Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cash Flow Statements: Needs of The Enterprise To Utilize Those Cash Flows
Uploaded by
ashishdbg2008Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cash Flow Statements: Needs of The Enterprise To Utilize Those Cash Flows
Uploaded by
ashishdbg2008Copyright:
Available Formats
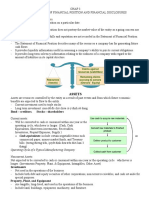
Cash Flow Statements
Statements of Accounting Standards (AS 3)
Objective - to assess the ability of the enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents and the
needs of the enterprise to utilize those cash flows.
Benefits of Cash Flow Information:
enables users to evaluate the changes in net assets of an enterprise, its financial
structure (including its liquidity and solvency)
an indicator of the amount, timing and certainty of future cash flows
Presentation of a Cash Flow Statement
Operating Activities: The principal revenue-producing activities of the enterprise and other
activities
• cash receipts from the sale of goods and the rendering of services;
• cash receipts from royalties, fees, commissions and other revenue;
• cash payments to suppliers for goods and services;
• cash payments to and on behalf of employees;
Investing Activities: Acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and other investments not
included in cash equivalents.
cash payments/receipts to acquire/ disposal fixed assets (including intangibles).
cash payments/ receipts to acquire shares, warrants or debt instruments of other
enterprises and interests in joint ventures
cash advances and loans made to third parties
cash payments/receipts for futures contracts, forward contracts, option contracts
and swap contracts.
Financing Activities: Activities that result in changes in the size and composition of the owners’
capital (including preference share capital in the case of a company) and borrowings of the
enterprise.
cash proceeds from issuing shares or other similar instruments;
cash proceeds from issuing debentures, loans, notes, bonds, and other short or long-
term borrowings
cash repayments of amounts borrowed.
You might also like
- Cash Flow Statements: Prof. Gourav Vallabh XLRI JamshedpurDocument3 pagesCash Flow Statements: Prof. Gourav Vallabh XLRI JamshedpursiddhasatishNo ratings yet
- Pas 7Document11 pagesPas 7Princess Jullyn ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Finacial Statement Analysis Cash Flow Statement and Its AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinacial Statement Analysis Cash Flow Statement and Its AnalysisLeomarc LavaNo ratings yet
- Cash Flows Statements (Classification of Cash Flows Sources)Document2 pagesCash Flows Statements (Classification of Cash Flows Sources)prabir kumer RoyNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statement Full TheoryDocument3 pagesCash Flow Statement Full TheoryShubham BhaiNo ratings yet
- Process For Cash Flow StatementsDocument33 pagesProcess For Cash Flow StatementsP3 PowersNo ratings yet
- Satish FinalDocument79 pagesSatish FinalAnonymous MhCdtwxQINo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statement Wit SumDocument27 pagesCash Flow Statement Wit SumSunay KhaireNo ratings yet
- International Accounting Standard 7 Statement of Cash FlowsDocument8 pagesInternational Accounting Standard 7 Statement of Cash Flowsইবনুল মাইজভাণ্ডারীNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument19 pagesCash Flow StatementRoy YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter: - 8Document16 pagesChapter: - 8Kanu SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows: Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesChapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows: Learning ObjectiveslcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 111Document35 pagesChapter 111rohanfyaz00No ratings yet
- Unit 10 - Cash Flow AnalysisDocument26 pagesUnit 10 - Cash Flow Analysisqwertyytrewq12No ratings yet
- CASH FLOW STATEMENTS-IAS 7 Power Point PresentationsDocument22 pagesCASH FLOW STATEMENTS-IAS 7 Power Point PresentationsTravion LopezNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cash Flow Statement NotesDocument4 pagesAccounting Cash Flow Statement NotesCephas PanguisaNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument7 pagesCash Flow StatementKuila PratyushaNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument2 pagesCash Flow Statementmark_torreonNo ratings yet
- Accountancy Project#Cash Flow Statement# Project 2020-21Document27 pagesAccountancy Project#Cash Flow Statement# Project 2020-21idumban_chandraNo ratings yet
- CASH FLOW StudentsDocument14 pagesCASH FLOW StudentsJirehJohnG.ArafolNo ratings yet
- Cash FlowDocument4 pagesCash FlowHrituparna_Pau_2988No ratings yet
- Activities - Cash Payments To Acquire PropertyDocument2 pagesActivities - Cash Payments To Acquire PropertyPrecious ViterboNo ratings yet
- Karan 2Document17 pagesKaran 2harishNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument14 pagesCash Flow StatementTrending TamizhanNo ratings yet
- CFSDocument20 pagesCFSDipak VakraniNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statements: by CA. Pramod Prabhu. S.HDocument17 pagesCash Flow Statements: by CA. Pramod Prabhu. S.HsonibijuNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statement AnalysisDocument29 pagesCash Flow Statement AnalysisCASAQUIT, IRA LORAINENo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard For Cash FlowDocument17 pagesAccounting Standard For Cash FlowKamal SoniNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument24 pagesCash Flow StatementSHENUNo ratings yet
- Accounting Assignment 2Document4 pagesAccounting Assignment 2Laddie LMNo ratings yet
- Write Up Components and StructuresDocument6 pagesWrite Up Components and StructuresJohn Fort Edwin AmoraNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Accounting PDFDocument11 pagesUnit Ii Accounting PDFMo ToNo ratings yet
- Ias 3Document21 pagesIas 3JyotiNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statements - Pdfshiv4Document10 pagesCash Flow Statements - Pdfshiv4Neha SinhaNo ratings yet
- PAS 7 - Statement of Cash FlowDocument14 pagesPAS 7 - Statement of Cash FlowCarlo Lopez Cantada100% (1)
- T9 Cash FlowDocument16 pagesT9 Cash FlowHD DNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument3 pagesCash Flow StatementMICHELLE MILANANo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard (AS) - 3 Cash Flow StatementsDocument16 pagesAccounting Standard (AS) - 3 Cash Flow StatementsChitra MudaliyarNo ratings yet
- CFAS - PAS 7 - Statement of Cash FlowDocument14 pagesCFAS - PAS 7 - Statement of Cash FlowCarlo Lopez CantadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Cash FlowsDocument6 pagesChapter 12 Cash FlowsgoerginamarquezNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 - 7 KTTCDocument14 pagesChap 4 - 7 KTTCQuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis, Gross Profit Analysis, Basic Earnings Per Share and Diluted Earnings Per ShareDocument135 pagesCash Flow Analysis, Gross Profit Analysis, Basic Earnings Per Share and Diluted Earnings Per ShareMariel de Lara100% (2)
- (Ana) Slide 1: What Is A Cash Flow Statement?Document4 pages(Ana) Slide 1: What Is A Cash Flow Statement?ketiNo ratings yet
- Finacc 2 IvDocument36 pagesFinacc 2 IvMarielle De LeonNo ratings yet
- Of Cash and Which Are Subject To An Insignificant Risk of Changes in ValueDocument2 pagesOf Cash and Which Are Subject To An Insignificant Risk of Changes in ValueJMClosedNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Cash Flow StatementDocument13 pagesMicrosoft Word - Cash Flow StatementAshishNo ratings yet
- Operating ActivitiesDocument3 pagesOperating Activitiesah7anNo ratings yet
- Gist On AS 3 - Cash FlowDocument3 pagesGist On AS 3 - Cash FlowselvikpNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis: Jerisse J. ParajesDocument15 pagesCash Flow Analysis: Jerisse J. ParajesLileth Lastra QuiridoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard (AS) - 3: Cash Flow Statements - Pratap Karmokar (ACA)Document20 pagesAccounting Standard (AS) - 3: Cash Flow Statements - Pratap Karmokar (ACA)Jasmeen GhaiNo ratings yet
- Statemet of Cash FlowDocument14 pagesStatemet of Cash FlowfatahkaryadiNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statements: Deepti Gurvinder Jitender Niraj PalakDocument29 pagesCash Flow Statements: Deepti Gurvinder Jitender Niraj PalakPalak GoelNo ratings yet
- FFS and CFSDocument28 pagesFFS and CFSAnuj DhamaNo ratings yet
- Cash ManagementDocument8 pagesCash ManagementsujkubvsNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statement-ShortDocument33 pagesCash Flow Statement-Shortadam jamesNo ratings yet
- Cahs Flow StatementDocument18 pagesCahs Flow Statementtaniya17No ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Basic Cost Concepts: Cost - Volume - Profit (CVP) AnalysisDocument2 pagesBasic Cost Concepts: Cost - Volume - Profit (CVP) Analysisashishdbg2008No ratings yet
- Accounting Equation Questions For PracticeDocument3 pagesAccounting Equation Questions For Practiceashishdbg2008No ratings yet
- Understanding Financial Statements: Classification of AccountsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Financial Statements: Classification of Accountsashishdbg2008No ratings yet
- Basic Cost Concepts: Cost - Volume - Profit (CVP) AnalysisDocument2 pagesBasic Cost Concepts: Cost - Volume - Profit (CVP) Analysisashishdbg2008No ratings yet
- The Theory and Practice of Space and Assortment Optimization FINALDocument46 pagesThe Theory and Practice of Space and Assortment Optimization FINALMariana BalanNo ratings yet
- Operations Research AssignmentDocument11 pagesOperations Research Assignmentashishdbg2008No ratings yet