Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aqua Regia Accident
Uploaded by
azwa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views1 pageOriginal Title
Aqua regia accident
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views1 pageAqua Regia Accident
Uploaded by
azwaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Environmental Health and Safety Office
Hazard Alert (03-002)
USING MIXTURES OF HIGHLY CORROSIVE CONCENTRATED ACIDS
Ex: AQUA REGIA and Piranha Solution
There have been accidents involving the use of aqua regia and Piranha Solution. In one incident, a graduate student at
the University of Manitoba used an etching solution of aqua regia and glycerol for electro-polishing a nickel superalloy.
Only a portion of the solution was used after preparation, the remainder was stored in a capped plastic bottle inside a
fume hood. Within 45 minutes, the bottle burst, spewing the contents everywhere, damaging computer equipment nearby
and filling the room with acid fumes. Fortunately there were no injuries. (No one was in the room when the container
failed.) In another similar incident, this one occurring in September 1998 in an Ontario University (http://www.uwo.ca/ohs/
hazalerts/aquareg.htm), a graduate student was using aqua regia for the cleaning of NMR tubes. After finishing with the
material, he placed the waste aqua regia, about 50-60 ml, in a 4L Winchester bottle, capping it tightly and storing it in a
flammable solvent storage cabinet prior to disposal. About an hour later it exploded, filling the lab with acid fumes. A
nearby bottle of pyridine broke and leaked onto the floor. It dissolved floor tiles and
created a lingering bad smell.
Aqua regia is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid. It
has been used for centuries for dissolving noble metals (gold, platinum). Piranha Solution
is a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide. Aqua regia and Piranha
solution are highly corrosive and very powerful oxidizing agents. Even without other
materials present, a slow chemical reaction occurs in aqua regia and brown fumes of
nitrogen peroxide are produced. The activity of Aqua Regia as a dissolving agent
decreases slowly and thus, by definition, the solution is unstable. Aqua Regia should be
freshly prepared, never stored in a closed vessel. Render it safe by dilution and
neutralization.
The following are proper procedures for handling and using highly corrosive
concentrated acids such as Aqua Regia and Piranha Solution.
1. These acids should only be prepared and used when absolutely necessary. If a
milder reagent will work, try to avoid using aqua regia and like. Aqua regia and
Piranha solution are not recommended for routine cleaning of glassware.
2. When using highly corrosive acids, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (safety splash goggles,
gloves and laboratory coat) and work in a clean, properly working chemical fume hood. Keep the fume hood’s
sash down at working height (usually 11 inches) when reactions are in progress. Leave the sash closed if the hood is
unattended. It is essential that any one working with such corrosives has unimpeded access to an emergency eye
wash and safety shower. These must be within 100 feet of the work area.
3. Prepare only the amount needed for immediate use. Label container as per WHMIS procedures. Never store
mixtures of highly corrosive acids and never put it in a sealed container, since pressure from evolving gases
accumulates and possibly cause an explosion. Never take these acids out of the fume hood in which they are
prepared and do not store them there either. Use them immediately after preparation and destroy any excess in the
fume hood in which they were prepared. Aqua regia can be destroyed safely by cautiously adding it to water to
dilute, and then neutralize the diluted solution with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda). The resulting contents can be
disposed as chemical laboratory waste through EHSO Hazardous Waste Program (474-6633). A box or two of
ordinary sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) or other commercial spill kits should be nearby to effectively neutralize
acid spills.
4. For any solutions containing aqua regia such as the etching solution mentioned in the beginning, follow the same
principles as outlined above. You can avoid accidents by adhering to the principles and getting specific instructions
from your supervisor before handling aqua regia or other potentially hazardous reagents.
5. The aqua regia container must be glass or plastic. Although cold aqua regia does not rapidly attack plastics, Teflon is
the only plastic truly resistant to oxidizing action of hot aqua regia. The container must be open or vented to allow the
escape of chlorine, which is produced slowly.
Main Office Bannatyne Office
191 Frank Kennedy Building T248 – 249 Basic Science Building
Winnipeg MB R3T 2N2 Winnipeg MB R3E 0W3
Tel: (204) 474-6633 Tel: (204) 789-3613
Fax: (204) 474-7629 Fax: (204) 789-3906
You might also like
- Recover Gold from Gold Plated Items, And Turn It Into 99.995% Pure GoldFrom EverandRecover Gold from Gold Plated Items, And Turn It Into 99.995% Pure GoldNo ratings yet
- AquaregiDocument2 pagesAquaregibambang82No ratings yet
- Sop For Aqua RegiaDocument4 pagesSop For Aqua RegiaAjay SinghlaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Safety Rules and Chemical HandlingDocument7 pages1.0 Safety Rules and Chemical HandlingThomas RayNo ratings yet
- Picric AcidDocument3 pagesPicric AcidAnonymous CXNLTvmNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure Concentrated AcidsDocument6 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Concentrated AcidsDibyendu GhoshNo ratings yet
- LTBFP NaOH Etch PDFDocument4 pagesLTBFP NaOH Etch PDFsayyadmannanNo ratings yet
- Arco VerrerieDocument92 pagesArco VerrerieFatimaezzahra FaouziNo ratings yet
- Australian National UniversityDocument3 pagesAustralian National Universitysantoshkumar1988No ratings yet
- May Chemical Caustic-Soda and Nitric-TrainingDocument30 pagesMay Chemical Caustic-Soda and Nitric-Trainingruba ganeshNo ratings yet
- Potassium HydroxideDocument5 pagesPotassium HydroxideSandhya RaiNo ratings yet
- Glassware CleaningDocument3 pagesGlassware CleaningSiti Nurazlin FariddunNo ratings yet
- Safety Issue and Enviromental EffectDocument4 pagesSafety Issue and Enviromental EffectHaziq AzliNo ratings yet
- Wafer CleaningDocument4 pagesWafer CleaningHisyamAl-MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Aqua Regia: Preparation, Handling and DisposalDocument2 pagesAqua Regia: Preparation, Handling and DisposalAjay SinghlaNo ratings yet
- CaohDocument4 pagesCaohOm Prakash RajNo ratings yet
- Perchloric AcidDocument3 pagesPerchloric AcidWilson SalasNo ratings yet
- Swancor 901 Data SheetDocument2 pagesSwancor 901 Data SheetErin Guillermo33% (3)
- Analytical Chemistry Laboratory GuideDocument9 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Laboratory GuideElprince MidoNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating ProcedureDocument3 pagesStandard Operating Procedureabcd efgNo ratings yet
- 2 Safety-RulesDocument4 pages2 Safety-RulesVanna AmarilloNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety Guideline: EHS Emergency Response GuideDocument2 pagesLaboratory Safety Guideline: EHS Emergency Response GuidemochdimaskuNo ratings yet
- Basics of Biochemistry - Bmls-106-18: Experiment-1 AIM: Cleaning of Laboratory GlasswareDocument3 pagesBasics of Biochemistry - Bmls-106-18: Experiment-1 AIM: Cleaning of Laboratory Glasswarehod MLSNo ratings yet
- Sds-Evamarine ExteriorDocument6 pagesSds-Evamarine ExteriorSaifuddin FahmiNo ratings yet
- APM002 Rotary EvaporatorDocument9 pagesAPM002 Rotary EvaporatorMukarram MudjahidNo ratings yet
- SOP Template Sulfuric AcidDocument3 pagesSOP Template Sulfuric AcidAzirul SambasNo ratings yet
- Sop Wet Silicon Rca 1Document3 pagesSop Wet Silicon Rca 1Adarsh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide and EthanolDocument6 pagesSodium Hydroxide and EthanololafNo ratings yet
- A Perchlorate Explosion Causes A Mans Death - pp17-19Document3 pagesA Perchlorate Explosion Causes A Mans Death - pp17-19Soeryanto SlametNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Amine Condensate PDFDocument3 pagesFatty Acid Amine Condensate PDFImam BukhoriNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Citric AcidDocument4 pagesMSDS - Citric AcidJose Luis Lucas ParedesNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure: Perchloric AcidDocument7 pagesStandard Operating Procedure: Perchloric AcidShahid AliNo ratings yet
- Contrad 70 Tech SheetDocument2 pagesContrad 70 Tech SheetPeter RichterNo ratings yet
- Aqua Regia SOPDocument4 pagesAqua Regia SOPshahinNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Etch SOPDocument3 pagesAluminum Etch SOPredmedicine9400No ratings yet
- Picric Acid Safe HandlingDocument1 pagePicric Acid Safe Handlingmavis16No ratings yet
- Picric AcidDocument1 pagePicric AcidHashir QuraishiNo ratings yet
- Borosilicate Glasses For Nuclear Waste ImmobilizatDocument8 pagesBorosilicate Glasses For Nuclear Waste ImmobilizatSankarNo ratings yet
- Piranha Solution SiDocument2 pagesPiranha Solution Simonica rodrinNo ratings yet
- LookupDocument3 pagesLookupenzooo2009No ratings yet
- Oxychem Caustic Soda HandbookDocument44 pagesOxychem Caustic Soda HandbookManoj PanchalNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Peroxide DeconDocument6 pagesHydrogen Peroxide DeconSurendar KesavanNo ratings yet
- What Is The Best Method For Cleaning Glassware?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Best Method For Cleaning Glassware?Muhammad YaseenNo ratings yet
- Quickdraw MSDS7 PDFDocument5 pagesQuickdraw MSDS7 PDFLuis Adrián ElguézabalNo ratings yet
- Practical Problems: Safety RulesDocument9 pagesPractical Problems: Safety RulesPopa ElenaNo ratings yet
- Sop Wet Silicon Rca 2Document3 pagesSop Wet Silicon Rca 2srihariNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Nitric AcidDocument5 pagesMSDS - Nitric AcidFkr JabarNo ratings yet
- Wattyl Colourthane Thinner Standard 6100-99 MSDS May13Document12 pagesWattyl Colourthane Thinner Standard 6100-99 MSDS May13Dil VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- PGPlus MSDSDocument10 pagesPGPlus MSDSmahmudiNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Laboratory WareDocument7 pages4.0 Laboratory WareHenry KarokiNo ratings yet
- Spill Tech BrochureDocument12 pagesSpill Tech Brochuremonique5617No ratings yet
- VapproVCI-749 ElectrolubeDocument2 pagesVapproVCI-749 ElectrolubeAbdulrehmanNo ratings yet
- Cleaning CuvettesDocument7 pagesCleaning CuvettesjanoscribdNo ratings yet
- Microwave SopDocument6 pagesMicrowave SopmambojumbNo ratings yet
- How Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial ROFrom EverandHow Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial RORating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Improvised Munitions Handbook – Learn How to Make Explosive Devices & Weapons from Scratch (Warfare Skills Series): Illustrated & With Clear InstructionsFrom EverandImprovised Munitions Handbook – Learn How to Make Explosive Devices & Weapons from Scratch (Warfare Skills Series): Illustrated & With Clear InstructionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Synthesis, Properties and Mineralogy of Important Inorganic MaterialsFrom EverandSynthesis, Properties and Mineralogy of Important Inorganic MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Hikikomori Phenomenon in East Asia: Regional Perspectives, Challenges, and Opportunities For Social Health AgenciesDocument7 pagesHikikomori Phenomenon in East Asia: Regional Perspectives, Challenges, and Opportunities For Social Health AgenciesazwaNo ratings yet
- Social Media and Suicide PsychosocialDocument7 pagesSocial Media and Suicide PsychosocialazwaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cruelty and Psychiatric DisordersDocument10 pagesAnimal Cruelty and Psychiatric DisordersazwaNo ratings yet
- DisciplinaryDocument12 pagesDisciplinaryazwaNo ratings yet
- HHHHHDocument2 pagesHHHHHazwaNo ratings yet
- TadaaDocument1 pageTadaaazwaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Requirements of BacteriaDocument25 pagesNutritional Requirements of BacteriaAira MiyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Determination of Corrosion Rate of Metals: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment 1: Determination of Corrosion Rate of Metals: Objective041Mir QazimNo ratings yet
- Topical, Gastrointestinal, NI, Radio-, MiscDocument113 pagesTopical, Gastrointestinal, NI, Radio-, MiscArk Olfato ParojinogNo ratings yet
- Ship PreCargo MatrixDocument4 pagesShip PreCargo MatrixRigel NathNo ratings yet
- What Has ChangedDocument132 pagesWhat Has ChangedVanessa VanegasNo ratings yet
- MT - CatFines-KIT PDFDocument12 pagesMT - CatFines-KIT PDFStefas DimitriosNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Biology Moddel ExamDocument8 pagesGR 12 Biology Moddel ExamDawit MarkosNo ratings yet
- PDS - BearingCheck 894 and BearingCheck 824Document1 pagePDS - BearingCheck 894 and BearingCheck 824ratninp9368No ratings yet
- Dutch Pollutant StandardsDocument5 pagesDutch Pollutant Standardsumair2kplus492No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes - Nucleotide MetabolismDocument5 pagesBiochemistry Notes - Nucleotide MetabolismneedthisforepiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Chemical Thermodynamics: 17.1 When Is A Process Spontaneous?Document4 pagesChapter 17: Chemical Thermodynamics: 17.1 When Is A Process Spontaneous?Carlos Mella-RijoNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of RadiopharmaceuticalsDocument9 pagesManufacture of RadiopharmaceuticalsRainMan75No ratings yet
- 8-Evaluation of Drugs, WHO & ICH Guidlines For StablityDocument23 pages8-Evaluation of Drugs, WHO & ICH Guidlines For StablityMamta Pant100% (5)
- 078-Mahoney-URANIO CALIBRACIONDocument32 pages078-Mahoney-URANIO CALIBRACIONNeider BurgosNo ratings yet
- PneumaticDocument13 pagesPneumaticVikas RaoNo ratings yet
- Classical ExperimentsDocument2 pagesClassical ExperimentsShane Cagas AcaoNo ratings yet
- TLC Staining Procedure TLC Stain Recipe Stain Chemistry / Physics CommentsDocument3 pagesTLC Staining Procedure TLC Stain Recipe Stain Chemistry / Physics CommentsLara DiasNo ratings yet
- Kluber PresentationDocument79 pagesKluber PresentationZegera MgendiNo ratings yet
- 3D Optical and Device Simulation of Surface Plasmonic Effects On Organic Solar Cells Using Silver Nano PrismsDocument5 pages3D Optical and Device Simulation of Surface Plasmonic Effects On Organic Solar Cells Using Silver Nano PrismsSakshiKoulNo ratings yet
- Hygroscopic (Osmotic) Blisters Tiny, Pin Head Size, Water Filled Blisters. Caused by Hygroscopic Salts (Iron Sulphates and Iron Chlorides)Document25 pagesHygroscopic (Osmotic) Blisters Tiny, Pin Head Size, Water Filled Blisters. Caused by Hygroscopic Salts (Iron Sulphates and Iron Chlorides)Usab GamalNo ratings yet
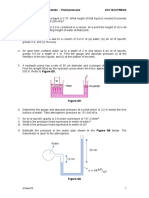
- 2 Tutorial Pressure Sept19Document7 pages2 Tutorial Pressure Sept19hairinnisaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (2023)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (2023)Dr. Aung Ko LattNo ratings yet
- BPCL Report MechanicalDocument44 pagesBPCL Report MechanicalritikaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids PDFDocument24 pagesProperties of Fluids PDFAnthony Leire MontealtoNo ratings yet
- Assay of Chloroquine Phosphate Experiment No.: Date: Aim: To Perform The Assay of Chloroquine Phosphate. Reference: RequirementsDocument3 pagesAssay of Chloroquine Phosphate Experiment No.: Date: Aim: To Perform The Assay of Chloroquine Phosphate. Reference: RequirementsDinesh ThakkarNo ratings yet
- MSDS All DNA RNA Purification KitsDocument6 pagesMSDS All DNA RNA Purification Kitsjusman sadorraNo ratings yet
- 2004.03 Salmonella en Alimentos ELFADocument3 pages2004.03 Salmonella en Alimentos ELFAJavier muñozNo ratings yet
- Finding An Alternative Binder For Asphalt Using Plastic-BitumenDocument11 pagesFinding An Alternative Binder For Asphalt Using Plastic-BitumenStephen BoachieNo ratings yet
- Filter DataDocument6 pagesFilter DataJohnNo ratings yet
- Van Urk Indole TLC Test PDFDocument11 pagesVan Urk Indole TLC Test PDFabazaba151No ratings yet