Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hazardous Location Guide: Class I Div 1 Groups A, B, C, D T4
Uploaded by
何吉飞Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazardous Location Guide: Class I Div 1 Groups A, B, C, D T4
Uploaded by
何吉飞Copyright:
Available Formats
Hazardous Location Guide
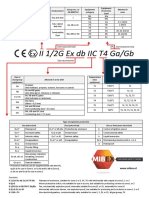
North American Markings (Divisions) ATEX Markings
Class I Div 1 Groups A, B, C, D T4 II (1) GD
Hazardous Atmosphere
Gas/Dust Group Temperature Class Equipment G = Gas
TYPICAL GAS Group D = Dust
A = Acetylene I = Mining
B = Hydrogen industry Equipment Category
C = Ethylene II = Surface
D = Propane industry
Permitted Class III = Surface
TYPICAL DUST dust
Class II = Dust E = Metal Dust
F = Coal Dust (..) = Mounted in safe area
(No group designation) G = Grain Dust No Parentheses = Mounted in hazardous area
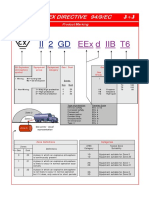
North American Markings (Zones) ATEX / IECEx
Class I Zone 0 A Ex ia IIC T4 Ga [Ex ia] IIC T4 Ga
Permitted Class Conformity to US Equipment Protection Level
Requirements Temperature Class
Brackets
Class II = Dust °C
°C Method of Temperature
Explosion Protection of Protection Class
°C Equipment Gas/Dust Group
°C Protection Level apparatus m = Encapsulation (Zone 0) °C
Method of Protection going into °C
°C IIA = Lowest requirements
m = Encapsulation (Zone 0) °C hazardous °C
gases or vapors (dust cloud) are IIB = Average requirements Ma = Mining “very high”
ia = Intrinsic safety (Zone 0) °C
present continuously or for IIC = Highest requirements
°C
long periods of time ia = Intrinsic safety (Zone 0) Gas/Dust Group apparatus °C
IIIB = Nonconductive dust
mounted in
gases or vapors (dust cloud) are IIA = Lowest requirements IIIC = Conductive dust
hazardous
IIB = Average requirements Ma = Mining “very high”
area.
operating conditions IIC = Highest requirements
gases or vapors (dust cloud) IIIB = Nonconductive dust
IIIC = Conductive dust
normal conditions and if they
do, only for short periods
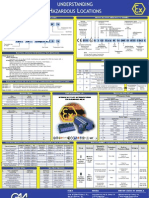
Zone Method Division Method
Enclosure Protection IP Rating Protection Concept Symbol Zones European Std International Std Canadian Std United States Std Division Canadian Std United States Std
Installation Authority — — CENELEC IEC —
Protection Against Ingress of Solids Protection Against Ingress of Liquids
General — — Relevant Safety Std Relevant Safety Std Basic Electrical
0 No protection against live or moving parts 0 No protection
1 1 Protection against drops of condensed Pressurization
Keep the gas away from
(i.e., the hand) — —
2 2 Protection against liquid drops at
° from vertical Encapsulation — — —
3 3 Protection against rain up to
60° from vertical
Powder Filled — — —
4 4 Protection against splashing from any
direction Increased Safety — — —
5 Complete protection against contact 5 Protection against water jets from any
Ingress of dust not in harmful quantities direction under stated conditions
Intrinsic Safety
6 Complete protection against contact 6 Protection against heavy sea water under Nonincendive Techniques
limit the temperature
Protection against ingress of dust stated conditions (C,A,R)
7 Protection against water immersion under
stated conditions of pressure and time — — — Keep dust away from hot surfaces
8 op — — —
dust from optical radiation
NEMA Type Rating and Comparison SAFETY INTREGRITY LEVEL (SIL)
Rating Type IP Code Protection Description
1
2
3
3R SIS SAFETY LIFE-CYCLE PHASES RESIDUAL RISK VS TOLERABLE RISK
3S
4
low medium high
4X
6 IP 67
6P IP 67
RISK ANALYSIS
7 —
8 —
9 —
10 —
12/12K Indoor use, protects against entry of dust, dirt, and dripping water. Protects against noncorrosive liquids.
RISK: NECESSARY RISK REDUCTION:
13 Indoor use, protects against entry of dust, dirt, dripping water, and oil. Protects against noncorrosive liquids.
of harm and the severity of that harm.
Comparison based on tests per IEC 60 529. Cannot be used to convert IP code to type rating
PROCESS RISK: RESIDUAL RISK:
associated with a process.
Typical IS Circuit
TOLERABLE RISK:
Hazardous Area Associated Apparatus Standard Control Equipment Entity Comparison Key Parts to SIL Explanation
SFF The share of the safe faults or safe failures
RISK REDUCTION
V oc
HFT
PFD
Connecting
Cables
C L I sc Tproof The test interval for the entire safety system
Ci + C a SFF=safe failure fraction HFT=hardware fault tolerance PFD=probability of failure on demand Tproof=test interval
Field Instrument Li + L a
Voc
V
Isc
I SAFETY LIFE CYCLE:
Ca
Ci = Internal unprotected capacitance Necessary activities involved in the implementation of
La
Li = Internal unprotected inductance safety instrumented function(s) occurring during a
period of time that starts at the concept phase of a
PEPPERL+FUCHS AND THE PROCESS AUTOMATION MARKET FOR MORE INFORMATION
Receive detailed information on hazardous location protection from the world’s most trusted and respected name in
intrinsic safety. Visit www.pfsolutions.info/hazloc and register to receive the most useful guides you’ll
ever read on hazardous location protection.
INTRINSIC SAFETY BARRIERS
®
for hazardous locations hazardous and corrosive atmospheres The Most Comprehensive Source for Intrinsic Safety:
for intrinsic safety. It includes useful information on installing intrinsically safe
systems, maintenance, applications, and future trends. It also contains a
Custom design and manufacturing for
Industrial solutions for rugged use—VisuNet comprehensive glossary on hazardous location terms.
hazardous locations all product catagories
HART MULTIPLEXERS
Interface products for HART Enclosures and solutions with ATEX, IECEX,
applications with diagnostics
You might also like
- Hazardous Location Guide: Class I Div 1 Groups A, B, C, D T4Document1 pageHazardous Location Guide: Class I Div 1 Groups A, B, C, D T4Er Prem PrincepsNo ratings yet
- Atex A2 WallplannerDocument1 pageAtex A2 WallplannerVishnu LalNo ratings yet
- NEC Poster e PDFDocument1 pageNEC Poster e PDFRahul PatilNo ratings yet
- ATEX IECEX Table B212271ENDocument1 pageATEX IECEX Table B212271ENOlivers CloudNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Chart - E&H PDFDocument2 pagesHazardous Area Chart - E&H PDFBuddy EkoNo ratings yet
- Standards, Zone DefinitionsDocument3 pagesStandards, Zone DefinitionsKhalifa AljahawiNo ratings yet
- Poster Is-EngDocument1 pagePoster Is-EngIsaac AwudiNo ratings yet
- II 1/2G Ex DB IIC T4 Ga/Gb: Internally/externally EPL Internally/externallyDocument2 pagesII 1/2G Ex DB IIC T4 Ga/Gb: Internally/externally EPL Internally/externallyDhananjay BhaldandNo ratings yet
- ATEX Poster-ISDocument1 pageATEX Poster-ISVivek NaikNo ratings yet
- Ex KodlariDocument1 pageEx KodlaridhnsekaranNo ratings yet
- ΑΝΤΙΕΚΡΗΚΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑDocument1 pageΑΝΤΙΕΚΡΗΚΤΙΚΟΤΗΤΑKonstantinos KantzavelosNo ratings yet
- Class I, Zone 1, Aex Ex Eex Ii 2 G: Ed Ed EdDocument1 pageClass I, Zone 1, Aex Ex Eex Ii 2 G: Ed Ed EdHéctor Raúl Bustos BernalNo ratings yet
- FM EXDust HazardPosterDocument1 pageFM EXDust HazardPosterTasawwur TahirNo ratings yet
- Explosion Protection Conform To 2014/34/EU: Ex Ia IIC T6 GaDocument1 pageExplosion Protection Conform To 2014/34/EU: Ex Ia IIC T6 GaMuhammad HannanNo ratings yet
- ATEXDocument1 pageATEXZayar LinnNo ratings yet
- FM EXDust HazardPoster PDFDocument1 pageFM EXDust HazardPoster PDFRicardo CardosoNo ratings yet
- FM EXDust HazardPosterDocument1 pageFM EXDust HazardPostertk2012No ratings yet
- FKS-CLM: Compact Air-Conditioning UnitDocument2 pagesFKS-CLM: Compact Air-Conditioning UnitNicolae VisanNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Locations: Guide To Equipment Certification Requirements ForDocument1 pageHazardous Locations: Guide To Equipment Certification Requirements ForVishnu LalNo ratings yet
- Denah Bangunan Industri KosmetikDocument1 pageDenah Bangunan Industri KosmetikRezky Ramadhan0% (1)
- Marking of Weighing Equipment For Hazardous AreasDocument1 pageMarking of Weighing Equipment For Hazardous AreasJOSE MARIA RedondoNo ratings yet
- ATEX Markings ExplainedDocument6 pagesATEX Markings Explainedceca celsaNo ratings yet
- PPM Task Sheet - LV MaintenanceDocument6 pagesPPM Task Sheet - LV MaintenanceJacobNo ratings yet
- Intertek MarkingsDocument15 pagesIntertek MarkingsAmir MobiniNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Use Of... : Electrical Equipment in Potentially Explosive AtmospheresDocument4 pagesA Guide To The Use Of... : Electrical Equipment in Potentially Explosive AtmospheresAsif Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Important Listing Information: Equipment CertificationDocument6 pagesImportant Listing Information: Equipment Certificationarif_setyaw4nNo ratings yet
- Areas clasificadas-IECDocument1 pageAreas clasificadas-IECChristian ChdNo ratings yet
- Atex MarkingDocument1 pageAtex Markinggangotri05No ratings yet
- Selection of Explosion Protected Equipment For Hazardous LoctionsDocument32 pagesSelection of Explosion Protected Equipment For Hazardous Loctionsasex4uNo ratings yet
- ATEX Plakat Ecom 05-16 enDocument1 pageATEX Plakat Ecom 05-16 enJorge MagneNo ratings yet
- Comparison FM Vs ATEX Flow Chart PDFDocument1 pageComparison FM Vs ATEX Flow Chart PDFGoogool YNo ratings yet
- ATEX Classification Labelling of Electric EquipmentDocument1 pageATEX Classification Labelling of Electric EquipmentLudi D. LunarNo ratings yet
- E2S Guide For Hazardous AreasDocument9 pagesE2S Guide For Hazardous AreasRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Abb Kopex Ex DTS A1 Poster 2018 AwDocument1 pageAbb Kopex Ex DTS A1 Poster 2018 Awmohamed abourayaNo ratings yet
- ATEXGuidelines LowDocument1 pageATEXGuidelines LowalphieNo ratings yet
- Systems: Atex/Iecex Markings ExplainedDocument2 pagesSystems: Atex/Iecex Markings ExplainedZayar LinnNo ratings yet
- Atex Markings ExplainedDocument5 pagesAtex Markings ExplainedBaba JohnehNo ratings yet
- ATEX Markings ExplainedDocument5 pagesATEX Markings Explainedritu sinhaNo ratings yet
- Reflector Led Explosion Proof Clase 1 Div 2 Light-A EpcDocument7 pagesReflector Led Explosion Proof Clase 1 Div 2 Light-A EpcjoelcarhuanchoNo ratings yet
- Wolf Safety Lamp Company - Atex Explained Leaflet Issue March 2018Document1 pageWolf Safety Lamp Company - Atex Explained Leaflet Issue March 2018Dhrubajyoti BoraNo ratings yet
- CSA Group WallchartDocument1 pageCSA Group WallcharttuNo ratings yet
- Exproof Standartlari Karsilastirma Tablosu 20110210 164702Document1 pageExproof Standartlari Karsilastirma Tablosu 20110210 164702HoangNo ratings yet
- CALC - Bungalow - Purlin DesignDocument37 pagesCALC - Bungalow - Purlin Designaxl skid santosNo ratings yet
- Classification of Hazardous AreasDocument26 pagesClassification of Hazardous AreasNaveen ReddyNo ratings yet
- ATEX - Poster - 52245Document1 pageATEX - Poster - 52245Michael WiseNo ratings yet
- Classification Labelling o EquipmentDocument1 pageClassification Labelling o EquipmentAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ashrae D 86142Document1 pageAshrae D 86142ดั๊มพ์ วาสนาทิพย์No ratings yet
- Certification of Mobile Offshore Units (Mous) The Electrical InstallationDocument26 pagesCertification of Mobile Offshore Units (Mous) The Electrical Installation何吉飞No ratings yet
- NR12 - Machinery and Work Equipment Safety - Brazilian NRDocument21 pagesNR12 - Machinery and Work Equipment Safety - Brazilian NR何吉飞No ratings yet
- Norsok - 001Document112 pagesNorsok - 001tkdrt2166100% (1)
- BSL D 5-1 EnglishDocument13 pagesBSL D 5-1 English何吉飞No ratings yet
- Bahamas Merchant Shipping (Crew Accommodation) Regulations 1978Document76 pagesBahamas Merchant Shipping (Crew Accommodation) Regulations 1978何吉飞No ratings yet
- Information Bulletin No. 03Document2 pagesInformation Bulletin No. 03何吉飞No ratings yet
- Explaining ATEX & IECEx Certifications NotesDocument3 pagesExplaining ATEX & IECEx Certifications Notes何吉飞No ratings yet
- T E S C 3 E: YPE Xamination Tatement Ategory QuipmentDocument3 pagesT E S C 3 E: YPE Xamination Tatement Ategory Quipment何吉飞No ratings yet
- Unused Cores in Multi-Core CablesDocument1 pageUnused Cores in Multi-Core Cables何吉飞No ratings yet
- Iec 62040-2-2016Document96 pagesIec 62040-2-2016何吉飞100% (1)
- 2's Complement Division C++ ProgramDocument11 pages2's Complement Division C++ ProgramAjitabh Gupta100% (2)
- Micro TeachingDocument3 pagesMicro Teachingapi-273530753No ratings yet
- Ob AssignmntDocument4 pagesOb AssignmntOwais AliNo ratings yet
- GooseberriesDocument10 pagesGooseberriesmoobin.jolfaNo ratings yet
- Fix Problems in Windows SearchDocument2 pagesFix Problems in Windows SearchSabah SalihNo ratings yet
- Death and The King's Horseman AnalysisDocument2 pagesDeath and The King's Horseman AnalysisCelinaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Ethical Dilemma?: Decision-Making ProcessDocument7 pagesWhat Is An Ethical Dilemma?: Decision-Making ProcessGauravsNo ratings yet
- Dumont's Theory of Caste.Document4 pagesDumont's Theory of Caste.Vikram Viner50% (2)
- ANI Network - Quick Bill Pay PDFDocument2 pagesANI Network - Quick Bill Pay PDFSandeep DwivediNo ratings yet
- Https Emedicine - Medscape.com Article 1831191-PrintDocument59 pagesHttps Emedicine - Medscape.com Article 1831191-PrintNoviatiPrayangsariNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be ExerciseDocument6 pagesVerb To Be Exercisejhon jairo tarapues cuaycalNo ratings yet
- Placement TestDocument6 pagesPlacement TestNovia YunitazamiNo ratings yet
- Panlilio vs. Regional Trial Court, Branch 51, City of ManilaDocument10 pagesPanlilio vs. Regional Trial Court, Branch 51, City of ManilaMaria Nicole VaneeteeNo ratings yet
- MEAL DPro Guide - EnglishDocument145 pagesMEAL DPro Guide - EnglishkatlehoNo ratings yet
- Sabbir 47MDocument25 pagesSabbir 47MMd.sabbir Hossen875No ratings yet
- Role of Commodity Exchange in Agricultural GrowthDocument63 pagesRole of Commodity Exchange in Agricultural GrowthSoumyalin Santy50% (2)
- Review Questions & Answers For Midterm1: BA 203 - Financial Accounting Fall 2019-2020Document11 pagesReview Questions & Answers For Midterm1: BA 203 - Financial Accounting Fall 2019-2020Ulaş GüllenoğluNo ratings yet
- Kozier Erbs Fundamentals of Nursing 8E Berman TBDocument4 pagesKozier Erbs Fundamentals of Nursing 8E Berman TBdanie_pojNo ratings yet
- Hanumaan Bajrang Baan by JDocument104 pagesHanumaan Bajrang Baan by JAnonymous R8qkzgNo ratings yet
- Cct4-1causal Learning PDFDocument48 pagesCct4-1causal Learning PDFsgonzalez_638672wNo ratings yet
- OPSS 415 Feb90Document7 pagesOPSS 415 Feb90Muhammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Jewish Standard, September 16, 2016Document72 pagesJewish Standard, September 16, 2016New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet
- Post Cold WarDocument70 pagesPost Cold WarZainab WaqarNo ratings yet
- Tesmec Catalogue TmeDocument208 pagesTesmec Catalogue TmeDidier solanoNo ratings yet
- ENTRAPRENEURSHIPDocument29 pagesENTRAPRENEURSHIPTanmay Mukherjee100% (1)
- ANSI-ISA-S5.4-1991 - Instrument Loop DiagramsDocument22 pagesANSI-ISA-S5.4-1991 - Instrument Loop DiagramsCarlos Poveda100% (2)
- 1-Gaikindo Category Data Jandec2020Document2 pages1-Gaikindo Category Data Jandec2020Tanjung YanugrohoNo ratings yet
- Allen F. y D. Gale. Comparative Financial SystemsDocument80 pagesAllen F. y D. Gale. Comparative Financial SystemsCliffordTorresNo ratings yet
- Lower Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument1 pageLower Gastrointestinal Bleedingmango91286No ratings yet
- Cabot - Conductive Carbon Black For Use in Acrylic and Epoxy CoatingsDocument2 pagesCabot - Conductive Carbon Black For Use in Acrylic and Epoxy CoatingsLin Niu0% (1)