Professional Documents
Culture Documents
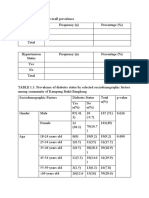
Table Distinguish
Uploaded by
Afifah Solehah HamdanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table Distinguish
Uploaded by
Afifah Solehah HamdanCopyright:
Available Formats
Disease Pneumonia Bronchiolitis
Mode of Air borne droplets where when there is an ill Air borne droplets where
transmission contact through sneeze or breathing when there is an ill contact
through sneeze or breathing
Causative In young infant, it may be due to RSV 80% due to Respiratory
agents infection if diseases occur after birth Synctial Virus in infant aged
(1-9 months) old and
Congenital pneumonia may be due her mother associated with immature
had been infected by Group B lungs function. However,
Streptococcous there are also may be due to
infection of other causes of
Older children tend to be infected by URTI such as rhinovirus and
Streptococcous Pneumoniae and other fungi adenovirus.
related such as Mycoplasma pneumonia
Pathophysiolog Infection of lungs will lead to local Acquisition of
y inflammation which causes formation of infectionInfect the upper
exudates and infiltrate alveoli and respiratory tractimmature
bronchioles Consolidation immune system in young
children fail to resist the
infectionNecrosis of
respiratory epithelium due to
certain local inflammatory
responseImpaired secretion
and elimination by
macrophagesSubmucosal
edema in
bronchiolesObstructive
airwaysV/Q Mismatch and
signs occursResolution and
healing
General The patient will look severely ill and the The patient are still looking
appearance of patient looks very restlessness and febrile fine but with coughing and not
patient episode occur lethargic
Management Based on the causative agent that cause Nebulised bronchodilators to
pneumoniae, broad spectrum antibiotic need supress the effect of
to be given based on the gram stain cultured bronchoconstriction.
in order to prevent any resistance to
antibiotics occur. Oxygen delivered by nasal
progs
Then, followed with adequate hydration
based on fluid correction calculation. Time will heal the symptoms
Additional ventilation CPAP in severe cases.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chest Tube ThoracostomyDocument5 pagesChest Tube ThoracostomyChristine AduvisoNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Chest DiseasesDocument184 pagesImaging of Chest DiseasesGembong Putro100% (1)
- Chapter 25: Assessment: Respiratory System Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionDocument9 pagesChapter 25: Assessment: Respiratory System Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionKrishna RamaNo ratings yet
- Haad ReviewerDocument11 pagesHaad ReviewerGhielyn Roque Baligod0% (1)
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationDocument22 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationChew Han Hoong0% (2)
- Pneumonia and TuberculosisDocument18 pagesPneumonia and TuberculosisVincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary ConditionsDocument42 pagesPulmonary ConditionsMinetteNo ratings yet
- The Adventures of A Frog That Was Once A Prince - English - PORTRAIT - V12020.07.02T183127+0000Document23 pagesThe Adventures of A Frog That Was Once A Prince - English - PORTRAIT - V12020.07.02T183127+0000Afifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- The Diary of A Martian Kid - English - PORTRAIT - V12020.07.02T183116+0000Document20 pagesThe Diary of A Martian Kid - English - PORTRAIT - V12020.07.02T183116+0000Afifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- The Cave of Fireflies - English - PORTRAIT - V12020.07.02T183122+0000Document23 pagesThe Cave of Fireflies - English - PORTRAIT - V12020.07.02T183122+0000Afifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Practical Sessions in Urinary System2018Document1 pageAnatomy Practical Sessions in Urinary System2018Afifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- DUMMY TABLE and OD Group 1Document5 pagesDUMMY TABLE and OD Group 1Afifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- Plan of ActionDocument1 pagePlan of ActionAfifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- Compare PEFR Value Obtained From PFM and SpirometrDocument3 pagesCompare PEFR Value Obtained From PFM and SpirometrAfifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- Group Number: Student Name Matric NumberDocument8 pagesGroup Number: Student Name Matric NumberAfifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- Thigh, Femoral Triangle, Adductor CanalDocument20 pagesThigh, Femoral Triangle, Adductor CanalAfifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- TBL 05 Diabetes & Metabollic SyndromeDocument57 pagesTBL 05 Diabetes & Metabollic SyndromeAfifah Solehah Hamdan100% (1)
- Electrocardiography: - Pacemaker CellsDocument16 pagesElectrocardiography: - Pacemaker CellsAfifah Solehah HamdanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Life ProcessesDocument13 pagesChapter 5 - Life ProcessesAnshika yadavNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Disorders Part 1Document70 pagesLower Respiratory Disorders Part 1Joseph Krafft100% (1)
- Inspection, Palpation, Percussion, Auscultation (IPPA) TipsDocument10 pagesInspection, Palpation, Percussion, Auscultation (IPPA) TipsMarjorie Joy GreciaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesDrugs Acting On The Respiratory SystemNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Test-True or False MCQ: Call - Me - Crush007Document40 pagesRespiratory System Test-True or False MCQ: Call - Me - Crush007امتیاز ہاشم بزنجوNo ratings yet
- Funda Notes Compilation Lecture and SkillsDocument21 pagesFunda Notes Compilation Lecture and SkillsmysterioushumaneNo ratings yet
- Faal Paru Dinamis: Jurnal RespirasiDocument8 pagesFaal Paru Dinamis: Jurnal RespirasiHafis HerdimanNo ratings yet
- HP-A 19 Lung VolumesDocument4 pagesHP-A 19 Lung Volumesvialis bellNo ratings yet
- Pathology For The Health Professions 5Th Edition Damjanov Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesPathology For The Health Professions 5Th Edition Damjanov Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcrastzfeiej100% (8)
- Key Changes Gold 2023 2Document16 pagesKey Changes Gold 2023 2Muhammad Nur Ardhi LahabuNo ratings yet
- Dr. Arlene Jane Sy-Reodica Clinical Applications Specialist - ASEAN Monitoring SolutionsDocument43 pagesDr. Arlene Jane Sy-Reodica Clinical Applications Specialist - ASEAN Monitoring SolutionsArNo ratings yet
- Ap. RespiratorDocument42 pagesAp. RespiratorElena-Raluca CiolanNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Present TenseDocument3 pagesTugas 1 Present TenseMas Eja Agip PramamaNo ratings yet
- THE SPEECH MECHANISMDocument7 pagesTHE SPEECH MECHANISMmortalizerNo ratings yet
- LPJ Human FactorsDocument189 pagesLPJ Human FactorsmuratNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment On AdultsDocument12 pagesPhysical Assessment On AdultsGen-GenMedranoGirayNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument18 pagesMechanical VentilationAlka GoyalNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Thorax and The LungsDocument9 pagesAssessing The Thorax and The LungsChrizzia Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Fracture CaseDocument15 pagesFracture CaseAnna Theresa Cruz100% (2)
- Phctlab - Topic 1 - PrelimsDocument5 pagesPhctlab - Topic 1 - PrelimsasdfdjfeonaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary ContusionDocument83 pagesPulmonary ContusionLouise Anne Agnazata GayoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledZeianne BosabicaNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Measurements of Pressure, Flow and Sound During Trumpet PlayingDocument7 pagesSimultaneous Measurements of Pressure, Flow and Sound During Trumpet PlayingSzymon ŚledzińskiNo ratings yet