Professional Documents
Culture Documents
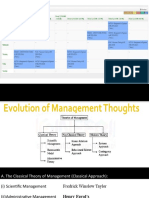
3) Emerson (1853-1936)
Uploaded by
babyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3) Emerson (1853-1936)
Uploaded by
babyCopyright:
Available Formats
Gantt was concerned with problems related to efficiency.
He contributed to scientific
management by refining the previous work of Taylor than introducing new concepts.
1. He studied the amount of work planned or completed on one axis to the time
needed or taken to complete a task on the other axis.
2. Gantt also developed a task and bonus remuneration plan whereby workers
received a guaranteed day‘s wages plus a bonus for production above the standard
to stimulate higher performance.
3. Gantt recommended to select workers scientifically and provided with detailed
instructions for their tasks.
4. He argued for a more Humanitarian approach by management, placing emphasis
on service rather than profit objectives.
5. He recognized useful non –monetary incentives such as job security and
encouraging staff development.
3) Emerson (1853-1936):
His emphasis was on conservation and organizational goals and objectives.
He defined principles of efficiency related to:
1. Interpersonal relations and to system in management.
2. Goals and ideas should be clear and well-defined as the primary objective is to
produce the best product as quickly as possible at minimal expense.
3. Changes should be evaluated-management should not ignore ―commonsense‖ by
assuming that big is necessarily better.
4. ―Competent counsel ―is essential.
His theory explains about
1. Management can strengthen discipline or adherence to the rules by justice, or
equal enforcement on all records, including adequate, reliable and immediate
information about the expenses of equipment and personnel should be available as
a basis for decisions.
2. Dispatching or production scheduling is recommended.
3. Standardized schedules, conditions and written instructions should be there to
facilitate performance.
4. ―Efficiency rewards ―should be given for successful completion of tasks.
5. Emerson moved further beyond scientific management to classic organizational
theory.
4. Charles Babbage (1792-1871): Charles Babbage ,a scientist mainly interested in
mathematics, contributed to the management theory by developing the principles of
cost and accounting and the nature of relationship between various disciplines.
Charles Babbage laid the foundation for much of the work that later come to be known
as scientific management. He concentrated on production problems and stressed the
Importance of-
1) Division and assignment of work on the basis of skill and
You might also like
- Principles of Management CLEP Quick Prep SheetFrom EverandPrinciples of Management CLEP Quick Prep SheetRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Management TheoryDocument20 pagesManagement TheoryAnusha Verghese100% (3)
- Theories of ManagementDocument12 pagesTheories of ManagementManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Management TheoryDocument15 pagesManagement TheoryMerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Early Management Thought: Adam Smith and Scientific ApproachDocument17 pagesEarly Management Thought: Adam Smith and Scientific ApproachShyam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 0 - Workshop Organization and ManagementDocument23 pages0 - Workshop Organization and ManagementRachael GatuuraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Development of Management TheoryDocument5 pagesLesson 2 The Development of Management TheoryiamamayNo ratings yet
- Wolaita Sodo University School of Graduate Studies Master of Business Administration Group Assignment For The Course Concept of ManagementDocument8 pagesWolaita Sodo University School of Graduate Studies Master of Business Administration Group Assignment For The Course Concept of ManagementDejene Bekalu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Management Theories PDFDocument61 pagesEvolution of Management Theories PDFJuzmille CanlasNo ratings yet
- Module 1. Unit 2 - Historical Development of Public AdministrationDocument10 pagesModule 1. Unit 2 - Historical Development of Public AdministrationDale ArbolanteNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 7Document20 pagesPDF Document 7Happi TummyNo ratings yet
- Presentation On FW Taylor and Henry GanttDocument25 pagesPresentation On FW Taylor and Henry GanttTerence Barretto0% (1)
- Evolution of Management ThoughtDocument71 pagesEvolution of Management ThoughtGaurav Basnet Nepali100% (1)
- Management AssignmentDocument13 pagesManagement AssignmentMehran KhalidNo ratings yet
- Scientific ManagementDocument1 pageScientific ManagementRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Assignment PomDocument5 pagesAssignment PomfictionalmensloveNo ratings yet
- B. Medina Classics of Organization and Management Scientific ManagementDocument5 pagesB. Medina Classics of Organization and Management Scientific ManagementCathy Pascual NonatoNo ratings yet
- TheoriesDocument33 pagesTheoriesJeanne Marie Vargas TesorioNo ratings yet
- 1 Frederick WDocument6 pages1 Frederick WPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- MGT Thought CHAPTER 3 & 5Document17 pagesMGT Thought CHAPTER 3 & 5Meklit TenaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Management ThoughtDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Management ThoughtSakshiGupta67% (3)
- Health Services ManagementDocument6 pagesHealth Services ManagementWanyonyi JustusNo ratings yet
- Different Approaches To ManagementDocument59 pagesDifferent Approaches To ManagementSushmita VermaNo ratings yet
- Commission On Higher Education: Christ The King College Calbayog CityDocument8 pagesCommission On Higher Education: Christ The King College Calbayog CityPrecious Nadine ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Taylor 2Document6 pagesTaylor 2Niharika ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Management Theories and Models ExplainedDocument41 pagesManagement Theories and Models ExplainedVirgelio Sayson Abes0% (1)
- Module3 EditedDocument10 pagesModule3 EditedHehe JeansNo ratings yet
- Module 03Document10 pagesModule 03sidharth psNo ratings yet
- Scientific ManagementDocument6 pagesScientific ManagementCharles MumbaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MGT ThoughtsDocument65 pagesEvolution of MGT ThoughtsShyam ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management (Grade 12)Document20 pagesPrinciples of Management (Grade 12)Supriya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- PPM - 2 Mgmt. TheoryDocument19 pagesPPM - 2 Mgmt. TheoryAlok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Management TheoriesDocument55 pagesChapter Two Management TheoriesSAMMYNo ratings yet
- MTC ReportDocument38 pagesMTC ReportREINANo ratings yet
- Evalution of Management ThoughtDocument16 pagesEvalution of Management ThoughtShweta SharmaNo ratings yet
- April 16,2023 Learning Activities by KAMIDDocument10 pagesApril 16,2023 Learning Activities by KAMIDKamarudin KamidNo ratings yet
- Development of Management ThoughtDocument51 pagesDevelopment of Management Thoughtbanchi gashawNo ratings yet
- Management Lec 3Document6 pagesManagement Lec 3alaaelkholi99No ratings yet
- Classical Management ApproachesDocument65 pagesClassical Management ApproachesBabusanker SunderrajNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two RVU MT&PDocument38 pagesChapter Two RVU MT&PSisay DeresaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Management ScienceDocument33 pagesEvolution of Management ScienceGuru Prasad80% (5)
- Principles of Management Chapter 2Document38 pagesPrinciples of Management Chapter 2karim kobeissi100% (1)
- Assignment ManagmentDocument8 pagesAssignment ManagmentAb CNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Two The Development of Management Thoughts / Theories Value of TheoryDocument11 pagesChapter - Two The Development of Management Thoughts / Theories Value of Theoryይርዳው ሲሳይ ወርቀልዑልNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Industrial Management EHU-601Document27 pagesUNIT-1 Industrial Management EHU-601sarvar aliNo ratings yet
- Tylor and FayolDocument65 pagesTylor and Fayolakash NegiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document13 pagesLecture 2SamairahNo ratings yet
- IT107 HandOut 004Document5 pagesIT107 HandOut 004jin_adrian100% (1)
- Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument10 pagesEvolution of Management TheoriesBinodBasnet100% (1)
- Management SkillsDocument16 pagesManagement SkillsSripriya TamilNo ratings yet
- ENV234 Lecture 3Document19 pagesENV234 Lecture 3Jeffrey BeloyNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Management TheoryDocument9 pagesThe Evolution of Management TheoryKimberly OngNo ratings yet
- Management Theories 2018Document16 pagesManagement Theories 2018Anusha KVNo ratings yet
- Theories of Management: A. Scientific Management TheoryDocument2 pagesTheories of Management: A. Scientific Management TheorybabyNo ratings yet
- Esb 420Document11 pagesEsb 420Chikwason Sarcozy MwanzaNo ratings yet
- A History of Management ThoughtDocument45 pagesA History of Management ThoughtDr-Sajjad Ul Aziz QadriNo ratings yet
- MGT ThoughtDocument46 pagesMGT Thoughtnishaudayshankar34No ratings yet
- Management Theory EvolutionDocument56 pagesManagement Theory Evolutionpoo printNo ratings yet
- 3.classical School of ThoughtDocument12 pages3.classical School of ThoughtmajhiajitNo ratings yet
- Chap 2.evolutionDocument26 pagesChap 2.evolutionAmit Ramchurn KoolchapNo ratings yet
- HEALTH EDUCATION Nursing Process PNCDocument2 pagesHEALTH EDUCATION Nursing Process PNCbabyNo ratings yet
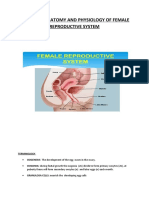
- Female Repro SystemDocument16 pagesFemale Repro SystembabyNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Antenatal AssessmentDocument4 pagesChecklist For Antenatal Assessmentbaby91% (11)
- National Drug Dependence Treatment Centre, Gaziabad: Identification DataDocument7 pagesNational Drug Dependence Treatment Centre, Gaziabad: Identification DatababyNo ratings yet
- Depth Study On PartoDocument40 pagesDepth Study On PartobabyNo ratings yet
- Rajkumari Amrit Kaur College of Nursing: SNO Date TopicsDocument1 pageRajkumari Amrit Kaur College of Nursing: SNO Date TopicsbabyNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Antenatal AssessmentDocument4 pagesChecklist For Antenatal Assessmentbaby91% (11)
- Management of Protected Areas Led To Socio Cultural DisruptionsDocument2 pagesManagement of Protected Areas Led To Socio Cultural DisruptionsbabyNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice PartoDocument12 pagesEvidence Based Practice PartobabyNo ratings yet
- Master Plan AssignmentDocument4 pagesMaster Plan AssignmentbabyNo ratings yet
- Farm Loan WaiversDocument2 pagesFarm Loan WaiversbabyNo ratings yet
- Waste ManagementDocument2 pagesWaste ManagementbabyNo ratings yet
- Rajkumari Amrit Kaur College of NursingDocument28 pagesRajkumari Amrit Kaur College of NursingbabyNo ratings yet
- Gig Economy:-: AdvantagesDocument2 pagesGig Economy:-: AdvantagesbabyNo ratings yet
- Bfhi Lesson PlanDocument26 pagesBfhi Lesson Planbaby100% (2)
- SEMINAR ON FACULTY SUPERVISOR POSITION IN NURSINGDocument8 pagesSEMINAR ON FACULTY SUPERVISOR POSITION IN NURSINGbabyNo ratings yet
- Bhfi Rationale 10 To 1Document4 pagesBhfi Rationale 10 To 1babyNo ratings yet
- Procedures and Nurses' Role in Material ManagementDocument28 pagesProcedures and Nurses' Role in Material ManagementbabyNo ratings yet
- MP ExcelDocument8 pagesMP ExcelbabyNo ratings yet
- Rajkumari Amrit Kaur College of NursingDocument28 pagesRajkumari Amrit Kaur College of NursingbabyNo ratings yet
- Postmodernism: Key Aspects and RootsDocument11 pagesPostmodernism: Key Aspects and RootsbabyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 PDFDocument18 pagesUnit 5 PDFchxhdy ugkjulNo ratings yet
- Different Theories of Management: Liezel Sabunod Bsee-IiiDocument8 pagesDifferent Theories of Management: Liezel Sabunod Bsee-IiibabyNo ratings yet
- Pres 1 - Oligo and PohydramniosDocument6 pagesPres 1 - Oligo and PohydramniosbabyNo ratings yet
- Material ManagementDocument41 pagesMaterial ManagementKumud Ranjan100% (1)
- Always, Better and Control - Vital, Essential, Desirable Matrix Analysis of The Drug Store of A Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital of North IndiaDocument5 pagesAlways, Better and Control - Vital, Essential, Desirable Matrix Analysis of The Drug Store of A Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital of North IndiababyNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation Of: Nursing ProgramDocument31 pagesCritical Evaluation Of: Nursing Programbaby100% (1)
- MATERIAL MANAGEMENT CONCEPTSDocument28 pagesMATERIAL MANAGEMENT CONCEPTSbabyNo ratings yet
- Postmodernism: Key Aspects and RootsDocument11 pagesPostmodernism: Key Aspects and RootsbabyNo ratings yet
- Annual Report - Year 2018-2019Document24 pagesAnnual Report - Year 2018-2019baby100% (1)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleFrom EverandThe 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- The Five Dysfunctions of a Team SummaryFrom EverandThe Five Dysfunctions of a Team SummaryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- The Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceFrom EverandThe Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (22)
- The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthFrom EverandThe Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- The Way of the Shepherd: Seven Secrets to Managing Productive PeopleFrom EverandThe Way of the Shepherd: Seven Secrets to Managing Productive PeopleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (112)
- 12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerFrom Everand12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerNo ratings yet
- Developing Coaching Skills: A Concise IntroductionFrom EverandDeveloping Coaching Skills: A Concise IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Getting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)From EverandGetting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Powerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesFrom EverandPowerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Powerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesFrom EverandPowerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Irresistible: The Seven Secrets of the World's Most Enduring, Employee-Focused OrganizationsFrom EverandIrresistible: The Seven Secrets of the World's Most Enduring, Employee-Focused OrganizationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Organizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementFrom EverandOrganizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementNo ratings yet
- 50 Top Tools for Coaching, 3rd Edition: A Complete Toolkit for Developing and Empowering PeopleFrom Everand50 Top Tools for Coaching, 3rd Edition: A Complete Toolkit for Developing and Empowering PeopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Crucial Conversations: Tools for Talking When Stakes are High, Third EditionFrom EverandCrucial Conversations: Tools for Talking When Stakes are High, Third EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Art of Active Listening: How People at Work Feel Heard, Valued, and UnderstoodFrom EverandThe Art of Active Listening: How People at Work Feel Heard, Valued, and UnderstoodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthFrom EverandThe Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (101)
- Management For Beginners: The Ultimate Guide for First Time ManagersFrom EverandManagement For Beginners: The Ultimate Guide for First Time ManagersNo ratings yet
- Goal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsFrom EverandGoal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- DEI Deconstructed: Your No-Nonsense Guide to Doing the Work and Doing It RightFrom EverandDEI Deconstructed: Your No-Nonsense Guide to Doing the Work and Doing It RightRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Strength-Based Leadership Coaching in Organizations: An Evidence-Based Guide to Positive Leadership DevelopmentFrom EverandStrength-Based Leadership Coaching in Organizations: An Evidence-Based Guide to Positive Leadership DevelopmentRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: Who Moved My Cheese?: An A-Mazing Way to Deal with Change in Your Work and in Your Life by Spencer Johnson M.D. and Kenneth Blanchard: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Who Moved My Cheese?: An A-Mazing Way to Deal with Change in Your Work and in Your Life by Spencer Johnson M.D. and Kenneth Blanchard: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Essential HR Handbook, 10th Anniversary Edition: A Quick and Handy Resource for Any Manager or HR ProfessionalFrom EverandThe Essential HR Handbook, 10th Anniversary Edition: A Quick and Handy Resource for Any Manager or HR ProfessionalRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (3)
- Crucial Conversations Tools for Talking When Stakes Are High, Second EditionFrom EverandCrucial Conversations Tools for Talking When Stakes Are High, Second EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (432)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeFrom EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (99)