Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Momentum Equation
Uploaded by
মোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Momentum Equation
Uploaded by
মোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীCopyright:
Available Formats
MOMENTUM EQUATION
The momentum equation is based on Newton's second law of motion which states that the
algebraic sum of all the external forces acting on a fluid mass in any particular direction is equal
to the time rate of change of momentum in that direction.
Let us consider the control volume bounded by sections 1 and 2 (Fig. 2.4). The various forces
acting on the control volume in the longitudinal direction are:
i) the resultant hydrostatic pressure forces Fp1 and Fp2 at the two end sections,
ii) the force due to gravity, Wsinθ, which is the component of the weight of water in the
longitudinal direction, and
The momentum equation is based on Newton's second law of motion which states that the
algebraic sum of all the external forces acting on a fluid mass in any particular direction is equal
to the time rate of change of momentum in that direction.
Let us consider the control volume bounded by sections 1 and 2 (Fig. 2.4). The various
forces acting on the control volume in the longitudinal direction are:
i) the resultant hydrostatic pressure forces Fp1 and Fp2 at the two end sections,
ii) the force due to gravity, Wsinθ, which is the component of the weight of water in the
longitudinal direction, and
iii) the external frictional force Ff due to boundary friction acting on the surface of contact
between water and the channel
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- BUET04 UDocument31 pagesBUET04 Uমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Chemical Water QualityDocument19 pagesChemical Water Qualityমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Applicability of The EquationsDocument1 pageApplicability of The Equationsমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument5 pagesEngineering Materialsমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting ManningDocument1 pageFactors Affecting Manningমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Mild Slope Channel Followed by Steep Slope ChannelDocument1 pageMild Slope Channel Followed by Steep Slope Channelমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Using Improved Subgrade According To The Rules of RHDDocument1 pageUsing Improved Subgrade According To The Rules of RHDমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
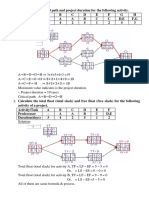
- Critical Path Method (CPM) PDFDocument2 pagesCritical Path Method (CPM) PDFমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Critical Path Method (CPM) PDFDocument2 pagesCritical Path Method (CPM) PDFমোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Question-2 Define: Quick Lime, Hydraulic Lime, Fat Lime, Poor Lime, and Hydrated Lime. (NPCBL '19)Document1 pageQuestion-2 Define: Quick Lime, Hydraulic Lime, Fat Lime, Poor Lime, and Hydrated Lime. (NPCBL '19)মোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet
- Question: Write Down The Advantages and Disadvantages of Flexible and Rigid Pavement. (BSEC'18)Document1 pageQuestion: Write Down The Advantages and Disadvantages of Flexible and Rigid Pavement. (BSEC'18)মোঃ ইনজামুল হক মেহেদীNo ratings yet