0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views62 pagesAcd 13 PDF
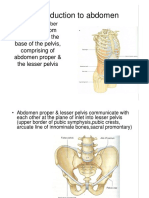
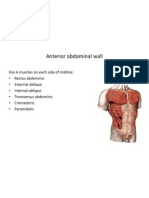
The document describes the anatomy of the abdominal wall and inguinal region. It discusses the boundaries and quadrants of the abdominal wall, as well as the nine abdominal regions. It then covers the neurovascular supply, lymphatic drainage, muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the rectus sheath, common incisions, and the inguinal canal.
Uploaded by
Igor AnsoffCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views62 pagesAcd 13 PDF
The document describes the anatomy of the abdominal wall and inguinal region. It discusses the boundaries and quadrants of the abdominal wall, as well as the nine abdominal regions. It then covers the neurovascular supply, lymphatic drainage, muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the rectus sheath, common incisions, and the inguinal canal.
Uploaded by
Igor AnsoffCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd