Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ENTJ-2007-07 - Laryngeal Squamous Papilloma
Uploaded by
Maulana MalikOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ENTJ-2007-07 - Laryngeal Squamous Papilloma
Uploaded by
Maulana MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
PATHOLOGY CLINIC
Laryngeal squamous papilloma
Lester D.R. Thompson, MD, FASCP
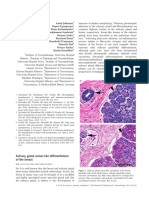
Figure. A: Multiple papillary projections arise from the surface. B: Koilocytic atypia exhibits crenated
nuclei surrounded by clear cytoplasm. Prominent cellular borders are seen at the surface of this squa-
mous papilloma.
Squamous papilloma (SP) is the most common benign parabasal cell hyperplasia with perpendicular orientation
laryngeal tumor. It is caused by the human papillomavirus. of the nuclei to the basement membrane. There may be
Clinically, SP rarely occurs as a solitary lesion; most arise a slight flattening at the surface with focal parakeratosis.
as multiple, recurrent tumors, usually in children. SPs gen- Mitotic figures are usually easy to identify, and are not
erally originate in the true and false vocal folds; they may atypical. Koilocytosis (wrinkled, hyperchromatic nuclei
spread to other sites in the oral cavity and aerodigestive surrounded by a cleared halo in cells with a well-defined
tract. They form at the juxtaposition of the squamous and cell border) is characteri stic of SP (figure, B). The major
respiratory epithelia. If an area ofjuxtaposition is artificially differential diagnoses are between papillary dysplasia
induced (such as by squamous metaplasia), spread of the and squamous cell carcinoma, both of which have more
disease may result. There is a characteristic bimodal age significant pleomorphism.
distribution, with a juvenile peak at 5 years and an adult The clinical course of patients with SP is unpredictable.
peak between 20 and 40 years . The disease course tends Even though SP is benign, mortality rates as high as 14%
to be more aggressive in children, who frequently develop have been reported. Surgery-frequently multiple proce-
recurrent and progressive disease. The relatively small dure s-is the mainstay of treatment, although additional
diameter of the airways in children may account for some medical therapies show promise.
of the severe respiratory embarrassment they experience.
There is a slight male predominance in adults. Patients Suggested reading
usually present with dysphonia and hoarseness. Derkay CS. Recu rrent respirator y papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 200 I;
111(1):57-69 .
Macroscopically, SPs are exophytic, branching, pe-
Gale N. Papilloma-papillomatosis. In: Barne s EL, Michael L, eds. Pa-
dunculated, or broad-based lesions. They are character- tholo gy and Geneti cs of Tumours of the Head and Neck. Kliehue s
ized by multiple branching mucosal projections that are P, Sobin LH, series eds. World Health Organi zation Classification
made up of hyperplastic squamous epithelium overlying of Tum ours. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2005: 147-8.
thin fibrovascular cores (figure, A). There is basal and
From the Department of Pathology, Woodland Hills Medic al Center, Southern California Perm anent e Medic al Group , Woodl and Hills, Calif.
Volume 86, Number 7 379
You might also like
- Atypical Spitz Tumors: A Diagnostic ChallengeDocument8 pagesAtypical Spitz Tumors: A Diagnostic ChallengeCristi PopescuNo ratings yet
- Cervicofacial LymphangiomasDocument11 pagesCervicofacial LymphangiomasCharmila Sari100% (1)
- Benign and Malignant Neoplasia of URTDocument48 pagesBenign and Malignant Neoplasia of URTsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- Infantile Hemangiomas: A Review: Pediatric Ophthalmology UpdateDocument9 pagesInfantile Hemangiomas: A Review: Pediatric Ophthalmology UpdateYipno Wanhar El MawardiNo ratings yet
- Nodular Swelling of The Buccal Mucosa: Clinical PresentationDocument7 pagesNodular Swelling of The Buccal Mucosa: Clinical Presentationotoralla1591No ratings yet
- Leung2004-Childhood Cervical LymphadenopathyDocument5 pagesLeung2004-Childhood Cervical LymphadenopathyCamilo Suescun NavarroNo ratings yet
- PVH OrofaringeDocument9 pagesPVH OrofaringeAna Cristina Gómez RíosNo ratings yet
- Ncbi Sinonasal IPDocument5 pagesNcbi Sinonasal IPReza RahadianNo ratings yet
- Epulis KongenitalDocument3 pagesEpulis KongenitalFriadi NataNo ratings yet
- Neoplasias SebaceasDocument25 pagesNeoplasias SebaceasKAREN ROCIO LATORRE RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 Epithelial PathoDocument10 pagesLecture 21 Epithelial PathoSRO oONo ratings yet
- Pathophysio HPVs Fall Into Different Subgroups With A Predilection For Arising From Either Mucosal Surfaces or The SkinDocument2 pagesPathophysio HPVs Fall Into Different Subgroups With A Predilection For Arising From Either Mucosal Surfaces or The SkinOstazNo ratings yet
- Rabdomyosarcoma Case ReportDocument7 pagesRabdomyosarcoma Case ReportAaslesha Jakkampudi100% (1)
- Congenital Epulis in A Newborn: A Case Report, Immunoprofiling and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesCongenital Epulis in A Newborn: A Case Report, Immunoprofiling and Review of LiteratureanggunNo ratings yet
- Pathologic Quiz Case: Ovarian Mass in A 2-Year-Old Girl Presenting With Pleural EffusionsDocument4 pagesPathologic Quiz Case: Ovarian Mass in A 2-Year-Old Girl Presenting With Pleural EffusionsMateen ShukriNo ratings yet
- Lymphangioma of The Dorsal TongueDocument4 pagesLymphangioma of The Dorsal TongueLaila FortunatoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledShintaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Chest ImagingDocument211 pagesPediatric Chest ImagingluisalejocmNo ratings yet
- Cancer de Testiculo e Down 2Document4 pagesCancer de Testiculo e Down 2paulinhamericoNo ratings yet
- Parotid MassDocument9 pagesParotid MassAndre Eka Putra PrakosaNo ratings yet
- Retropharyngeal AbscessDocument3 pagesRetropharyngeal AbscessDwi Utari PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Neck Mass ProtocolDocument8 pagesNeck Mass ProtocolCharlene FernándezNo ratings yet
- An Approach To The Neck Masses: BY: Hardi H. QaderDocument49 pagesAn Approach To The Neck Masses: BY: Hardi H. QaderEmad AlryashiNo ratings yet
- Lateral Neck SwellingDocument62 pagesLateral Neck Swellingசுபத்ரா சந்திரசேகர்No ratings yet
- Nevus Spitz - Everlasting Diagnostic Difficulties - The ReviewDocument6 pagesNevus Spitz - Everlasting Diagnostic Difficulties - The ReviewCristi PopescuNo ratings yet
- Craniopharyngioma: Case SummaryDocument3 pagesCraniopharyngioma: Case SummaryeugeniaNo ratings yet
- Squamous Epithelial Changes of The Larynx: Diagnosis and TherapyDocument8 pagesSquamous Epithelial Changes of The Larynx: Diagnosis and TherapyIsrael BlancoNo ratings yet
- 50 PDFDocument2 pages50 PDFiqbalNo ratings yet
- HPV Molecular Biology and Disease Association: Abbreviations UsedDocument4 pagesHPV Molecular Biology and Disease Association: Abbreviations UsedAulia Rahman AmbiyaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Desmoid Fibromatosis of TheDocument4 pagesPediatric Desmoid Fibromatosis of ThevatankhahpooyaNo ratings yet
- Anancephaly 2Document3 pagesAnancephaly 2Metta SariNo ratings yet
- Squamous Papilloma On Hard Palate: Case Report and Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesSquamous Papilloma On Hard Palate: Case Report and Literature ReviewadelNo ratings yet
- Caso Radiculitis TBCDocument3 pagesCaso Radiculitis TBCBatgirl xoxoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Lobar EmphysemaDocument4 pagesCongenital Lobar EmphysemaIjahss JournalNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma of NasopharynxDocument15 pagesCarcinoma of NasopharynxAmeliana KamaludinNo ratings yet
- Update On Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Ó Humana 2007Document6 pagesUpdate On Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Ó Humana 2007Zakia AjaNo ratings yet
- Wolvius 1996Document3 pagesWolvius 1996pamela queirozNo ratings yet
- Correos Electrónicos Lisan2016Document5 pagesCorreos Electrónicos Lisan2016Cesar Mauricio Daza CajasNo ratings yet
- Keratoses IIDocument83 pagesKeratoses IIGomogi SouqNo ratings yet
- 80-Article Text-153-1-10-20161118Document4 pages80-Article Text-153-1-10-20161118Rania SalwanabilaNo ratings yet
- Articulo 3Document23 pagesArticulo 3Kari SanguilNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma (JNA)Document19 pagesJuvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma (JNA)YogiHadityaNo ratings yet
- Glandula Salivar HeterotopicaDocument2 pagesGlandula Salivar HeterotopicaJuan Esteban RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pararapharyngeal Schwannoma Arising From Lingual Nerve: (A Rare Case Report) AbstractDocument4 pagesPararapharyngeal Schwannoma Arising From Lingual Nerve: (A Rare Case Report) AbstractDivyanisaAvantikaRahayuNo ratings yet
- Update On Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma: ReviewDocument4 pagesUpdate On Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma: ReviewPhn StanleyNo ratings yet
- NHL BaileyDocument26 pagesNHL BaileyFitria WaffiNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Management of Parapharyngeal TumorsDocument5 pagesContemporary Management of Parapharyngeal TumorsSilvia SoareNo ratings yet
- Phleboliths and The Vascular Maxillofacial LesionDocument4 pagesPhleboliths and The Vascular Maxillofacial LesionVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Develpmental Lung AnomaliDocument11 pagesDevelpmental Lung AnomaliSiti Amalia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- KalmarDocument8 pagesKalmarKING COMICNo ratings yet
- Acino in BreastDocument2 pagesAcino in BreastDima PathNo ratings yet
- Spindle Cell LesionsDocument8 pagesSpindle Cell LesionsdrmanishsharmaNo ratings yet
- SWAIMANDocument18 pagesSWAIMANVan John MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Oral Squamous Papilloma in A Pediatric Patient A Case ReportDocument4 pagesOral Squamous Papilloma in A Pediatric Patient A Case Reportaulia lubisNo ratings yet
- Hamartomatous Polyposis Syndromes: A ReviewDocument10 pagesHamartomatous Polyposis Syndromes: A ReviewDaniel Marin AriasNo ratings yet
- 2006 A Suprarenal Mass in A Child. Pulmonary Sequestration. EJPDocument3 pages2006 A Suprarenal Mass in A Child. Pulmonary Sequestration. EJPJoseloNo ratings yet
- Friedberg 1940Document14 pagesFriedberg 1940YPramudiyaNo ratings yet
- BurgDocument16 pagesBurgGrazyele SantanaNo ratings yet
- The Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our Children, Expanded and Revised EditionFrom EverandThe Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our Children, Expanded and Revised EditionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- The Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our ChildrenFrom EverandThe Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our ChildrenRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (8)
- Use of Dyes in OphthalmologyDocument4 pagesUse of Dyes in OphthalmologyMaulana MalikNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis or Laryngeal PapillomatosisDocument4 pagesRecurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis or Laryngeal PapillomatosisMaulana MalikNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal Papillomatosis: Morphological Study by Light and Electron Microscopy of The HPV-6Document5 pagesLaryngeal Papillomatosis: Morphological Study by Light and Electron Microscopy of The HPV-6emilia candraNo ratings yet
- Reccurent Laryngeal Papilloma: Case ReportDocument4 pagesReccurent Laryngeal Papilloma: Case ReportMaulana MalikNo ratings yet
- Fluorescein Dye Concentration As A Factor in Tear Film FluorescenceDocument5 pagesFluorescein Dye Concentration As A Factor in Tear Film FluorescenceMaulana MalikNo ratings yet
- Ipi350425 PDFDocument7 pagesIpi350425 PDFaderiaNo ratings yet
- 2 Teksbook PDFDocument556 pages2 Teksbook PDFNurlatifah Almaida AmalNo ratings yet
- Encopresis in Children An Overview of Recent FindiDocument5 pagesEncopresis in Children An Overview of Recent FindiMaulana MalikNo ratings yet
- Classification of Anemias: What Is Anemia, How Do You Diagnose Anemia, and How Are The Different Anemias Classified?Document78 pagesClassification of Anemias: What Is Anemia, How Do You Diagnose Anemia, and How Are The Different Anemias Classified?Kaushik BhuvaNo ratings yet
- SLEDAIDocument2 pagesSLEDAIKomang Adhi AmertajayaNo ratings yet
- BHF Cardiac ArrestDocument4 pagesBHF Cardiac ArrestEdi Saputra SNo ratings yet
- SLEDAIDocument2 pagesSLEDAIKomang Adhi AmertajayaNo ratings yet
- Scope and Framewrok of Nursing PracticeDocument13 pagesScope and Framewrok of Nursing PracticeAru VermaNo ratings yet
- Cytology Project in 18 PageDocument17 pagesCytology Project in 18 PageAnil Amrawanshi67% (3)
- Important Information and AIHM Application Form For Overseas Applicants Revised v050412 VPDocument16 pagesImportant Information and AIHM Application Form For Overseas Applicants Revised v050412 VPWalter TripNo ratings yet
- Modified Trauma ScoringDocument63 pagesModified Trauma ScoringparuNo ratings yet
- Sample Case Analysis UuDocument7 pagesSample Case Analysis UuLailiWafaNo ratings yet
- Useful Websites For Medical StudentsDocument1 pageUseful Websites For Medical StudentsRakesh DudiNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Congestion Secondary To PneumoniaDocument104 pagesPulmonary Congestion Secondary To PneumoniaAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Author: Tuazon, Josefina A. RN, BSN, MN, DRPH: Learning Objective 1: Appreciate OneDocument6 pagesAuthor: Tuazon, Josefina A. RN, BSN, MN, DRPH: Learning Objective 1: Appreciate OneJohn Robert PescadorNo ratings yet
- Resume For Health HubDocument1 pageResume For Health Hubapi-490093193No ratings yet
- He Ma To Pathology MilestonesDocument21 pagesHe Ma To Pathology MilestonesCristyan David Quintero MuneraNo ratings yet
- Ede QDocument5 pagesEde Qapi-286166842No ratings yet
- Decubitus Ulcer: Presenters: Angod, Lady Aizahlyn I. Apat, Joselle Janina F. Araune, Trixie Mariel EDocument32 pagesDecubitus Ulcer: Presenters: Angod, Lady Aizahlyn I. Apat, Joselle Janina F. Araune, Trixie Mariel EXaxa AngodNo ratings yet
- Jurnal SinusitisDocument49 pagesJurnal SinusitisAramanda Dian100% (1)
- Cephalothin SodiumDocument6 pagesCephalothin SodiumBeans JohnNo ratings yet
- High Risk Babies Resuscitation Stabilitation and Management IDAIDocument23 pagesHigh Risk Babies Resuscitation Stabilitation and Management IDAIaulianaNo ratings yet
- Jenny E. Pennycuff, M.D., M.S.: Present PositionDocument10 pagesJenny E. Pennycuff, M.D., M.S.: Present Positionapi-625759582No ratings yet
- ShiJiang LuDocument20 pagesShiJiang LuSinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management Systems and Patients Records Management in RwandaDocument86 pagesHospital Management Systems and Patients Records Management in RwandaMsc Celestin NiyonizigiyeNo ratings yet
- Garcin2018 PDFDocument9 pagesGarcin2018 PDFjoao marcelo lealNo ratings yet
- Canadas Physician ShortageDocument11 pagesCanadas Physician ShortageFion LamNo ratings yet
- NABH Quality ConnectDocument16 pagesNABH Quality ConnectNeeraj JoshiNo ratings yet
- Egg Allergy - Management - UpToDateDocument17 pagesEgg Allergy - Management - UpToDatealinaNo ratings yet
- AfricanDiasporaConferenceBooklet v2Document72 pagesAfricanDiasporaConferenceBooklet v2AKNTAI002No ratings yet
- FREUDDocument6 pagesFREUDIsai LVazquezNo ratings yet
- MGR MPT SyllabusDocument3 pagesMGR MPT Syllabusvictor_venki9955No ratings yet
- ptj4008504 PDFDocument8 pagesptj4008504 PDFDiva VashtiNo ratings yet
- Em Coding TablesDocument2 pagesEm Coding Tablesapi-270179959No ratings yet
- Directory Update July. 2012Document208 pagesDirectory Update July. 2012Raj KamalNo ratings yet
- Auditing of AuditDocument2 pagesAuditing of AuditMeli N DaNo ratings yet
- Classic Imaging Signs A Guide To The Whole Body - 1stDocument382 pagesClassic Imaging Signs A Guide To The Whole Body - 1stclaudiuNo ratings yet