Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SER Plagiarism Report
Uploaded by
mayankOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SER Plagiarism Report
Uploaded by
mayankCopyright:
Available Formats
Plagiarism Scan Report
Report Generation Date: July 19,2020 Words: 1986 Characters: 12260
Exclude URL :
28% 72%
Plagiarism Unique
28 71
Plagiarized Sentences Unique Sentences
Content Checked for Plagiarism
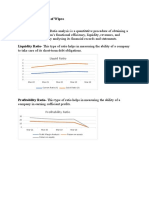
RATIO ANALYSIS Ratio analysis is a process of determining and interpreting relationships between the items of
financial statements to provide a meaningful understanding of the performance and financial position of an
enterprise. Thus it is a technique of analyzing the financial statements by computing ratios. 1. Liquidity Ratios-
liquidity ratios demonstrate a company’s ability to pay its current obligations. In other words, they relate to the
availability of cash and other assets to cover account payables, short-term debt and other liabilities. Common
liquidity ratio includes the following: Current Ratio: - Current ratio is a relationship of current assets and current
liabilities and is computed to assess the short term financial position of the enterprise i.e. company’s ability to meet
its short financial obligation. Ideal current is 2:1. Table 1 YEAR MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19
CURRENT RATIO 2.22 2.3 2.35 2.37 2.67 Chart 1 2.22 2.3 2.35 2.37 2.67 MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18
MARCH,19 CURRENT RATIO CURRENT RATIO 23 Interpretation: - Company’s current ratio is increasing year over year
and it stood at 2.67 in FY2019 and showing good shine. The number should be above 1, and it’s usually a sign of
strength if it exceeds 2. Increasing current ratio shows company’s better capacity to meet its current obligation. This
ratio shows short term financial soundness of company. Quick ratio: - The acid test ratio is a more severe and
stringent test of a firm’s ability to pay its short term obligations as and when they become due. Quick ratio is a
relationship of liquid assets with current liabilities and is computed to assess the short term liquidity of enterprise. It
is also known as acid test ratio or liquidity ratio. Ideal quick ratio is 1:1. Table 2 YEAR MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17
MARCH,18 MARCH,19 QUICK RATIO 2.2 2.28 2.33 2.35 2.65 Chart 2 2.2 2.28 2.33 2.35 2.65 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 MARCH,15
MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 QUICK RATIO QUICK RATIO 24 Interpretation: - Company’s quick ratio is
increasing year over year and stood at 2.65 in FY2019. It is more than its standard ratio every year. It means
company’s liquid assets is more than current liabilities for all the five years and firm is in position to meet its
immediate obligation in all years. It assesses the short term solvency of company. This ratio is an indicator of short
term debt paying capacity of company. 2. Efficiency Ratios- Efficiency ratios are also known as activity financial ratios,
are used to measure how well a company utilizing its assets and resources. Efficiency ratios may be also termed as
turnover ratios or activity ratios. Common efficiency ratios include: Asset turnover ratio: - The asset turnover ratio is
an efficiency ratio that measures a company’s ability to generate sales from its assets by comparing net sales with
average total assets. In other words, this ratio shows how efficiently a company can use its assets to generate sales.
Table 3 YEAR MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 ASSET TURNOVER RATIO 80.42 71.15 70.2 71.98
71.17 Chart 3 80.42 71.15 70.2 71.98 71.17 64 66 68 70 72 74 76 78 80 82 MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18
MARCH,19 ASSET TURNOVER RATIO (%) ASSET TURNOVER RATIO (%) 25 Interpretation: - After observing the figures,
Asset turnover ratio is fluctuating. It is highest during FY15 as 80.42 and then it declines and stood at 70.2 during
FY17 and then it slightly increases in FY18 and again slightly declines in FY19 and stood 71.17. It is very obvious that
higher turnover ratio is preferred to reflect a better state of affairs at the company. Inventory turnover ratio: -
Inventory turnover ratio establishes relationship between cost of revenue from operations, i.e., cost of goods sold
and average inventory carried during that period. It measures how many times an enterprise sells and replaces its
inventory, i.e., how many times inventory was converted into sales during the period. Table 4 YEAR MARCH,15
MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO 96.83 95.07 141.63 161.68 149.38 Chart 4
96.83 95.07 141.63 161.68 149.38 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18
MARCH,19 INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO 26 Interpretation: - In FY15 ITR was 96.83 and
in FY16 it slightly decreases and then it increasing in next two financial years and stood at 161.68. it is highest in FY18
because percent change in sales is 1.74 and percent change in inventory is 13.92. it is deteriorated in FY19 up to
149.38 as compared to FY18. 3. Leverage Ratio- Leverage ratio measures the amount of capital that comes from debt.
In other words, leverage financial ratios are used to evaluate a company’ debt levels. It indicates whether a
company’s cash flow is sufficient to meet its short and long term liability. Common leverage ratios include the
following: Interest coverage ratio: - The interest coverage ratio is a debt ratio used to measure of company’s ability to
meet its interest payments on its outstanding debts. The ratio establishes the relationship between net profit before
interest and tax and interest on long term debts. Table 5 YEAR MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19
INTEREST COVERAGE RATIO 33.08 21.59 19.58 18.57 16.66 Chart 5 33.08 21.59 19.58 18.57 16.66 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 INTEREST COVERAGE RATIO(%) INTEREST COVERAGE RATIO(%)
27 Interpretation: - After observing the figures, it shows that company’s interest coverage ratio is declining year on
year. It is highest during FY15 as 33.08 and after that deteriorated and stood at 16.66 during FY19. As the figure shows
interest coverage ratio is decline. It means company may be unable to pay its debts. Higher interest coverage ratio is
considered better for the lenders as it means higher safety of margin. Debt to equity ratio: - Debt to equity ratio is
computed to assess long term financial soundness of the enterprise. The ratio expresses the relationship between
external equities, i.e., external debts and internal equities, i.e., shareholder funds of the enterprise. External equities
or external debts are liabilities of the enterprise to outsiders. Table 6 YEAR MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17
MARCH,18 MARCH,19 DEBT TO EQUITY 0.21 0.26 0.26 0.26 0.17 Chart 6 Interpretation: - The ratio suggests the claims of
creditors and owners over the assets of the company. Debt to equity ratio was 0.21 in the FY15 after that it increases
and remains constant for next three years. In FY19, it declines and stood at 01.7. 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 MARCH,15
MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 0.21 0.26 0.26 0.26 0.17 DEBT TO EQUITY DEBT TO EQUITY 28 4. Profitability
Ratios- Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate income relative to revenue, balance sheet assets,
operating costs and equity. Common profitability ratios include the following: I. Profitability ratios related to sales II.
Profitability ratios related to overall return on investments III. Profitability ratios related to analysis from owner’s
point of view IV. Profitability ratios related to valuation Profitability ratios related to sales Gross profit ratio: - Gross
profit ratio establishes the relationship of gross profit and revenue from operations, i.e., net sales of an enterprise.
This ratio is computed by dividing gross profit by the revenue from operations, i.e., net sales and multiplied by 100.
Any fluctuation in gross profit is the result of a change either in revenue from operations or cost of revenue from
operations or cost of goods sold or both. Thus, this ratio shows the average margin on good sold. Table 7 YEAR
MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 GROSS PROFIT MARGIN (%) 27.15 26.43 25.14 23.74 24.11 Chart 7
27.15 26.43 25.14 23.74 24.11 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 GROSS PROFIT
MARGIN (%) GROSS PROFIT MARGIN (%) 29 Interpretation: - Gross profit margin was 27.15 in FY15 and thereafter it
starts decline and stood at 23.74 in FY18. The reason of declining margin may be the higher cost of goods sold. After
FY18 it is slightly increased. This ratio indicates the relationship between gross profit and net sales. Higher the ratio,
lower the cost of goods sold. Operating ratio: - Operating ratio is computed to establish relationship between
operating costs and revenue from operations, i.e., net sales. It shows the proportion of cost of revenue from
operation or cost of goods sold and operating expenses (operating cost) to revenue from operations, i.e., net sales.
Table 8 YEAR MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 OPERATING MARGIN (%) 24.65 23.51 20.98 19.86
20.81 Chart 8 Interpretation: - Operating margin slightly declines every year from FY15 to FY18 and then it starts
increasing in FY19. A decline in the operating ratio, is better because it means higher margin, and thus, more profit.
This ratio is calculated to assess the operational efficiency of business. 0 5 10 15 20 25 MARCH,15 MARCH,16
MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 24.65 23.51 20.98 19.86 20.81 OPERATING MARGIN (%) OPERATING MARGIN (%) 30 Net
profit ratio: - Net profit ratio is also termed as sales margin ratio or profit margin ratio or net profit to sales ratio. This
ratio reveals the firm’s overall efficiency in operating the business. Net profit ratio establishes the relationship
between net profit and revenue from operations, i.e., net sales. It shows the percentage of net profit earned on
revenue from operations. Table 9 YEAR MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 NET PROFIT MARGIN
(%) 18.55 17.47 15.36 14.68 15.28 Chart 9 Interpretation: - Shareholders look at net profit margin closely because it
shows how good a company is at converting revenue into profits available for shareholders. Net profit ratio
continuously declines and stood at 14.68 in FY18 and after that in FY19 it starts increasing. Declining ratio indicates
low efficiency of business. Higher the net profit ratio, better the business. It indicates overall efficiency of company.
18.55 17.47 15.36 14.68 15.28 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 NET
PROFIT MARGIN (%) NET PROFIT MARGIN (%) 31 Profitability ratios related to overall return on investments Return on
Net worth: - Return on net worth is a ratio developed from the perspective of the investor and not the company. By
looking at this, the investor sees if the entire net profit was passed on to him, how much return he would be getting.
It explains the efficiency of the stakeholders’ capital to generate profit. Table 10 YEARS MARCH,15 MARCH,16
MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 RETURN ON NETWORTH/EQUITY(%) 23.34 19.3 16.43 16.69 15.95 Chart 10
Interpretation: -ROE is declining year over year from FY15 to 19. It is declining may be because of increasing in share
capital. Declining ROE indicates the company is becoming less efficient at increasing shareholders value. Return on
capital employed: - Return on capital employed ratio measures a relationship between profit and capital employed.
This ratio is also called as Return on Investment ratio. The term return means profit or net profits. The term capital
employed means total investments made in the business. 0 5 10 15 20 25 MARCH,15 MARCH,16 MARCH,17 MARCH,18
MARCH,19 23.34 19.3 16.43 16.69 15.95 RETURN ON NETWORTH/EQUITY(%) 32 Table 11 YEARS MARCH,15 MARCH,16
MARCH,17 MARCH,18 MARCH,19 RETURN ON CAPITAL EMPLOYED (%) 22.24 17.75 20.76 19.91 19.97 Chart 11
Interpretation: -It assess the overall performance of company. From the above observation it can be seen that ratio is
fluctuating. In FY15 the ratio was highest as 22.24 and in FY16 it was declined and stood at 17.75 because company’s
total assets increased 23% compared to sales. After that in FY17 it starts increasing and in next two years i.e., FY18
and 19 it is declined. Return on Assets: - Return on assets (ROA) is an indicator of how profitable a company is
relative to its total assets. ROA gives a manager, investor or analysts an idea as to how efficient a company’s
management is at using its assets to generate earnings. Higher ROA indicates more asset efficiency. Return on
assets is di
Sources
Ratio Analysis Formulas, Objectives, Limitation and Advantages
25%
https://www.toppr.com/guides/principles-and-practices-of-accounting/accounting-ratios/ratio-analysis/
Financial Ratio Analysis I.pdf - Course Hero
... relationships between the items of financial statements to provide a meaningful understan 25%
ding of the performance and financial position of an enterprise.
https://www.coursehero.com/forgot_password.php/file/31581574/Financial-Ratio-Analysis-Ipdf/
twitter.docx - Aliya Yesdauletova ITM-141 Financial Ratios ...
In other words, they relate to the availability of cash and other assets to cover accounts paya 25%
ble, short-term debt, and other liabilities. All small businesses ...
https://www.coursehero.com/file/27299260/twitterdocx/
1. Liquidity Ratio(short- term solvency) by melvita pinto on ...
Current ratio is a realtionship of current assets and current liabilities and is computed to asse 13%
ss the short term financial position of the enterprise. It means current ...
https://prezi.com/twk3yloswsjb/1-liquidity-ratioshort-term-solvency/
A company's ability to meet its short-term financial obligations ...
13%
https://www.examveda.com/a-companys-ability-to-meet-its-short-term-financial-obligations-is-measured-
by-which-of-the-following-categories-33543/
Chapter 9 ratio analysis - SlideShare
Dec 12, 2016 - The acid test ratio is a more severe and stringent test of a firm's ability to pay its 9%
short-term obligations 'as and when they become due.
https://www.slideshare.net/KowshikChakraborty/chapter-9-ratio-analysis-70041496
The market price of a firms stock represents the assessment of all ...
B) Liquid Ratio Liquidity Ratio is a relationship of liquid assets with current liabilities and is com 7%
puted to assess the short- term liquidity of the enterprise in its ...
https://www.coursehero.com/file/p3sd6veg/The-market-price-of-a-firms-stock-represents-the-assessme
nt-of-all-market/
Givia Pty Limited and Bangarie Investments Pty limited Craig ...
Quick ratio: It is also known as Acid test ratio or Liquidity ratio. Quick ratio= (Current Assets-Inv 7%
entory-prepaid expenses) / Current liabilities Quick ratio of Xero ...
https://www.coursehero.com/file/p2kih7l/Givia-Pty-Limited-and-Bangarie-Investments-Pty-limited-Craig-
Winkler-holds-1043/
Asset Turnover Ratio-effeciancy ratio - Course Hero
Asset Turnover Ratio The asset turnover ratio is an efficiency ratio that measures a company' 5%
s ability to generate sales from its assets by comparing net sales ...
https://www.coursehero.com/file/15253953/Asset-Turnover-Ratio-effeciancy-ratio/
Asset Turnover Ratio | Analysis | Formula | Example
The asset turnover ratio is an efficiency ratio that measures a company's ability to generate s 8%
ales from its assets by comparing net sales with average total assets. In other words, this ratio
shows how efficiently a company can use its assets to generate sales.
https://www.myaccountingcourse.com/financial-ratios/asset-turnover-ratio
Ratio Analysis | Dividend | Stocks - Scribd
Current Assets Turnover Ratio Inventory Turnover Ratio Inventory turnover ratio establishes r 4%
elationship between the cost of goods sold during a given period ...
https://pt.scribd.com/document/73462704/Ratio-Analysis
Financial Ratios - Complete List and Guide to All Financial ...
In other words, leverage financial ratios are used to evaluate a company's debt levels. Comm 3%
on leverage ratios include the following: The debt ratioDebt to Asset ...
https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/financial-ratios/
Finance Departmental Finals Reviewer Flashcards | Quizlet
It indicates whether a company's cash flow is sufficient to meet its short-term and long-term 3%
liabilities. The lower a company's solvency ratio, the greater the ...
https://quizlet.com/170750598/finance-departmental-finals-reviewer-flash-cards/
09 chapter 2.pdf - Shodhganga
3%
Interest and Tax and Interest on long term debts. This ratio is of paramount importance for de
benture holders and lenders of long term funds. This ratio is.
https://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/jspui/bitstream/10603/219442/10/09%20chapter%202.pdf
Sustainability antecedents distributions 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 ...
Download scientific diagram | Sustainability antecedents distributions 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 fro 3%
m publication: Scoping research on sustainability performance ...
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sustainability-antecedents-distributions-0-5-10-15-20-25-30-35_fig
2_332922389
Project Report Of Ratio Analysis - PDFSLIDE.NET
Dec 28, 2015 - ... For Year 2010 0.60 For Year 2011 0.55 Interpretation: The ratio suggests the clai 2%
ms of creditors and owners over the assets of the company.
https://pdfslide.net/documents/project-report-of-ratio-analysis.html
Study 33 Terms | Financial Ratios Flashcards | Quizlet
Evaluate the ability of a company to generate income relative to revenue, balance sheet asse 2%
ts, operating costs, and equity. Click again to see term. Tap again ...
https://quizlet.com/445354165/financial-ratios-flash-cards/
Profitability Ratio: Meaning, Formulas, and Types with ... - Toppr
Operating Profit Ratio measures the relationship between Operating Profit and Revenue from
Operations, i.e. Net Sales. We compute Operating Profit Ratio by dividing operating profit by re 2%
venue from operations (Net Sales) and is express in Percentage.
https://www.toppr.com/guides/principles-and-practices-of-accounting/accounting-ratios/profitability-ratio
s/
Current Assets. Current Liabilities. Quick Assets or Liquid ...
Higher the Ratio, lower the cost of goods sold. Gross Profit = Net Sales Cost of Goods Sold. 2. Op 2%
erating Ratio Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses 100 ...
https://docplayer.net/18741565-Current-assets-current-liabilities-quick-assets-or-liquid-assets-current-li
abilities-1-liquidity-ratios-1-current-ratio-formula.html
Page 54 - AFS12
A decline in the operating ratio, is better because it means higher margin, and thus, more pro 2%
fit. The objective of computing this ratio is to determine the ...
https://www.sultan-chand.com/ws/afs12/files/basic-html/page54.html
Formulae of ratios with their brief interpretations - SRCC GBO
This ratio is calculated to assess the liquidity position of the firm. How fast can the firm pay its 2%
present obligations? This ratio is a more rigorous test of liquidity ...
http://srccgbo.edu.in/pdf/2a4737c6d7f24cb36019322fffb7fd27.pdf
WAN0055_EKF_B6202_6202R010_2019.pdf - DSpace VŠB ...
2%
https://dspace.vsb.cz/bitstream/handle/10084/135676/WAN0055_EKF_B6202_6202R010_2019.pdf?se
quence=1
Net Profit Margin Definition & Example - InvestingAnswers.com 2%
https://investinganswers.com/dictionary/n/net-profit-margin
(Profitability Ratios): © The Institute of Chartered Accountants ...
Oct 4, 2019 - (Profitability Ratios related to Overall Return on investments). (a) (Return on Invest 2%
ment, ROI) : ROI. © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of ...
https://www.scribd.com/document/428714025/50154bosfndhm-p1-Cp11-Part4
An Analysis of Financial Factors Affecting the Performance of ...
ROI = Profit before interest and tax Capital employed × 100 Return on Net worth “Return on Net 2%
worth is a ratio developed from the ...
http://search.proquest.com/openview/ca547771bcc9c43738ed7282b80af8e8/1?pq-origsite=gscholar
245453476-Ratio-analysis-Comments.doc | Dividend | Debt
Mar 11, 2020 - From the above observation it can be seen that ratio is fluctuating. For the past 5 2%
years Rate of Return on Investment is ever increasing.
https://www.scribd.com/document/451214186/245453476-Ratio-analysis-Comments-doc
ii Return on assets Return on assets ROA is an indicator of ...
ii Return on assets Return on assets ROA is an indicator of how profitable a from MANUFACTUR 2%
4MM3 at McMaster University.
https://www.coursehero.com/file/p51cdcg/ii-Return-on-assets-Return-on-assets-ROA-is-an-indicator-of-
how-profitable-a/
You might also like
- Cognizant Accounts. FinalDocument9 pagesCognizant Accounts. FinalkrunalNo ratings yet
- ROI, Fixed Asset, Debt Ratios AnalyzedDocument2 pagesROI, Fixed Asset, Debt Ratios AnalyzedhariharanpNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis Report of Raymond FinalDocument14 pagesFinancial Analysis Report of Raymond FinalAnkit prakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18. Accounting PrinciplesDocument49 pagesChapter 18. Accounting PrinciplesNazifa AfrozeNo ratings yet
- I. Comparative Income Statement:: Malaluan, Joselito S. 17-56760 BA-506 1. Comparative Financial StatementsDocument9 pagesI. Comparative Income Statement:: Malaluan, Joselito S. 17-56760 BA-506 1. Comparative Financial StatementsJo MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Assignment - 2Document4 pagesFinancial Management: Assignment - 2Aishu KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Accounts Ail Activity: Nam E: Yas Hvi Rana Class: Xii-C Roll No.:34Document19 pagesAccounts Ail Activity: Nam E: Yas Hvi Rana Class: Xii-C Roll No.:341464Yashvi RanaNo ratings yet
- Financial ratio analysis guideDocument7 pagesFinancial ratio analysis guideYasirNo ratings yet
- FAUE InterpretationDocument4 pagesFAUE InterpretationAnkit PatidarNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of SpicejetDocument6 pagesFinancial Analysis of SpicejetChandan SaigalNo ratings yet
- ACF 361 4 To 6Document157 pagesACF 361 4 To 6edithyemehNo ratings yet
- SER Plagiarism ReportDocument5 pagesSER Plagiarism ReportmayankNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument2 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysisjjay_santosNo ratings yet
- 4 Financial Analysis MethodsDocument20 pages4 Financial Analysis MethodsAddae ClintonNo ratings yet
- FIN 422 (Takibul 18100042)Document53 pagesFIN 422 (Takibul 18100042)Takibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Fsa Assignment Report On Financial Health of Companies by Group 3 Industry - It Companies - Wipro, TCS, Infosys. Ratio AnalysisDocument20 pagesFsa Assignment Report On Financial Health of Companies by Group 3 Industry - It Companies - Wipro, TCS, Infosys. Ratio AnalysissanhithNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Assignment: Financial AccountingDocument7 pagesMid Term Assignment: Financial AccountingKumar VivekNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Fundamentals of Banking: Assignment No: 01 Course Code: BNK-201Document11 pagesCourse Title: Fundamentals of Banking: Assignment No: 01 Course Code: BNK-201TAWHID ARMANNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Financial StatementsAlyssa Camille CabelloNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis InsightsDocument23 pagesRatio Analysis InsightsManoj KumawatNo ratings yet
- Far 1Document13 pagesFar 1Sonu NayakNo ratings yet
- Accouting TermpaperDocument14 pagesAccouting TermpaperSadia NoorNo ratings yet
- Task 2 Strategic Financial Management (20800) Financial AnalysisDocument7 pagesTask 2 Strategic Financial Management (20800) Financial AnalysisperelapelNo ratings yet
- 5.5 - Analysis of Accounts: Business StudiesDocument11 pages5.5 - Analysis of Accounts: Business StudiesUpasana ChaubeNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Asian PaintsDocument34 pagesRatio Analysis of Asian PaintsAmit Pandey25% (4)
- Course Project Week 11,12Document5 pagesCourse Project Week 11,12Nae InsaengNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 and 8 - FINANCIAL STATEMENT AND ANALYSISDocument14 pagesMODULE 7 and 8 - FINANCIAL STATEMENT AND ANALYSISMICHELLE MILANANo ratings yet
- Part C: Figure 1:astrazeneca Financial Position 2021Document11 pagesPart C: Figure 1:astrazeneca Financial Position 2021Unzillah AzharNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Manager: Name of The Student: Student ID: Name of The UniversityDocument12 pagesAccounting For Manager: Name of The Student: Student ID: Name of The Universitykomal singhNo ratings yet
- HOD Assignment 2Document15 pagesHOD Assignment 2KUMARAGURU PONRAJNo ratings yet
- Profitability AnalysisDocument9 pagesProfitability AnalysisBurhan Al MessiNo ratings yet
- Accountancy Project TopicDocument14 pagesAccountancy Project TopicIsha BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument5 pagesRatio AnalysisDharmesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document20 pagesAssignment No.1sarvesh patilNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument24 pagesRatio Analysisrleo_19871982100% (1)
- Profitability Ratio PDFDocument37 pagesProfitability Ratio PDFSiddharth Arora100% (2)
- Financial Statements AnalysisDocument42 pagesFinancial Statements AnalysisSulle DadyNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Asian PaintsDocument19 pagesRatio Analysis of Asian Paintssaran mkNo ratings yet
- Nike Financial Analysis - EditedDocument12 pagesNike Financial Analysis - EditedmosesNo ratings yet
- Financial AnalysisDocument7 pagesFinancial AnalysisReyza Mikaela AngloNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument3 pagesProjectGeetu SachdevNo ratings yet
- 2021 Finance ReportDocument25 pages2021 Finance ReportSanjana SinghNo ratings yet
- Ratio analysisDocument17 pagesRatio analysisgamerfleet211No ratings yet
- Reliance IndustriesDocument16 pagesReliance IndustriesDarshan RNo ratings yet
- Board QuestionsDocument3 pagesBoard Questionspiash246No ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture FSADocument50 pages3rd Lecture FSAUmair KhatriNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Renata Limited PPPDocument32 pagesRatio Analysis of Renata Limited PPPmdnabab0% (1)
- Ratio Analysis Reveals LG Display's Financial PerformanceDocument10 pagesRatio Analysis Reveals LG Display's Financial PerformanceSahal Ahmed SyedNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis Excel Case StudyDocument17 pagesRatio Analysis Excel Case StudyPuran SinghNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of HulDocument11 pagesRatio Analysis of HulRohit SanghviNo ratings yet
- FRA Report: GMR Infrastructure: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument12 pagesFRA Report: GMR Infrastructure: Submitted To: Submitted bySunil KumarNo ratings yet
- PRESENTATION ON Finincial Statement FinalDocument28 pagesPRESENTATION ON Finincial Statement FinalNollecy Takudzwa Bere100% (2)
- Financial Statement Analysis of Fauji Fertilizer Company FFC Vs Engro CorporationDocument6 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis of Fauji Fertilizer Company FFC Vs Engro Corporationqurban balochNo ratings yet
- Linde Bangladesh LTDDocument4 pagesLinde Bangladesh LTDNabil mahmudNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of WiproDocument3 pagesQuantitative Analysis of WiproAditi DaryanNo ratings yet
- Beneish's M-Score: The Detection ofDocument23 pagesBeneish's M-Score: The Detection ofraghavendra_20835414No ratings yet
- Credit Evaluation Process AnalysisDocument73 pagesCredit Evaluation Process AnalysisNeeRaz Kunwar100% (2)
- Case Study Group 9Document8 pagesCase Study Group 9AJ67% (3)
- LearningDocument24 pagesLearningmayankNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Viewers' Behaviour Over Traditional Television Channels and Over Ott Video Platforms in MaharashtraDocument12 pagesComparative Study of Viewers' Behaviour Over Traditional Television Channels and Over Ott Video Platforms in MaharashtraSuhas AvgNo ratings yet
- 1 IiphoneDocument1 page1 IiphonemayankNo ratings yet
- Change: - Your Opinion ?Document10 pagesChange: - Your Opinion ?mayankNo ratings yet
- Membership privacy policyDocument6 pagesMembership privacy policymayankNo ratings yet
- Understanding how human values are shapedDocument11 pagesUnderstanding how human values are shapedmayankNo ratings yet
- Training and Developing Employees: Global Edition 12eDocument47 pagesTraining and Developing Employees: Global Edition 12eRohit Kumar 4170No ratings yet
- Prepared For: Term Paper On Marketing Analysis of PumaDocument38 pagesPrepared For: Term Paper On Marketing Analysis of PumamayankNo ratings yet
- Blueprint of Banking SectorDocument33 pagesBlueprint of Banking SectormayankNo ratings yet
- What Kind of Career Do You Want To Pursue in Future and WhyDocument6 pagesWhat Kind of Career Do You Want To Pursue in Future and WhymayankNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 HRMDocument21 pagesUnit 1 HRMmayankNo ratings yet
- L9 PerceptionDocument23 pagesL9 PerceptionmayankNo ratings yet
- L1L2 OB Models and Challenges in Individual BehaviorDocument22 pagesL1L2 OB Models and Challenges in Individual BehaviormayankNo ratings yet
- L3 Personality Types and TheoriesDocument34 pagesL3 Personality Types and TheoriesmayankNo ratings yet
- LawDocument17 pagesLawmayankNo ratings yet
- L1L2 OB Models and Challenges in Individual BehaviorDocument22 pagesL1L2 OB Models and Challenges in Individual BehaviormayankNo ratings yet
- MGN572 L11 Case Study PDFDocument3 pagesMGN572 L11 Case Study PDFmayankNo ratings yet
- Income Statement QuestionDocument2 pagesIncome Statement QuestionmayankNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument16 pagesMotivationmayankNo ratings yet
- Z ScoreDocument1 pageZ ScoremayankNo ratings yet
- Change: - Your Opinion ?Document10 pagesChange: - Your Opinion ?mayankNo ratings yet
- Trend and RegressionDocument12 pagesTrend and RegressionmayankNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DissonananceDocument16 pagesCognitive DissonanancemayankNo ratings yet
- SOCIAL SKILLS ASSESSMENTDocument12 pagesSOCIAL SKILLS ASSESSMENTmayankNo ratings yet
- Personality Assessment Tutorial 1: Dr. Sunil Msob LPUDocument15 pagesPersonality Assessment Tutorial 1: Dr. Sunil Msob LPUmayankNo ratings yet
- Class Test 2Document14 pagesClass Test 2Jyoti Arvind PathakNo ratings yet
- LearningDocument24 pagesLearningmayankNo ratings yet
- OB Chapter 10 PDFDocument21 pagesOB Chapter 10 PDFmurshid Iqbal100% (1)
- Q1. Find The Odd One Out A) Custodial Model B) Autocratic Model C) Supportive ModelDocument10 pagesQ1. Find The Odd One Out A) Custodial Model B) Autocratic Model C) Supportive ModelmayankNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Employee Management SystemDocument20 pagesProject Report On Employee Management Systemsadsa saiaafgNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - PROJECT Management For Donor Funded Project - Cape Town - 2013 - 2014Document5 pagesCourse Outline - PROJECT Management For Donor Funded Project - Cape Town - 2013 - 2014profession0% (1)
- Test Bank: To AccompanyDocument3 pagesTest Bank: To AccompanyShashwat Chakraborti0% (1)
- Black Book General Insurance 2017Document67 pagesBlack Book General Insurance 2017girish pilse100% (1)
- Final Customer Proje TDocument18 pagesFinal Customer Proje Tpreetiarora891No ratings yet
- Invitation To Bid: General GuidelinesDocument29 pagesInvitation To Bid: General GuidelinesRenier Palma CruzNo ratings yet
- MC QuestionsDocument11 pagesMC QuestionsKatrina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Consumer Perception Towards Amul ProductsDocument10 pagesSynopsis Consumer Perception Towards Amul ProductsMansha BhatNo ratings yet
- Mediation Problem IDocument3 pagesMediation Problem Isukriti shrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Bata India LTD PDFDocument4 pagesBata India LTD PDFparchure123No ratings yet
- Kelompok FGD GPTP 14 Batch 2 (Responses)Document16 pagesKelompok FGD GPTP 14 Batch 2 (Responses)Tia AgustinnNo ratings yet
- Banking Regulations in The PhilippinesDocument36 pagesBanking Regulations in The PhilippinesEmerlyn Charlotte Fonte100% (1)
- Corporate Governance vs. Corporate Crime: S. N. Mahapatra Sanjay PandeyDocument3 pagesCorporate Governance vs. Corporate Crime: S. N. Mahapatra Sanjay PandeyPriyanka TamhankarNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Going The Startup Way Amazon - With QuestionsDocument3 pagesCase Study - Going The Startup Way Amazon - With QuestionsVishal MarhattaNo ratings yet
- Debtors CircularizationDocument7 pagesDebtors Circularizationobezap100% (10)
- Change Management in Hewlett Packard & Role of Carly FiorinaDocument38 pagesChange Management in Hewlett Packard & Role of Carly FiorinaSunil KatalNo ratings yet
- Procurement PolicyDocument7 pagesProcurement Policytess100% (2)
- Trump University - Fortune Without Fear - Real Estate Riches in An Unceertain MarketDocument94 pagesTrump University - Fortune Without Fear - Real Estate Riches in An Unceertain MarketJohn HowardNo ratings yet
- Gujarat IT & ITeS Subsidy SchemeDocument2 pagesGujarat IT & ITeS Subsidy SchemeHardik KapadiaNo ratings yet
- CAT Review Qs PDFDocument4 pagesCAT Review Qs PDFSuy YanghearNo ratings yet
- MuhammadFasieh - KIWI ShoeDocument6 pagesMuhammadFasieh - KIWI ShoeErfan MirxaNo ratings yet
- Certification in Business Data Analytics Handbook: The Iiba® Guide To Pursuing The Iiba®-CbdaDocument7 pagesCertification in Business Data Analytics Handbook: The Iiba® Guide To Pursuing The Iiba®-CbdaJeezNo ratings yet
- Turkish Economy (1980-1989)Document15 pagesTurkish Economy (1980-1989)ademNo ratings yet
- Lenzing Plastics Order Confirmation for PTFE Packing YarnDocument2 pagesLenzing Plastics Order Confirmation for PTFE Packing Yarnirfan dadiNo ratings yet
- HP Delivery Note For Delivery ECF5883192Document4 pagesHP Delivery Note For Delivery ECF5883192always_975382984No ratings yet
- Ms Business AnalyticsDocument1 pageMs Business AnalyticsSaitejNo ratings yet
- Inventory and Cost of Goods Sold (Practice Quiz)Document4 pagesInventory and Cost of Goods Sold (Practice Quiz)Monique100% (1)
- REPORTDocument51 pagesREPORTmalik noman0% (1)
- Wind & Storm Proof UmbrellaDocument17 pagesWind & Storm Proof UmbrellaIbrahim KhanNo ratings yet
- AGDBR-LMS RespShortAnalysis 20230207 061156Document1 pageAGDBR-LMS RespShortAnalysis 20230207 061156ManzoorNo ratings yet
- The Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindFrom EverandThe Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (231)
- Getting to Yes: How to Negotiate Agreement Without Giving InFrom EverandGetting to Yes: How to Negotiate Agreement Without Giving InRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (652)
- I Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)From EverandI Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- How to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)From EverandHow to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanFrom EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (79)
- Bookkeeping: A Beginner’s Guide to Accounting and Bookkeeping for Small BusinessesFrom EverandBookkeeping: A Beginner’s Guide to Accounting and Bookkeeping for Small BusinessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Profit First for Therapists: A Simple Framework for Financial FreedomFrom EverandProfit First for Therapists: A Simple Framework for Financial FreedomNo ratings yet
- Tax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesFrom EverandTax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesNo ratings yet
- Love Your Life Not Theirs: 7 Money Habits for Living the Life You WantFrom EverandLove Your Life Not Theirs: 7 Money Habits for Living the Life You WantRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (146)
- LLC Beginner's Guide: The Most Updated Guide on How to Start, Grow, and Run your Single-Member Limited Liability CompanyFrom EverandLLC Beginner's Guide: The Most Updated Guide on How to Start, Grow, and Run your Single-Member Limited Liability CompanyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Financial Accounting For Dummies: 2nd EditionFrom EverandFinancial Accounting For Dummies: 2nd EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (10)
- Financial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?From EverandFinancial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelFrom Everand7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelNo ratings yet
- The Accounting Game: Learn the Basics of Financial Accounting - As Easy as Running a Lemonade Stand (Basics for Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners)From EverandThe Accounting Game: Learn the Basics of Financial Accounting - As Easy as Running a Lemonade Stand (Basics for Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Accounting 101: From Calculating Revenues and Profits to Determining Assets and Liabilities, an Essential Guide to Accounting BasicsFrom EverandAccounting 101: From Calculating Revenues and Profits to Determining Assets and Liabilities, an Essential Guide to Accounting BasicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- The ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!From EverandThe ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Accounting Principles: Learn The Simple and Effective Methods of Basic Accounting And Bookkeeping Using This comprehensive Guide for Beginners(quick-books,made simple,easy,managerial,finance)From EverandAccounting Principles: Learn The Simple and Effective Methods of Basic Accounting And Bookkeeping Using This comprehensive Guide for Beginners(quick-books,made simple,easy,managerial,finance)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Full Charge Bookkeeping, For the Beginner, Intermediate & Advanced BookkeeperFrom EverandFull Charge Bookkeeping, For the Beginner, Intermediate & Advanced BookkeeperRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Excel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetFrom EverandExcel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetNo ratings yet
- Ledger Legends: A Bookkeeper's Handbook for Financial Success: Navigating the World of Business Finances with ConfidenceFrom EverandLedger Legends: A Bookkeeper's Handbook for Financial Success: Navigating the World of Business Finances with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- NLP:The Essential Handbook for Business: The Essential Handbook for Business: Communication Techniques to Build Relationships, Influence Others, and Achieve Your GoalsFrom EverandNLP:The Essential Handbook for Business: The Essential Handbook for Business: Communication Techniques to Build Relationships, Influence Others, and Achieve Your GoalsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)