0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views2 pagesCompetitive Actions and Market Strategies
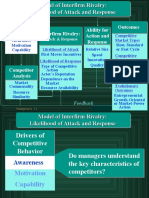
The document discusses competitive rivalry between firms. It defines competitive action as moves taken by firms to build or defend competitive advantages, and competitive response as moves taken to counter a competitor's actions. Strategic actions require significant resources and are difficult to reverse, while tactical actions involve fewer resources and are easier to reverse. The likelihood of a firm initiating competitive attacks depends on factors like first-mover benefits, organizational size, and perceived quality - with first movers, smaller and higher quality firms more likely to attack.
Uploaded by
Lyn LegazpiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views2 pagesCompetitive Actions and Market Strategies
The document discusses competitive rivalry between firms. It defines competitive action as moves taken by firms to build or defend competitive advantages, and competitive response as moves taken to counter a competitor's actions. Strategic actions require significant resources and are difficult to reverse, while tactical actions involve fewer resources and are easier to reverse. The likelihood of a firm initiating competitive attacks depends on factors like first-mover benefits, organizational size, and perceived quality - with first movers, smaller and higher quality firms more likely to attack.
Uploaded by
Lyn LegazpiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd