Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Markets: Specific Roles of Financial Institutions
Financial Markets: Specific Roles of Financial Institutions
Uploaded by
Viktoria BorgoniaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Financial Markets: Specific Roles of Financial Institutions
Financial Markets: Specific Roles of Financial Institutions
Uploaded by
Viktoria BorgoniaCopyright:
Available Formats
BORGONIA,VIKTORIA VENICE
3030
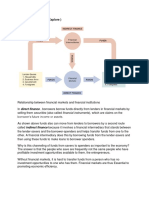
OVERVIEW OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Financial markets
-are imperfect
-there is information asymmetry therefore, risk is high
-because they are imperfect, we need FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
-they resolve the imperfections of the financial markets
-they accept FUNDS from the SURPLUS UNITS and channel these funds to the DEFICIT UNITS
-when it is time for the DEFICIT UNITS to repay, they channel this back to the SURPLUS UNITS to
give them back the return
-in effect, when the investors and borrowers meet, the financial institutions act as an
INTERMEDIARY so there is an INDIRECT TRANSFER
-ROLE: Institutions that perform the essential function of channeling funds from those with
surplus funds to those with shortage of funds
Specific Roles of Financial Institutions
They offer deposit accounts that can accommodate the amount and liquidity
characteristics desired by most surplus units
They repackage funds received from deposits to provide loans of the size and maturity
desired by deficit units
They accept the risk on loans provided
They have more expertise than individual surplus units in evaluating the
creditworthiness of deficit units
They diversify their loans among numerous deficit units and therefore can absorb
defaulted loans better than individual surplus units could
Unique economic functions
1. MONITORING COSTS
Financial institutions pool the resources of small savers, and because they
intermediate between savers and borrowers of all sizes, they can collect
information about deficit units at a relatively low average cost.
2. LIQUIDITY ANN PRICE RISK
By pooling savings, financial institutions supply liquidity to the financial markets.
The size of financial institutions also put them in a better position to lessen price
risk.
3. TRANSACTION COSTS
This is an example of economies of scale. This simply means that financial
institutions have a cost advantage because it represents many savers and
borrowers.
4. MATURITY INTERMEDIATION
Financial institutions can better bear the risk of mismatching their assets and
their liabilities. This means that financial institutions can afford to have liabilities
which are current (i.e. deposits from savers) & assets that are non current (i.e.
loans receivable from borrowers). This is because their sources of funds are as
varied as their users of funds.
5. DENOMINATION INTER MEDIATION
Financial institutions such as mutual funds allow small investors to overcome
constraints to buying assets imposed by large minimum denomination size.
Services provided that benefit the overall company
1. MONEY SUPPLY TRANSMISSION
Depository financial institutions channel the effects of monetary policies to the
entire financial system and economy.
2. CREDIT ALLOCATION
Financial institutions are often viewed as a major source of financing for deficit
units.
3. INTERGENERATIONAL WEALTH TRANSFER
This service is particularly true for insurance companies and pension funds,
which provides savers with the ability to transfer wealth from one generation to
another.
4. PAYMENT SERVICES
The efficiency with which depository institutions provide payment services
directly benefits the economy.
You might also like
- The Coming Perfect Storm - John Paul JacksonDocument27 pagesThe Coming Perfect Storm - John Paul JacksonMSMolla96% (25)
- Cost Benefit AnalysisDocument5 pagesCost Benefit AnalysisDEEPAK GROVERNo ratings yet
- Financial IntermediariesDocument11 pagesFinancial IntermediariesrachealllNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets, Institutions, and InstrumentsDocument58 pagesFinancial Markets, Institutions, and InstrumentsDaniela MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Financial InstitutionsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - Financial InstitutionssleshiNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Financial MarketsDocument9 pagesAssignment - Financial MarketsTaruntej Singh100% (3)
- Case - Stuart Injection Molding CompanyDocument1 pageCase - Stuart Injection Molding CompanyViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Union Gaming Feasibility StudyDocument51 pagesUnion Gaming Feasibility StudyAnn DwyerNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic Developmentrevathi alekhya80% (10)
- Overview of The Financial SystemDocument46 pagesOverview of The Financial SystemAhmad Rahhal100% (1)
- Post Merger IntegrationDocument19 pagesPost Merger IntegrationvvvmmmyyyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Pure and Conditional ObligationDocument37 pagesLesson 3 Pure and Conditional ObligationJoseph Santos GacayanNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 - PT SugusDocument12 pagesTugas 1 - PT SugusFarizal WahyuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Basics of Financial MarketsDocument46 pagesLecture 1 - Basics of Financial MarketsNitesh BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Bachrach vs. Seifert and ElianoffDocument2 pagesBachrach vs. Seifert and ElianoffaceamulongNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Overview of Financial InstitutionsDocument1 pageNotes On The Overview of Financial InstitutionsjeanneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial IntermediationDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Financial IntermediationbugmenomoreNo ratings yet
- Financial EnvironmentDocument30 pagesFinancial EnvironmentIan TattaoNo ratings yet
- CH2@Financial InstitutionsDocument10 pagesCH2@Financial Institutionstamiratg24No ratings yet
- Function of Financial Intermediaries PDFDocument29 pagesFunction of Financial Intermediaries PDFOliwaOrdanezaNo ratings yet
- Finmar NotesDocument5 pagesFinmar NotesariannejonesmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2desktopmarsNo ratings yet
- Money Banking Chapter 5Document12 pagesMoney Banking Chapter 5ebsa ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Financial Intermediaries and Other ParticipantsDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Financial Intermediaries and Other ParticipantsWill De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Financial: IntermediariesDocument50 pagesFinancial: IntermediariesVirly VizcarraNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Lecture Notes (Jeff Madura)Document5 pagesMODULE 2 Lecture Notes (Jeff Madura)Romen CenizaNo ratings yet
- CFI 321 Lesson 3 June 2023Document3 pagesCFI 321 Lesson 3 June 2023nyambura jacklineNo ratings yet
- Financial Intermediaries PDFDocument44 pagesFinancial Intermediaries PDFKriztel CuñadoNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document36 pagesCH 1OmerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2Olana SufiyanNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions in The Financial SystemDocument15 pagesFinancial Institutions in The Financial SystemNigussie Berhanu100% (1)
- The Kenyan Financial SystemDocument90 pagesThe Kenyan Financial SystemBondoobiero87% (15)
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2Lencho MusaNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets Lesson 4Document4 pagesCapital Markets Lesson 4Jane AtendidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1tamirat tadeseNo ratings yet
- BBMF2013 Tutorial Answers Chapter 2 Financial EnvironmentDocument3 pagesBBMF2013 Tutorial Answers Chapter 2 Financial Environmentmathisfun.malaysiaNo ratings yet
- Financial Institution and MarketDocument52 pagesFinancial Institution and Marketsabit hussenNo ratings yet
- ACC 212 - Chapter 1Document14 pagesACC 212 - Chapter 1Jocelyn LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Financial SystemDocument46 pagesOverview of The Financial SystemMehdi SamNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2powerpointDocument33 pagesCHAPTER 2powerpointMintayto TebekaNo ratings yet
- Without Financial InstitutionsDocument2 pagesWithout Financial InstitutionsLevi Emmanuel Veloso BravoNo ratings yet
- Financial IntermediaryDocument10 pagesFinancial Intermediaryalajar opticalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1xyzNo ratings yet
- Financial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesDocument3 pagesFinancial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesRishikaysh KaakandikarNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 FRMDocument11 pagesBab 1 FRMartaninditaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - The Financial SystemDocument6 pagesWeek 1 - The Financial SystemKhen CaballesNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument7 pagesFinancial InstitutionsSteven SalehNo ratings yet
- Fin Chapter ThreeDocument15 pagesFin Chapter Threeyihun0521No ratings yet
- Overview of The Financial System PDFDocument33 pagesOverview of The Financial System PDFFlorence Joy AbkilanNo ratings yet
- Finman 4Document11 pagesFinman 4Karen Tapnio VillamartinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Financial Institutions in The Financial SystemDocument21 pagesChapter 2-Financial Institutions in The Financial SystemKalkayeNo ratings yet
- Christiene P. Schwandner: Financial Sector DefinedDocument4 pagesChristiene P. Schwandner: Financial Sector DefinedGladys Gaccion OpitzNo ratings yet
- BBA FMI Unit 1 - NoDocument31 pagesBBA FMI Unit 1 - NoRuhani AroraNo ratings yet
- FinMar Module2Document58 pagesFinMar Module2Kent CabreraNo ratings yet
- Function of Financial MarketsDocument6 pagesFunction of Financial MarketsChristian FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document25 pagesChapter 4Sakilah ArbaniNo ratings yet
- Fiim S02Document45 pagesFiim S02Ali MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Lending and Borrowing in The Financial System (Part I)Document6 pagesLesson 4: Lending and Borrowing in The Financial System (Part I)Jamille Rose PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Suppliers of FundsDocument2 pagesSuppliers of FundsShandyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Function of Financial IntermediariesDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 - Function of Financial IntermediariesJea Ann CariñozaNo ratings yet
- IFS - Chapter 4Document28 pagesIFS - Chapter 4riashahNo ratings yet
- What Is A Financial Intermediary (Final)Document6 pagesWhat Is A Financial Intermediary (Final)Mark PlancaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Market Participants and Financial InnovationDocument52 pagesOverview of Market Participants and Financial Innovationlinda zyongweNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument14 pagesDebre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- FMI REPORTING Group 1Document18 pagesFMI REPORTING Group 1Stephanie DesembranaNo ratings yet
- Trust Funds: Hometown Investments and Mutual Funds for BeginnersFrom EverandTrust Funds: Hometown Investments and Mutual Funds for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Resume Workbook-Cariño FinishedDocument6 pagesResume Workbook-Cariño FinishedViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Agency: DAV's Personal NotesDocument26 pagesAgency: DAV's Personal NotesViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- BORGONIA Stuart Injection Molding CompanyDocument1 pageBORGONIA Stuart Injection Molding CompanyViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Parental Consent: VIKTORIA VENICE Y. BORGONIA of BSA-2 Block 6, Give Our Permission For OurDocument1 pageParental Consent: VIKTORIA VENICE Y. BORGONIA of BSA-2 Block 6, Give Our Permission For OurViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Borgonia, Viktoria Venice 3099: Application 5-Design For Quality and Product ExcellenceDocument2 pagesBorgonia, Viktoria Venice 3099: Application 5-Design For Quality and Product ExcellenceViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Notes in Agency (Second Part)Document6 pagesNotes in Agency (Second Part)Viktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Golden Plaza HotelDocument1 pageGolden Plaza HotelViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Approach The Tailor For Sizing PAY Downpayment To The Cashier Keep The ReceiptDocument1 pageApproach The Tailor For Sizing PAY Downpayment To The Cashier Keep The ReceiptViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Money Market Securities - Securities Which Are Short TermDocument2 pagesMoney Market Securities - Securities Which Are Short TermViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Stocks Shares Total Cost Market Value Profit Blue Chip? Cyclical/ Defensive/Other? Capitalization?Document1 pageStocks Shares Total Cost Market Value Profit Blue Chip? Cyclical/ Defensive/Other? Capitalization?Viktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Fin Markets - BorgoniaDocument2 pagesFin Markets - BorgoniaViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Types and Risk - BorgoniaDocument2 pagesTypes and Risk - BorgoniaViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Om Case - Mercantile StoresDocument1 pageOm Case - Mercantile StoresViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- SAVETHEEDUCATIONLESSCHILDRENDocument1 pageSAVETHEEDUCATIONLESSCHILDRENViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document2 pagesCase Study 1Viktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Overview of Financial SystemDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Overview of Financial SystemViktoria BorgoniaNo ratings yet
- A Present Economic Resource Controlled by The Entity As A Result of Past EventsDocument11 pagesA Present Economic Resource Controlled by The Entity As A Result of Past EventsValeria PetrovNo ratings yet
- PFRS For SMEs - Summary NotesDocument5 pagesPFRS For SMEs - Summary NotesMaha Bianca Charisma CastroNo ratings yet
- Report Piper Sandler On QualcommDocument9 pagesReport Piper Sandler On QualcommLuigi NocitaNo ratings yet
- GLCA DA MS Excel HBFC Project Modified-1Document3 pagesGLCA DA MS Excel HBFC Project Modified-1Subhan Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Nomura Initiaties GoldDocument105 pagesNomura Initiaties Goldsovereign01No ratings yet
- The Effect of Debt Capacity On Firms Growth - CompletedDocument10 pagesThe Effect of Debt Capacity On Firms Growth - CompletedThanh Xuân100% (1)
- Diy-Exercises (Questionnaires)Document31 pagesDiy-Exercises (Questionnaires)May RamosNo ratings yet
- DonorsDocument11 pagesDonorsboniglai50% (1)
- The University of Lahore: Regular Fee VoucherDocument1 pageThe University of Lahore: Regular Fee VoucherDure ShehwarNo ratings yet
- Cases 9 & 10 Aquintey Vs Tibong and Vda de Jayme Vs CADocument3 pagesCases 9 & 10 Aquintey Vs Tibong and Vda de Jayme Vs CAColeenNo ratings yet
- QutotionDocument1 pageQutotionmanishsngh24No ratings yet
- Best Unit Trust Investment Plans in Malaysia - Compare & ApplyDocument5 pagesBest Unit Trust Investment Plans in Malaysia - Compare & Applysara finaNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics & Social Responsibilities: Lesson 1.1Document15 pagesBusiness Ethics & Social Responsibilities: Lesson 1.1Aurea Breanna PabloNo ratings yet
- Paper 18: Corporate Financial Reporting (CFR) 100 MarksDocument3 pagesPaper 18: Corporate Financial Reporting (CFR) 100 MarksSridhanyas kitchenNo ratings yet
- A Statement From The Family of Anshu Jain 13 August 2022Document2 pagesA Statement From The Family of Anshu Jain 13 August 2022Swam T WNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard Notes by Anand R. BhangariyaDocument96 pagesAccounting Standard Notes by Anand R. BhangariyaSanjana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Financing Decision (FIN 502) MBA Kathmandu University School of ManagementDocument13 pagesCorporate Financing Decision (FIN 502) MBA Kathmandu University School of ManagementShreeya SigdelNo ratings yet
- The Blockchain RevolutionDocument27 pagesThe Blockchain RevolutionAlaa' Deen ManasraNo ratings yet
- Blue Moon Hotel Quezon, City: Guest Registration FormDocument2 pagesBlue Moon Hotel Quezon, City: Guest Registration FormMary Carol FabiculanaNo ratings yet
- Slides of Internship Report NBPDocument51 pagesSlides of Internship Report NBPUmm E MaryamNo ratings yet
- Birla Sun Life T-20 Fund: Scheme Information DocumentDocument41 pagesBirla Sun Life T-20 Fund: Scheme Information DocumentSatya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Compendium PDIC Final 2013Document232 pagesEbook Compendium PDIC Final 2013Raymond VallejoNo ratings yet
- Niti Ayaog Test of Implied RepealDocument12 pagesNiti Ayaog Test of Implied RepealparthNo ratings yet