Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Enamel Hypoplasia?
Uploaded by
Haha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views3 pagesenamel hypoplasia treatment and prevention
Original Title
enamel hypoplasia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentenamel hypoplasia treatment and prevention
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views3 pagesWhat Is Enamel Hypoplasia?
Uploaded by
Hahaenamel hypoplasia treatment and prevention
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA
WHAT IS ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA?
Enamel Hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is hard but thin and deficient in
amount, caused by defective enamel matrix formation.
Hypoplasia is an enamel deficiency that leaves the teeth vulnerable to damage and decay. It
often takes the form of grooves, pits, or lines within teeth, either across the surface or in
certain spots. Depending on the severity, Enamel hypoplasia can look like a small dent in the
tooth, or take up several teeth throughout the mouth. There can be localized discoloration, or
the entire tooth can turn a dark brown color.
There are two types of causes attributed to Enamel Hypoplasia: Hereditary and Environmental.
HEREDITARY ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA
Often genetic Enamel Hypoplasia means that both the baby teeth and the adult teeth will be
affected. The hereditary defects mean that the enamel is missing one of the three critical
developmental phases: formation, mineralization and maturation. When the creation process is
unable to develop completely, the enamel is either brittle or susceptible to cracks, or soft or
easy to wear down.
In the hereditary condition, the child and the parents have no way to prevent enamel
hypoplasia and will have to treat the tooth or teeth as they start coming in and showing signs of
malformation.
ENVIRONMENTAL ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA
Environmental Enamel Hypoplasia is somewhat preventable in most cases. According to the
European Council on Pediatric Dentistry, environmental factors during early childhood can
affect baby teeth, permanent teeth or both. These events occur in the womb, during delivery
and in the months following birth.
A few causes of Environmental Enamel Hypoplasia include:
1. Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies: particularly vitamins A, C and D.
2. Bacterial and viral infections like syphilis, measles, chickenpox and other illnesses that
causes high fever.
3. A prolonged delivery, prematurity, birth injury
4. Infections that result in long-lasting diarrhea and vomiting.
If the mother suffers from malnutrition or becomes ill with a high fever, she is at high risk of
causing enamel hypoplasia to the infant when they are born.
However, even perfectly healthy infants can suffer from Enamel Hypoplasia as a result of
trauma to the newly developed teeth.
Environmental factors that may cause Enamel Hypoplasia include an array of chemicals and
medications. Chemotherapeutic drugs used in the treatment of childhood malignancies are
implicated in this category, since they inhibit the normal the normal cellular mechanisms
involved in matrix deposition and calcification. Fluoride and tetracycline medications are the
best known causative agents of Enamel Hypoplasia
TREATMENT FOR ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA
The treatment process for enamel hypoplasia varies depending on the severity of the condition
and the age of the child. For light cases where there is only mild discoloration, dentist might
suggest bleaching the affected tooth to make it appear white next to its healthy counterparts.
Some patients may need to have their teeth regularly bleached with hydrogen peroxide after
the initial treatment fades.
For more serious problems, like visible pits or decay, the dentist might drill out the affected
areas and fill in the cavities. This will reduce sensitivity and pain if the enamel Hypoplasia is only
located in a small part of the tooth, but won’t completely solve the problem if the entire tooth
is affected. In that case, the dentist might recommend a more permanent solution, as the
addition of a crown or onlay.
In advanced cases, the tooth may need to be removed altogether and replaced with a bridge or
dental implant. The purpose of the dental implant is to prevent other teeth from shifting to
bridge the gap to aid chewing, resulting in a crooked smile.
ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA PREVENTION
One of the most important factors in treating Enamel Hypoplasia is catching it early. It’s better
for the dentist to spot a sensitive area or fill a small cavity early than to remove the whole tooth
due to extensive decay.
The addition of vitamins A and D can assist in strengthening developing teeth. Patients can
either take vitamin supplements or increase their consumption of milk and green leafy
vegetables.
Enamel Hypoplasia patients need to constantly maintain good oral hygiene to prevent further
decay. Dentist may require patients to come in for additional cleaning throughout the year and
require professional toothpaste and brushes.
REFERENCE
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enamel_hypoplasia
healthline.com/health/enamel-hypoplasia
crest.com/en-us/oral-health/conditions/enamel/enamel-hypoplasia
You might also like
- Dentin Hypersensitivity2 PDFDocument5 pagesDentin Hypersensitivity2 PDFIvan TerresNo ratings yet
- Department of Conservative Dentistry and EndodonticsDocument20 pagesDepartment of Conservative Dentistry and EndodonticsMusthafa KuttikkatoorNo ratings yet
- Basic Level of Dental Resins - Material Science & Technology: 4th Edition, 2nd VersionFrom EverandBasic Level of Dental Resins - Material Science & Technology: 4th Edition, 2nd VersionNo ratings yet
- Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Practical GuideFrom EverandFixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Practical GuideRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- My 3rd Seminar - DentinDocument25 pagesMy 3rd Seminar - DentinJon YorkNo ratings yet
- Silver Diamine Fluoride - A Futuristic Remedy For Caries TerminationDocument5 pagesSilver Diamine Fluoride - A Futuristic Remedy For Caries TerminationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cavity Liners and Bases 2Document9 pagesCavity Liners and Bases 2hp1903No ratings yet
- 7 Kottoor-BiomimeticsDocument11 pages7 Kottoor-BiomimeticsVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Microleakage and NanoleakgeDocument61 pagesMicroleakage and NanoleakgemahaNo ratings yet
- 04 - 003 Dental Luting CementsDocument2 pages04 - 003 Dental Luting CementskaniaNo ratings yet
- Esthetic Crowns For Primary Teeth A Review PDFDocument7 pagesEsthetic Crowns For Primary Teeth A Review PDFSan SanNo ratings yet
- Dental CementDocument12 pagesDental Cementshaniaz19785112No ratings yet
- Dentin EtchingDocument31 pagesDentin EtchingteodoraNo ratings yet
- Biological Properties of Dental Materials 1-General Dentistry / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument76 pagesBiological Properties of Dental Materials 1-General Dentistry / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Irrigation and Intracanal Medicaments - Lecture 2 - LDocument49 pagesIrrigation and Intracanal Medicaments - Lecture 2 - Lshobhana20100% (1)
- Coronoplasty: January 2021Document14 pagesCoronoplasty: January 2021khalisha salsabila100% (1)
- Orthodontic Adhesives / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument137 pagesOrthodontic Adhesives / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Silorane CompztDocument5 pagesSilorane CompztNaila AmanNo ratings yet
- Field Isolation and Moisture ControlDocument39 pagesField Isolation and Moisture ControlDr. Nikhil saran100% (1)
- Calcium Hydroxide in DentistryDocument17 pagesCalcium Hydroxide in DentistryTarek RabiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Aesthetic DentistryDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Aesthetic Dentistryladzville1014860No ratings yet
- Self Applied Topical Fluorides ClassDocument23 pagesSelf Applied Topical Fluorides ClassultraswamyNo ratings yet
- 5 - Calcium Hydroxide Vs Mineral Trioxide Aggregates For Partial Pulpotomy of Permanent Molars With Deep Caries PDFDocument6 pages5 - Calcium Hydroxide Vs Mineral Trioxide Aggregates For Partial Pulpotomy of Permanent Molars With Deep Caries PDFAbdul Rahman AlmishhdanyNo ratings yet
- EnamelDocument9 pagesEnamelhustla7100% (1)
- Cieszynski' Rule of IsometryDocument5 pagesCieszynski' Rule of Isometrynishant_tewari_1No ratings yet
- Estrogenicity of CompositesDocument8 pagesEstrogenicity of CompositesSubhashini RajshekarNo ratings yet
- Dentalcements1 151002150529 Lva1 App6891Document80 pagesDentalcements1 151002150529 Lva1 App6891itsme543210No ratings yet
- Wax PatternDocument34 pagesWax PatternMariam SherifNo ratings yet
- Glass Ionomer Restoration: DefinitionDocument11 pagesGlass Ionomer Restoration: Definitionmohamed saad100% (1)
- Anat of Root Apex - Review ArticleDocument9 pagesAnat of Root Apex - Review ArticleRevathy ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Resin Cememt - 2Document108 pagesResin Cememt - 2Shrinidhi R PoonjaNo ratings yet
- Use of Polyethylene Ribbon To Create A Provisional Fixed Partial DentureDocument4 pagesUse of Polyethylene Ribbon To Create A Provisional Fixed Partial DentureAhmed AbdulazeezNo ratings yet
- Flouride Relessing Material-FinalDocument95 pagesFlouride Relessing Material-FinalDr. Nikhil saranNo ratings yet
- Preliminary ConsiderationsDocument22 pagesPreliminary ConsiderationsDayen LimNo ratings yet
- Modern Dental Ceramics An OverviewDocument6 pagesModern Dental Ceramics An OverviewDilesh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Stress Treatment Theorem For Implant Dentistry: Niranjana R I Year Postgraduate Department of ProsthodonticsDocument43 pagesStress Treatment Theorem For Implant Dentistry: Niranjana R I Year Postgraduate Department of ProsthodonticsNiranjanaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Composite Resins ReviewDocument5 pagesRecent Advances in Composite Resins ReviewChitrang KolawaleNo ratings yet
- Post Insertion InstructionsDocument23 pagesPost Insertion InstructionsAnkita Reddy VallapNo ratings yet
- Intra Canal MedicamentsDocument14 pagesIntra Canal MedicamentsS Noshin ShimiNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument158 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationSutapa Roy100% (1)
- Dentin Bonding Agents - An OverviewDocument4 pagesDentin Bonding Agents - An OverviewIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- 2 - PULPAL, Dental PainDocument10 pages2 - PULPAL, Dental PainAbod NaserNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operative Dentistry by DR - AshrafDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Operative Dentistry by DR - Ashrafyahya100% (1)
- Glass Ionomer CementsDocument8 pagesGlass Ionomer CementsNenaMikiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal DentistDocument8 pagesJurnal DentistAnugrah AztriNo ratings yet
- Restorative ResinsDocument23 pagesRestorative ResinsNaveen Kumar0% (1)
- Effect of Ultrasonic Activation of Endodontic Sealers On Intratubular Penetration and Bond Strength To Root DentinDocument22 pagesEffect of Ultrasonic Activation of Endodontic Sealers On Intratubular Penetration and Bond Strength To Root DentinNajla MohammedNo ratings yet
- Flasking and Dewaxing of Complete DentureDocument10 pagesFlasking and Dewaxing of Complete Dentureyusra tahirNo ratings yet
- Luting CementsDocument13 pagesLuting CementsPanah SalahiNo ratings yet
- Avulsion: DEFINITION: - Tooth Avulsion (Exarticulation) Implies Total Displacement of The ToothDocument39 pagesAvulsion: DEFINITION: - Tooth Avulsion (Exarticulation) Implies Total Displacement of The Toothshailesh_shenoyNo ratings yet
- Pulp Dentin BiologyDocument21 pagesPulp Dentin BiologyCristiane VazNo ratings yet
- Minmal Invasive Dentistry PedoDocument61 pagesMinmal Invasive Dentistry PedoFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- DIAGNOSTIC METHODS (Emphasis On Recent Advances) IN EndodonticsDocument51 pagesDIAGNOSTIC METHODS (Emphasis On Recent Advances) IN EndodonticsKalpesh DeyNo ratings yet
- Dental AdhesionDocument215 pagesDental AdhesionMonica RoopChanderNo ratings yet
- Biologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryDocument25 pagesBiologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryNofal MundathoduNo ratings yet
- Dental Impression Materials and Techniques - ClinicalKeyDocument24 pagesDental Impression Materials and Techniques - ClinicalKeyBavilonia K PaolaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in DentistryDocument2 pagesRecent Advances in DentistrySudarsan SangeethaNo ratings yet
- Method StatementDocument29 pagesMethod StatementZakwan Hisyam100% (1)
- Doctors ListDocument212 pagesDoctors ListSaranya Chandrasekar33% (3)
- Mycotoxin in Food Supply Chain (Peanuts)Document2 pagesMycotoxin in Food Supply Chain (Peanuts)Ghanthimathi GvsNo ratings yet
- 6 Kuliah Liver CirrhosisDocument55 pages6 Kuliah Liver CirrhosisAnonymous vUEDx8100% (1)
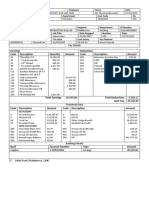
- Pay Details: Earnings Deductions Code Description Quantity Amount Code Description AmountDocument1 pagePay Details: Earnings Deductions Code Description Quantity Amount Code Description AmountVee-kay Vicky KatekaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual PDFDocument68 pagesLab Manual PDFSantino AwetNo ratings yet
- SanMilan Inigo Cycling Physiology and Physiological TestingDocument67 pagesSanMilan Inigo Cycling Physiology and Physiological Testingjesus.clemente.90No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering-II - R2015 - 10-04-2018Document2 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering-II - R2015 - 10-04-201818135A0806 MAKKUVA BHAVYANo ratings yet
- Method Statement (RC Slab)Document3 pagesMethod Statement (RC Slab)group2sd131486% (7)
- Kyocera Fleet Services White Paper: SecurityDocument20 pagesKyocera Fleet Services White Paper: SecurityHoratiu OanaNo ratings yet
- Guideline On Smacna Through Penetration Fire StoppingDocument48 pagesGuideline On Smacna Through Penetration Fire Stoppingwguindy70No ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Notes DR - Mahmoud RamadanDocument83 pagesMaxillofacial Notes DR - Mahmoud Ramadanaziz200775% (4)
- Rules For State Competitions and Iabf Approved TournamentsDocument56 pagesRules For State Competitions and Iabf Approved TournamentsQuality management systems documentsNo ratings yet
- Chia (Salvia Hispanica L.) Oil Stability Study of The Effect of NaturDocument7 pagesChia (Salvia Hispanica L.) Oil Stability Study of The Effect of NaturInta Nur IlmiNo ratings yet
- CBEU Service ConditionsDocument623 pagesCBEU Service ConditionsAtul ModiNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Granular Silica GelDocument3 pagesMSDS - Granular Silica GelLailal HaqimNo ratings yet
- Arsenal Strength Catalog 6.2-1Document41 pagesArsenal Strength Catalog 6.2-1Mohammed NavedNo ratings yet
- 7 UpDocument3 pages7 UpRajeev TripathiNo ratings yet
- NORSOK M-630 Edition 6 Draft For HearingDocument146 pagesNORSOK M-630 Edition 6 Draft For Hearingcaod1712100% (1)
- As ISO 9919-2004 Pulse Oximeters For Medical Use - RequirementsDocument10 pagesAs ISO 9919-2004 Pulse Oximeters For Medical Use - RequirementsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- 5SDD 71B0210Document4 pages5SDD 71B0210Merter TolunNo ratings yet
- Making Creams With Olive M 1000Document28 pagesMaking Creams With Olive M 1000Nicoleta Chiric0% (1)
- The Emom Manual: 25 Kettlebell Conditioning WorkoutsDocument14 pagesThe Emom Manual: 25 Kettlebell Conditioning WorkoutsguilleNo ratings yet
- Benzil PDFDocument5 pagesBenzil PDFAijaz NawazNo ratings yet
- RRC Group D Notification 70812Document11 pagesRRC Group D Notification 70812admin2772No ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure in The Intensive Care Unit: Steven D. Weisbord, M.D., M.Sc. and Paul M. Palevsky, M.DDocument12 pagesAcute Renal Failure in The Intensive Care Unit: Steven D. Weisbord, M.D., M.Sc. and Paul M. Palevsky, M.Dkerm6991No ratings yet
- Bio411 C1Document1 pageBio411 C1Aqiena BalqisNo ratings yet
- Fill The Gaps With The Correct WordsDocument2 pagesFill The Gaps With The Correct WordsAlayza ChangNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletins For Engine Model I0360kb.3Document6 pagesService Bulletins For Engine Model I0360kb.3Randy Johel Cova FlórezNo ratings yet
- Wisconsin Humane Society To Acquire Kenosha's Safe Harbor Humane Society - Press ReleaseDocument3 pagesWisconsin Humane Society To Acquire Kenosha's Safe Harbor Humane Society - Press ReleaseTMJ4 NewsNo ratings yet