Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prob Set 3 2nd Sem 2017 PDF
Uploaded by
Jeric_QOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prob Set 3 2nd Sem 2017 PDF
Uploaded by
Jeric_QCopyright:
Available Formats
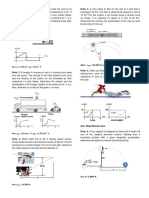
1.
Bar AB rotates at ω = 12 rad/s in the instant illustrated, determine the angular velocity
clockwise direction. Use instantaneous center of of rod BC and the velocity of point C,
zero velocity to determine the velocity of point E. ω = 5 rad/s
B
B
400 A 45º
mm
12 rad/s C D E
A
r=2m
45º C
700 mm 400 mm 700 mm
5. The crankshaft AB has an angular velocity of
2. Rod AB is supported by a smooth wall and ω = 10 rad/s, counterclockwise. Determine the
floor. If point A is given a velocity and an velocity of piston P at the instant shown. Use
acceleration shown below, determine the ICR method.
angular acceleration of the rod and the
acceleration of its center G.
2 ft
G
2 ft
vA = 2 ft/s, →
A
aA = 4 ft/s2, → 60º
3. Shaft S rotates gear A with the angular
velocity and angular acceleration with the
direction shown. Gear B and disc C are fixed-
connected and act as a single rigid body. Disc C
and shaft D are connected by a cross belt that 6. The double gear rolls between moving gear
racks B and C. Given the velocities of the gear
does not slip on any surface. Determine the
racks below, determine the velocity of gear
angular velocity and angular acceleration of the
center A and the the angular velocity of the
fan.
double gear.
vB = 18 ft/s
B B
C
D
A
S
ωS = 2 rad/s 2
αS = 4 rad/s 2 ft
A
rA = 4 in rC = 3 in
rB = 5 in rD = 1 in 3 ft
4. A huge cylinder A rolls without slipping at an
angular velocity of 5 rad/s as shown. One end of C
rod BC is connected to the cylinder’s edge and vC = 3 ft/s
its other end slides on the ground. For the
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- ENSC 12 Rectilinear Kinematics of A Particle PDFDocument19 pagesENSC 12 Rectilinear Kinematics of A Particle PDFJeric_QNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Pinoy Henyo WordsDocument1 pagePinoy Henyo WordsJeric_QNo ratings yet
- Physics 51 Review: Module Questions Prepared By: Uplb Ieso and Up AchesDocument26 pagesPhysics 51 Review: Module Questions Prepared By: Uplb Ieso and Up AchesJeric_QNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Prob Set 2 Exam Based Rev1 PDFDocument1 pageProb Set 2 Exam Based Rev1 PDFJeric_QNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- ENSC 12 Rectilinear Kinematics of A Particle PDFDocument19 pagesENSC 12 Rectilinear Kinematics of A Particle PDFJeric_QNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Prob Set 1 (1st Sem 2016) PDFDocument1 pageProb Set 1 (1st Sem 2016) PDFRoxanne de RoxasNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Post Lab Report PDFDocument16 pagesPost Lab Report PDFJeric_QNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- OutlineDocument2 pagesOutlineJeric_QNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Quirona Che 152 W Midrf 2say1617Document4 pagesQuirona Che 152 W Midrf 2say1617Jeric_QNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Chem 112 B 2010Document149 pagesChem 112 B 2010Jeric_QNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Sci PaperDocument11 pagesSci PaperAngela Sietereales RamosNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Chemical Process IndustriesDocument1,013 pagesChemical Process IndustriesHameed Bin Ahmad100% (1)
- QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF THE ACIDITY OF SOFTDRINKS-prelabDocument9 pagesQUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF THE ACIDITY OF SOFTDRINKS-prelabJeric_QNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Rizal's Speech Honoring Luna and HidalgoDocument12 pagesRizal's Speech Honoring Luna and HidalgoJeric_Q0% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Pamphlet of Bower-Barff ProcessDocument68 pagesPamphlet of Bower-Barff ProcessJeric_QNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Effectiveness of ERDB Charcoal Briquette in Sequestrating CarbonDocument2 pagesEffectiveness of ERDB Charcoal Briquette in Sequestrating CarbonAnonymous VNSytXNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Effectiveness of ERDB Charcoal Briquette in Sequestrating CarbonDocument2 pagesEffectiveness of ERDB Charcoal Briquette in Sequestrating CarbonAnonymous VNSytXNo ratings yet
- CodeDocument1 pageCodemur dwiNo ratings yet
- Gr21 EmbragueDocument26 pagesGr21 EmbragueJosue Alvarez VegaNo ratings yet
- SIS News 3500 SeriesDocument56 pagesSIS News 3500 SeriesЕвгений АбрамовNo ratings yet
- Thermal and Structural Analysis of 4-Cylinder Inline EngineDocument10 pagesThermal and Structural Analysis of 4-Cylinder Inline EngineRamzi BrkNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EVI Room Heating Heat Pump - HeatProDocument2 pagesEVI Room Heating Heat Pump - HeatProshibly anastasNo ratings yet
- Partbook PC850SE-8RDocument573 pagesPartbook PC850SE-8RHeng Heng100% (1)
- Karcher K4400G Parts List and Diagram - (1.133-208.0) - eReplacementPartsDocument31 pagesKarcher K4400G Parts List and Diagram - (1.133-208.0) - eReplacementPartsNagaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- EBS e PDFDocument92 pagesEBS e PDFRowan Cornelius100% (2)
- 86-88 GSXR1100 (G, H & J) Parts DiagramDocument155 pages86-88 GSXR1100 (G, H & J) Parts DiagramIgnacio Valderrama Lemos100% (1)
- L404F, T, V Pressuretrol Controllers: FeaturesDocument8 pagesL404F, T, V Pressuretrol Controllers: FeaturesGabriel BustamanteNo ratings yet
- DTS - Course Plan - Iii-BDocument6 pagesDTS - Course Plan - Iii-BDhileepan Kumarasamy100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Axilok InstallatTuercasDocument1 pageAxilok InstallatTuercasalxsscabal100% (1)
- F-720-155 Rev. D Piston & Piston KitsDocument3 pagesF-720-155 Rev. D Piston & Piston KitsСергейИгнатовNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: ZMP 710VDocument2 pagesData Sheet: ZMP 710VJulian FraileNo ratings yet
- Clutch M5S-C9 Manual Transmission Propeller Shaft Rear Differential Rear Axle Suspension Brake Steering System Spare TireDocument24 pagesClutch M5S-C9 Manual Transmission Propeller Shaft Rear Differential Rear Axle Suspension Brake Steering System Spare TireHaris PurnawanNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - 2 Hydraulic Power PacksDocument63 pagesModule 10 - 2 Hydraulic Power PacksJaphet GabatanNo ratings yet
- An Improved Design of A String Hopper Machine To Suit The Local RequirementsDocument1 pageAn Improved Design of A String Hopper Machine To Suit The Local RequirementsAll in OneNo ratings yet
- Active Air Suspension SystemDocument14 pagesActive Air Suspension SystemRoshan SahNo ratings yet
- 2AZ-FE Cooling CO 1-35Document36 pages2AZ-FE Cooling CO 1-35AlelukinNo ratings yet
- Water Heater: Thermo Top Evo Parking HeaterDocument38 pagesWater Heater: Thermo Top Evo Parking Heaterlartsim115100% (1)
- Rheavendors ArquivosDocument87 pagesRheavendors ArquivosAlessandro Capitani FilhoNo ratings yet
- MD ProjectDocument35 pagesMD ProjectDar AkhtNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- SCC GPRGP2Housing InsInstallationDocument8 pagesSCC GPRGP2Housing InsInstallationmanoj_sitecNo ratings yet
- ZOOMLION 40T QY40V Tech Specs PDFDocument30 pagesZOOMLION 40T QY40V Tech Specs PDFvikrantathavaleNo ratings yet
- Current InventoryDocument52 pagesCurrent InventoryCarlos A RomeroNo ratings yet
- C165D6Document4 pagesC165D6WilmerNo ratings yet
- Testing and Commissioning of Starter Panels Variable Frequency Drives VFDsDocument3 pagesTesting and Commissioning of Starter Panels Variable Frequency Drives VFDsHumaid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 0 Pump Citrus Sprayer Bertolini PAS 908.1Document2 pages0 Pump Citrus Sprayer Bertolini PAS 908.1Danilo TorresNo ratings yet
- QA335 - Troca Do Rolamento Da Caixa Da PeneiraDocument52 pagesQA335 - Troca Do Rolamento Da Caixa Da PeneiraGleidson DjalmaNo ratings yet
- Section K: Service Manual - JS200 Asia PacificDocument6 pagesSection K: Service Manual - JS200 Asia PacificKo ZayNo ratings yet