish Irregular Verbs List04Aretta Widanie Lia HapsariNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs ListDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs ListSofigutiofcNo ratings yet
- REGULAR VERBS and IRREGULAR VERBSDocument4 pagesREGULAR VERBS and IRREGULAR VERBScheng09No ratings yet
- English SPM A+Document97 pagesEnglish SPM A+慈心100% (1)
- Push Into /attach/ Put STH TemporarillDocument1 pagePush Into /attach/ Put STH TemporarillAlexaXimenaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Handout NEW MAY 2018Document8 pagesVerb Tenses Handout NEW MAY 2018ecole mirabelleNo ratings yet
- Tense FormationDocument3 pagesTense FormationJelenaJosijevićNo ratings yet
- Present Past Past ParticipleDocument5 pagesPresent Past Past Participleprathamesh kerkarNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense GuideDocument4 pagesSimple Past Tense GuideSamuel RivasNo ratings yet
- Regular & Irregular Verbs PDFDocument4 pagesRegular & Irregular Verbs PDFDANADANIKA107998100% (1)
- Simple To Past Part.Document21 pagesSimple To Past Part.Dina ValdezNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs 24Document9 pagesIrregular Verbs 24andruortegavargasxNo ratings yet
- Regular and irregular verbs appendixDocument2 pagesRegular and irregular verbs appendixPilarNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument5 pagesIrregular VerbsechevarrialorainneNo ratings yet
- Ensino Médio Módulo 4-1Document10 pagesEnsino Médio Módulo 4-1Rogério MaruyamaNo ratings yet
- Past ParticipleDocument3 pagesPast ParticipleStephen KokoNo ratings yet
- Regular Verbs Irregular VerbsDocument6 pagesRegular Verbs Irregular Verbsgladyme mananayNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs (Canva)Document11 pagesIrregular Verbs (Canva)Héctor Alonso Pérez GómezNo ratings yet
- L.engleza, notiuniDocument13 pagesL.engleza, notiuniLidia GuzunNo ratings yet
- Latihan Bahasa Inggris V2-V3Document2 pagesLatihan Bahasa Inggris V2-V3den2fighterNo ratings yet
- Gram 1 Structure of Present Tense & PAST TENSESDocument5 pagesGram 1 Structure of Present Tense & PAST TENSESMOSES7 WISENo ratings yet
- V1 Base Form of Verb V2 Past Simple V3 Past ParticipleDocument4 pagesV1 Base Form of Verb V2 Past Simple V3 Past Participlealinastepanyan9No ratings yet
- Base Form Past Simple Past Participle Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument3 pagesBase Form Past Simple Past Participle Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleJohn Eboy SantosNo ratings yet
- Study English verb formsDocument5 pagesStudy English verb formselabozkurt054491No ratings yet
- Infinitive, Past Simple and Past Participle ConjugationsDocument4 pagesInfinitive, Past Simple and Past Participle Conjugationstom100% (1)
- Verb TensesDocument20 pagesVerb TensesadnanNo ratings yet
- Simple Form Simple Simple Past of Verb Present Tense Past Tense ParticipleDocument4 pagesSimple Form Simple Simple Past of Verb Present Tense Past Tense Participlealex sanchezNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verb ListDocument7 pagesIrregular Verb ListMartha SánchezNo ratings yet
- Grammar Vocabulary First and First For Schools Irregular VerbsDocument4 pagesGrammar Vocabulary First and First For Schools Irregular VerbsCOMPU ALEX MORELIANo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs EngDocument4 pagesIrregular Verbs EngChristos FloridisNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs (Bang Dong Tu Bat Quy Tac) PDFDocument2 pagesIrregular Verbs (Bang Dong Tu Bat Quy Tac) PDFHân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Irregular VerbsDocument9 pagesPast Simple Irregular VerbsCómoNo ratings yet
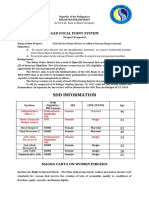
- Major Final Output Listing - ADMINISTRATIVEDocument45 pagesMajor Final Output Listing - ADMINISTRATIVEBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document1 pageQuiz 2Bulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Pre - AssignmentDocument1 pagePre - AssignmentBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Bulan Water District Freedom of Information ManualDocument22 pagesBulan Water District Freedom of Information ManualBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document1 pageQuiz 1Bulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Quiz: Grammar PracticeDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Quiz: Grammar PracticeBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Sentence Pattern QuizDocument1 pageSentence Pattern QuizBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Prepositions, Conjunctions, and Interjections ExplainedDocument3 pagesPrepositions, Conjunctions, and Interjections ExplainedBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- To Convert A Fraction To A Decimal Manually, Follow These StepsDocument2 pagesTo Convert A Fraction To A Decimal Manually, Follow These StepsBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Idiomatic ExpressionDocument1 pageIdiomatic ExpressionBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Exam Review Project for Women EmpowermentDocument2 pagesCivil Service Exam Review Project for Women EmpowermentBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Identify Sentence Patterns and TypesDocument4 pagesIdentify Sentence Patterns and TypesBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Status of Watershed Management in Brgy. Dolos, Bulan, Sorsogon As Perceived by LGU Officials, BWD Employees and Its Residents For C.Y 2017-2018.Document17 pagesStatus of Watershed Management in Brgy. Dolos, Bulan, Sorsogon As Perceived by LGU Officials, BWD Employees and Its Residents For C.Y 2017-2018.Bulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- PCW Memorandum Circular 2018-04Document6 pagesPCW Memorandum Circular 2018-04Alvin Cloyd Dakis, MHSS, RN, CGDPNo ratings yet
- Annex A - Sample Memo To Next-in-RankDocument1 pageAnnex A - Sample Memo To Next-in-RankBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Annex M - Sample PublicationDocument5 pagesAnnex M - Sample PublicationBulan Water DistrictNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Present ContinuousDocument7 pagesFunctions of The Present ContinuousEdison Pareja EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Mystery StoriesDocument1 pageMystery StoriesTalk Language Training Academia de idiomasNo ratings yet
- Língua InglesaDocument41 pagesLíngua InglesaGiselle de PaulaNo ratings yet
- THINK L3 Unit 1 Grammar Basic - 10-1-InglesDocument1 pageTHINK L3 Unit 1 Grammar Basic - 10-1-Inglesgeraldine lancheros100% (1)
- Past Progressive I - PresentationDocument11 pagesPast Progressive I - PresentationMarla PeppersNo ratings yet
- Class Vi Final Examination 2021-22Document4 pagesClass Vi Final Examination 2021-22Udit JindalNo ratings yet
- Presentation TENSESDocument39 pagesPresentation TENSESdyah sekar pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice (Simple Past and Past Progressive)Document17 pagesPassive Voice (Simple Past and Past Progressive)VerónicaNo ratings yet
- Bab 8Document32 pagesBab 8Amir DgreatNo ratings yet
- 7.razred - Test 1Document3 pages7.razred - Test 1Dejan Lazic81% (37)
- English Grammar Table of ContentsDocument46 pagesEnglish Grammar Table of ContentsartijolaNo ratings yet
- 3 Modul: Present and Past SpeculationDocument3 pages3 Modul: Present and Past SpeculationBakin FejsNo ratings yet
- BPO Training ModuleDocument67 pagesBPO Training Modulemhean1991No ratings yet
- грамматика 8 классDocument47 pagesграмматика 8 классАнастасия МашинаNo ratings yet
- C1 - Unit 4 - Class 1 - Future Tenses - WorksheetDocument2 pagesC1 - Unit 4 - Class 1 - Future Tenses - WorksheetMai Xuân TiếnNo ratings yet
- A1 A2 SyllabusDocument12 pagesA1 A2 Syllabusjoog100% (1)
- Using A Timeline To Find The Correct Verb Form CLT Communicative Language Teaching Resources Gram 72073Document4 pagesUsing A Timeline To Find The Correct Verb Form CLT Communicative Language Teaching Resources Gram 72073MarikBálintNo ratings yet
- English Handbook for Nursing StudentsDocument65 pagesEnglish Handbook for Nursing StudentsfifiNo ratings yet
- A Quick Way To Learn English Tenses - Learn Now (Free PDFDocument3 pagesA Quick Way To Learn English Tenses - Learn Now (Free PDFAhmad AliNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument2 pagesEnglish TensesGustavo SteffenNo ratings yet
- Tense Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesTense Direct Speech Reported SpeechRozanne AvrilNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN WeekendingOct.14th, 2022Document17 pagesLESSON PLAN WeekendingOct.14th, 2022Athlyn DurandNo ratings yet
- Actividades Pre ADocument19 pagesActividades Pre ANicole BelmarNo ratings yet
- Grammar Basics - Simple Present, Present Continuous, Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous TensesDocument31 pagesGrammar Basics - Simple Present, Present Continuous, Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous TensesParth Parekh100% (2)
- Sequence of TensesDocument16 pagesSequence of Tensesnfaisha885No ratings yet
- P4 English Primary Lessons Participles Otherness SuffixesDocument3 pagesP4 English Primary Lessons Participles Otherness SuffixesMs YolaNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument9 pagesPassive VoiceMoka VimerNo ratings yet
- Spotting Error RulesDocument18 pagesSpotting Error Rulespriya uppala100% (2)
- Enterprise 4 (Unit 5 Grammar) PresentationDocument18 pagesEnterprise 4 (Unit 5 Grammar) Presentationdaiva2simonaNo ratings yet
- Formule VremenaDocument2 pagesFormule VremenaLjubomir SušićNo ratings yet