Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Markets and Industries: Forces (Michael Porter)
Markets and Industries: Forces (Michael Porter)
Uploaded by
Baher William0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
Module 5k
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageMarkets and Industries: Forces (Michael Porter)
Markets and Industries: Forces (Michael Porter)
Uploaded by
Baher WilliamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
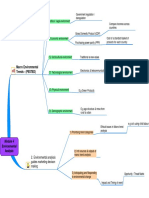
Generic Category
Items that are technically similar
1. Awareness
Levels of analysis Product type
2. Interest Markets and Industries Product class e.g cereal
3. Evaluation
Adoption process
4. Trial A market is comprised of
individuals and organisations who An industry is a group of firms
are interested and willing to buy a that offer a product or class of
5. Adoption good or service to obtain benefits products that are similar and are 1. Change in Industry's growth
that will satisfy a particular need or close substitutes for one another rate
want and who have the resources
to engage in such a transaction 2. Changes in key buyer
Risk segment
Macro level issues - Driving 3. Diffusion of propriety
Relative advantage forces (Michael Porter) knowledge
4. Changes in cost & efficiency
Relative simplicity 3. Diffusion of Innovation Rivalry is greater if:
Theory 5. Changes in Government
Compatibility with current Rate of Adoption depends on: regulations
Seeks to explain the adoption of a High investment intensity
behaviour
product /service over time amongst a
group of potential buyers No dominant firm exists / only
Ease of small trial use 1. Rivalry among present small fims
competitors
Ese of ommunication benefits Little product differentiation
The greater the competitive
rivalry the less attractive the
industry High cost to changing suppliers
Porters 5 Competitive forces
Module 5 (determines industry's long term
2.5% of individuals attractiveness) Entry is more difficult if:
Industry Analysis Strong economies of scale are
High income earners Innovators
and present
Competitive Advantage Industry Analysis to
receptive to new ideas Industry has strong capital
determine attractiveness of 2. Threat of new competitors requirements
Industry: Strong product differentiation
13-14% The greater the threat of new
entrants, the less attractive the exists
industry Gaining distribution is particulary
Opinion leaders early adopters difficult
Introduction
Participate in communities Impact is significant if:
Growth
34% Limited # of suppliers service
Shakeout
different industries
Adopter categories
active in community Early majority Maturity
Switching costs of substitutes is
No risks - product successful high
before they adopt it Product life cycle 3. Bargaining power of suppliers
Decline
34% They can threaten forward
integration
The greater the bargaining
Adopt whe forced to Late majority PAGE 55 - marketing mix power of suppliers, the less
decisions in life cycle phases attractive the industry Suppliers product is large part of
buyers value add
rarely assume leader role Put a ceiling on the profitability
of an industry by limiting the
price that can be charged Extent of power depends on:
16% Substitute products are
alternative product types (not 5. Threat of substitute products Extent of buyer concentration
Laggards brands) that perform the same
The most local
functions e.g cans vs bottles
Switching costs
4. Bargaining power of buyers
Resist change
They can threaten backward
integration
The greater the power of high
volume customers, the less Buyer profitability - if buyer
attractive the industry earns low profits more agressive
negotiations
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Biology 12 Unit 5 Dna Worksheet - Dna Strucuture 1Document2 pagesBiology 12 Unit 5 Dna Worksheet - Dna Strucuture 1api-354531819100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Miyamoto Musashi - The Book of Five RingsDocument34 pagesMiyamoto Musashi - The Book of Five Ringsauto3871No ratings yet
- RSPPLDocument1 pageRSPPLMohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Course Summary - Tamer 2011 - 2 of 2Document37 pagesOrganizational Behavior Course Summary - Tamer 2011 - 2 of 2Mohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Goods Classification New Product DevelopmentDocument1 pageGoods Classification New Product DevelopmentMohamed KableNo ratings yet
- LWD For SLB PDFDocument21 pagesLWD For SLB PDFMohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Module 4 PDFDocument1 pageModule 4 PDFMohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Marketing EXAM CASE STUDY 1Document5 pagesMarketing EXAM CASE STUDY 1Mohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Ebs Exam Analysis-2Document39 pagesEbs Exam Analysis-2Mohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Finace Ex. Dec 2008Document4 pagesFinace Ex. Dec 2008Mohamed Kable50% (2)
- Module 9Document1 pageModule 9Mohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Why Stories Are Important: Why Read With Children? How Books and Stories Help ChildrenDocument4 pagesWhy Stories Are Important: Why Read With Children? How Books and Stories Help ChildrenChristina KiuNo ratings yet
- Sample Thesis in Computer ScienceDocument8 pagesSample Thesis in Computer Sciencedqaucoikd100% (2)
- 7 Sign Post To Your Assignment - Mike MurdockDocument49 pages7 Sign Post To Your Assignment - Mike MurdockAzuogu Uchechukwu Samuel100% (2)
- The Leyend of JorjeDocument1 pageThe Leyend of JorjeANGELA PATRICIA MANCERA RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Vibration Induced Pipework Failure PDFDocument8 pagesVibration Induced Pipework Failure PDFAlvin SmithNo ratings yet
- African Values: GreetingDocument5 pagesAfrican Values: GreetingJcee EsurenaNo ratings yet
- Abhishek BTP2xDocument57 pagesAbhishek BTP2xAbhishek SaxenaNo ratings yet
- List of Deep Learning and NLP ResourcesDocument69 pagesList of Deep Learning and NLP ResourcesBartoszSowul100% (1)
- Tugas B. Ing RestuDocument2 pagesTugas B. Ing RestuWahyuniNo ratings yet
- HDSD Va Calib May PH 330 PDFDocument69 pagesHDSD Va Calib May PH 330 PDFThanh Sơn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Why Is Academic Research ImportantDocument5 pagesWhy Is Academic Research ImportantEli EzraNo ratings yet
- Response and Sdof Ce 6122Document106 pagesResponse and Sdof Ce 6122RafiqulIslamNo ratings yet
- Location Facilities QuizDocument29 pagesLocation Facilities QuizDiane CabiscuelasNo ratings yet
- Sleep Apnea Home Monitor and Analysis SystemDocument10 pagesSleep Apnea Home Monitor and Analysis SystemS Jagadish PatilNo ratings yet
- 1920 Mystery BookDocument16 pages1920 Mystery BookAce Valderrama100% (1)
- Proceedings Formec Poland 2016Document342 pagesProceedings Formec Poland 2016Hugo SilvaNo ratings yet
- ConfederationDocument3 pagesConfederationdsqairNo ratings yet
- Velazco Vs BlasDocument9 pagesVelazco Vs BlasMark John Geronimo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Routledge History of Philosophy Volume 10 Philosophy of Meaning, Knowledge and Value in The Twentieth Century - John V.canfieldDocument350 pagesRoutledge History of Philosophy Volume 10 Philosophy of Meaning, Knowledge and Value in The Twentieth Century - John V.canfieldGabriel Paiva Rega100% (2)
- Dela Cruz, Mary Julieanne DR. BSLM-3B ICL 304 Case DIgestsDocument5 pagesDela Cruz, Mary Julieanne DR. BSLM-3B ICL 304 Case DIgeststherouguedragonrider14No ratings yet
- SDS Conbextra Cable GroutDocument8 pagesSDS Conbextra Cable GroutArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Markus Tanpa NamaDocument8 pagesJurnal Markus Tanpa NamaMarkus Koko Nur BudiantoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Roman EducationDocument14 pagesVocabulary: Roman EducationBibek Chapagain100% (1)
- How To Proceed With TroubleshootingDocument9 pagesHow To Proceed With TroubleshootingdiemnganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BWDDocument63 pagesChapter 6 BWDcpawan_699508No ratings yet
- The Silk Road Journal #8Document139 pagesThe Silk Road Journal #8Cecilia CarnevaleNo ratings yet
- IWASAWA v. GANGANDocument2 pagesIWASAWA v. GANGANTootsie GuzmaNo ratings yet
- Sublime Conduct of RasulullahDocument426 pagesSublime Conduct of RasulullahzaynabteladiaNo ratings yet