Professional Documents
Culture Documents
First Question
Uploaded by
محمد احسان علي باقر ال جاسم الحسيني0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOriginal Title
H5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesFirst Question
Uploaded by
محمد احسان علي باقر ال جاسم الحسينيCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
First question
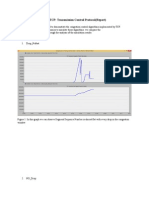
a. TCP slow start is operating in the intervals [1,6] and [23,26].
b. TCP congestion avoidance is operating in the intervals [6,16] and
[17,22].
c. packet loss is identified by a 3 duplicate because congestion window
dose not drop to 1 and the increase has become linearly.
d. packet loss is detected because timeout and congestion window is set to
1.
e. 32.
f. the threshold is 21 during the 18th transmission round.
g. the threshold is 14 during the 24th transmission round.
h. packets 64 – 96 are sent in the 7th transmission round. So packet 70 is
sent in the 7th transmission round.
i. the new values of the ssthresh and congestion window size will be 4 and
7 because (4+3 =7).
Short answers:
1.
Both client and server need to know that they can be connected.
For client: actually, a two-way handshake is enough because it sends to
server and server sends back
For server: three-way handshake is needed since the server needs to
know the message it sends back to client (second message) is
successful. The third message from client proves that the server's
message (second message) is successful so the third message is
needed.
2. Since TCP does not know whether a duplicate ACK is caused by a
lost segment or just a reordering of segments, it waits for a small
number of duplicate ACKs to be received.
It is assumed that if there is just a reordering of the segments, there will
be only one or two duplicate ACKs before the reordered segment is
processed, which will then generate a new ACK. If three or more
duplicate ACKs are received in a row, it is a strong indication that a
segment has been lost.
3. The 2MSL timer makes the client wait for a duration that is enough time
for an ACK to be lost (one MSL) and a FIN to arrive (another MSL). If
during the TIME-WAIT state, a new FIN arrives, the client sends a new
ACK and restarts the 2MSL timer.
BY: MOHAMMED AHSAN ALI;
You might also like
- HW 3Document4 pagesHW 3Ahmed Biggie MajeedNo ratings yet
- TCP 3-Way HandshakeDocument3 pagesTCP 3-Way Handshakeakademi menembakNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet3 SolutionDocument13 pagesProblemSet3 SolutionAny FrankNo ratings yet
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- csd4652 Ilias Kapsis cs335 hw3Document6 pagescsd4652 Ilias Kapsis cs335 hw3persa.mavromanolakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Sample QuestionsArthue1316No ratings yet
- Transport AnswersDocument5 pagesTransport AnswersPebo GreenNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesHomework 2 SolutionsJosh at nightNo ratings yet
- CCE546 AAss 005Document6 pagesCCE546 AAss 005Aly KarkabaNo ratings yet
- Transport Layer Protocols II: Dept. of Computer Science Faculty of Science and TechnologyDocument23 pagesTransport Layer Protocols II: Dept. of Computer Science Faculty of Science and TechnologyAhmed KaushiqNo ratings yet
- NS Simulation Implementing Large Window Over TCP SACKDocument5 pagesNS Simulation Implementing Large Window Over TCP SACKElizabeth FlowersNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Transport Layer IIDocument10 pagesLecture 6 Transport Layer IITanvir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Practice Problems SolutionsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Practice Problems SolutionsRana ElshamyNo ratings yet
- TCP Connection Establishment: Juniper Business Use OnlyDocument5 pagesTCP Connection Establishment: Juniper Business Use OnlySandeep Kumar100% (1)
- Network Management 001Document7 pagesNetwork Management 001Gourav BansalNo ratings yet
- Solution To Practice Problem Set 5Document5 pagesSolution To Practice Problem Set 5agentrangomanNo ratings yet
- Comp2322 Midterm-2022sDocument5 pagesComp2322 Midterm-2022salibekuantkhanNo ratings yet
- TCP Model For Short Lived Flows: Marco Mellia, Member, IEEE, Ion Stoica, Member, IEEE, and Hui Zhang, Member, IEEEDocument3 pagesTCP Model For Short Lived Flows: Marco Mellia, Member, IEEE, Ion Stoica, Member, IEEE, and Hui Zhang, Member, IEEEFernando MendozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Lec3Document11 pagesUnit 4 Lec3SangetaNo ratings yet
- Sample Solutions: TH TH THDocument6 pagesSample Solutions: TH TH THDivyankk VyasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document6 pagesLecture 6Rylan2911No ratings yet
- Congestion Control UpdatedDocument57 pagesCongestion Control Updatedishidhim17No ratings yet
- Computer Network LabDocument5 pagesComputer Network Labమోహన్ తేజ కారపకులNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 TCPDocument24 pagesLab 9 TCPDavid SiegfriedNo ratings yet
- Transport Layer Protocol: What Is TCP?Document16 pagesTransport Layer Protocol: What Is TCP?Clarita PintoNo ratings yet
- CN NotesDocument10 pagesCN Notesbhavya gNo ratings yet
- COM210: Computer Networks (CN) : Chapter 3: TCPDocument64 pagesCOM210: Computer Networks (CN) : Chapter 3: TCPalolmani_oopNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document35 pagesWeek 5AKANKSHA RAJNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-4 Imp QA'sDocument22 pagesCN Unit-4 Imp QA'shajirasabuhiNo ratings yet
- 3315test2 PDFDocument27 pages3315test2 PDFKennyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Transport Layer IDocument25 pagesLecture 5 Transport Layer ISadatur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Only Q A PDFDocument18 pagesCh3 Only Q A PDFF JarmanNo ratings yet
- Homework PDFDocument4 pagesHomework PDFNafi SiamNo ratings yet
- 3.5 TCP-Transport LayerDocument3 pages3.5 TCP-Transport Layerkaushik surikuchiNo ratings yet
- CN Notes-Unit VDocument5 pagesCN Notes-Unit Vapi-278882881No ratings yet
- TCP: Overview: Full Duplex Data: Point-To-Point: Reliable, In-Order PipelinedDocument35 pagesTCP: Overview: Full Duplex Data: Point-To-Point: Reliable, In-Order PipelinedNirmalJeldiNo ratings yet
- Ee534 Lab10 (Duong - Le)Document6 pagesEe534 Lab10 (Duong - Le)Rock RáchNo ratings yet
- NWC203c PE23Document4 pagesNWC203c PE23hayhe2910No ratings yet
- EE450 Sample Set 6 TCPCC PDFDocument3 pagesEE450 Sample Set 6 TCPCC PDFKaishavi UmrethwalaNo ratings yet
- CCN Module 4Document120 pagesCCN Module 4venkateshprasad1562812No ratings yet
- Sliding Window ProtocolsDocument3 pagesSliding Window ProtocolsksivadreamsNo ratings yet
- ComputerNetworks ClassTest2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesComputerNetworks ClassTest2 Solutionshuyencttde180614No ratings yet
- Advanced Computer Networks: MS-2 SemesterDocument21 pagesAdvanced Computer Networks: MS-2 SemesterAmir ButtNo ratings yet
- TCP Congestion ControlDocument16 pagesTCP Congestion Controlpy thonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Problems - Kurose 8Document3 pagesChapter 3 - Problems - Kurose 8Luis Gomes Damasceno Neto UFCNo ratings yet
- Solution Guide-CAP3Document30 pagesSolution Guide-CAP3SidneyNo ratings yet
- Review TCPDocument26 pagesReview TCPAyyappaGolluNo ratings yet
- Cnip W5Document6 pagesCnip W5Rahul PurbeyNo ratings yet
- Week5a OneDocument25 pagesWeek5a Oneriteshdubey24No ratings yet
- CN - Unit4.2-1Document23 pagesCN - Unit4.2-1Kanika TyagiNo ratings yet
- Lecture16 TCPOverviewDocument12 pagesLecture16 TCPOverviewraw.junkNo ratings yet
- Int Ant Week3Document32 pagesInt Ant Week3Ahmet ÇakıroğluNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Vivek GuptaDocument17 pagesAssignment 3: Vivek Guptavgvivekgupta2No ratings yet
- Lab 4handoutDocument11 pagesLab 4handoutAlamgir KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document24 pagesUnit 3LakshmiSuvarna MattupalliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Transport ProtocolsDocument38 pagesChapter 12 Transport ProtocolsAjeetNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Transaction TCP-Design and Implementation: 1.1 What Is T/TCP 1.2 Why T/TCPDocument10 pagesEnhanced Transaction TCP-Design and Implementation: 1.1 What Is T/TCP 1.2 Why T/TCPJetesh DevgunNo ratings yet
- DCyt MICRO PROJECTDocument13 pagesDCyt MICRO PROJECTRed Light Hackers0% (1)
- Configuration of Postfix Mail Server Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusFrom EverandConfiguration of Postfix Mail Server Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusNo ratings yet