Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and Unemployment PDF
Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and Unemployment PDF
Uploaded by
Shyam Kumar BanikOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and Unemployment PDF
Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and Unemployment PDF
Uploaded by
Shyam Kumar BanikCopyright:
Available Formats
Warning: These handouts are NOT a substitute for class lectures.
ALL concepts and examples illustrated
in class are required for the Midterm Exam!!!
Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and Unemployment
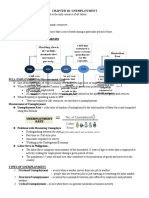
Labor Market Indicators – These show the condition of the labor market. There are 3 types of labor
market indicators:
1. Unemployment Rate
2. Labor Force Participation Rate
3. Employment-to-Population Ratio
Unemployment Rate – Indicates the extent to which people who want jobs can’t find them.
Unemployment Rate = No. of People Unemployed x 100%
Civilian Labor Force
Where,
Civilian Labor Force = No. of people Employed + No. of people Unemployed
Labor Force Participation Rate – Percentage of Civilian Non-institutional population who are
members of the labor force. It indicates the willingness of people of working age to take jobs.
Labor Force Participation Rate = Civilian Labor Force x 100%
Civilian Non-Institutional Population
Employment-to-Population Ratio – Percentage of people of working age who have jobs. It
indicates availability of jobs and degree of match between people’s skills and jobs.
Employment to = No. of people Employed x 100%
Population Ratio Civilian Non-Institutional Population
Increase in the employment-to-population ratio means the economy has created jobs at a
faster rate than the civilian non-institutional population has grown. Its fluctuations are in the
opposite direction to changes in the unemployment rate. It falls during recession and
increases during expansion.
Sources of Unemployment:
Unemployment can occur in the following ways:
1. Job losers
2. Job leavers
3. Entrants into the Labor Force
4. Re-entrants into the Labor Force
Duration of Unemployment: Average duration of unemployment varies over the business cycle.
ECO104: Introduction to Macroeconomics
Faculty: Raisa Afsana (RsA)
Warning: These handouts are NOT a substitute for class lectures. ALL concepts and examples illustrated
in class are required for the Midterm Exam!!!
Demographics of Unemployment:
Unemployment is highest among young workers and ethnic minorities
High rates of job turnover among the young
Most young people are hired as temporary workers higher job loss
Types of Unemployment:
1. Frictional Unemployment – This is created from people entering and leaving the labor force
and the ongoing creation and destruction of jobs. It arises due to job searching by individuals
and firms and is a healthy sign of a growing economy. However, this is often induced and
prolonged by unemployment benefits and unemployment insurance.
2. Structural Unemployment – This arises from change in skills needed to perform jobs, due to
technological changes or international competition. Duration is usually longer than frictional
unemployment because workers need to re-train or re-locate. It can be a serious long-term
problem and affects older workers the most.
3. Cyclical Unemployment – This occurs due to the business cycle. It increases during recession
and decreases during expansion.
Full Employment Level of Unemployment:
This is also known as the “Natural Rate of Unemployment”
There is no cyclical unemployment
All unemployment is either structural or frictional
Real
GDP
Potential
GDP
Actual
GDP
Unemployment Rate fluctuates around the
Natural Rate of Unemployment as real GDP
fluctuates around potential GDP.
Year
Real GDP equals Potential GDP when there is
Unemployment full employment (i.e. unemployment rate
Rate equals to natural rate of unemployment)
If Unemployment < Natural Rate,
Real GDP > Potential GDP
Unemployment If Unemployment > Natural Rate,
Rate Real GDP < Potential GDP
Natural Rate of
Unemployment
Year
ECO104: Introduction to Macroeconomics
Faculty: Raisa Afsana (RsA)
You might also like
- International Economics 9th Edition Appleyard Test BankDocument10 pagesInternational Economics 9th Edition Appleyard Test Banka159411610100% (1)
- Wedding Service Expo (2019190032)Document57 pagesWedding Service Expo (2019190032)phyu treza100% (1)
- Measuring Employment and UnemploymentDocument2 pagesMeasuring Employment and UnemploymentMohammad A. HasanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Monitoring Jobs and InflationDocument5 pagesMacroeconomics Monitoring Jobs and InflationJoeNo ratings yet
- Unemployment and Inflation: Krugman/WellsDocument55 pagesUnemployment and Inflation: Krugman/WellsTine RobisoNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Lecturer: Mr. AllicockDocument73 pagesMacroeconomics: Lecturer: Mr. AllicockPrecious MarksNo ratings yet
- Marxist Theory of UnemploymentDocument5 pagesMarxist Theory of UnemploymentSON OF WRATH HOLLOW POLNo ratings yet
- LunemploymentDocument27 pagesLunemploymentmayadaNo ratings yet
- BSF II Lecture Notes On Unemployment - Money and Banking and IT - AY 2016-17Document27 pagesBSF II Lecture Notes On Unemployment - Money and Banking and IT - AY 2016-17Jeff SmithNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 and 4 Unemployment and Inflation (Student)Document54 pagesLecture 3 and 4 Unemployment and Inflation (Student)cuteserese roseNo ratings yet
- Jobs and UnemploymentDocument4 pagesJobs and Unemploymentelvira evy edwardNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Unemployment (Updated 15 May 2017)Document12 pagesTopic 7 Unemployment (Updated 15 May 2017)Arun GhatanNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Jobs and InflationDocument2 pagesMonitoring Jobs and InflationNovi AlbitaNo ratings yet
- Costs of UnemploymentDocument15 pagesCosts of UnemploymentNandy Raghoo GopaulNo ratings yet
- Business Cycle and UnemploymentDocument20 pagesBusiness Cycle and UnemploymentTomasina Portia OrteaNo ratings yet
- (Econ) UnemploymentDocument10 pages(Econ) UnemploymentTricia KiethNo ratings yet
- Indian Eco Dev 2Document11 pagesIndian Eco Dev 2Badavath JeethendraNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Principles of Economics Course Code: Eco 205W Topic: UnemploymentDocument7 pagesCourse Title: Principles of Economics Course Code: Eco 205W Topic: UnemploymentHoripriya Das ArpitaNo ratings yet
- CH 5 UnemploymentDocument37 pagesCH 5 UnemploymentMattin SharifNo ratings yet
- Theme 5 Unemployment and InflationDocument19 pagesTheme 5 Unemployment and InflationNadineNo ratings yet
- Employment and UnemploymentDocument8 pagesEmployment and Unemploymentдаша синицкаяNo ratings yet
- Unemployment: DR G K KalkotiDocument18 pagesUnemployment: DR G K KalkotiSanket HirlekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Employment Growth Informalisation and Other Issues 2Document47 pagesChapter 7 Employment Growth Informalisation and Other Issues 2Lavina GurbaniNo ratings yet
- 08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, InflationDocument3 pages08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, Inflationcatherine tucayNo ratings yet
- Report RPHDocument4 pagesReport RPHDela Cruz, Carlie Belle, F.No ratings yet
- Eco PTT 2Document1 pageEco PTT 2angelinstanley2003No ratings yet
- Effects of Unemployment On EconomyDocument19 pagesEffects of Unemployment On EconomyJeet SummerNo ratings yet
- ECON - CH 02 P-II Macro Economics ProblemsDocument51 pagesECON - CH 02 P-II Macro Economics ProblemsHanaMengstu IelremaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesDocument35 pagesTheories of Employment and Income: Learning Objectivesmuhammedsadiq abdullaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two, Final Labour Supply NoteDocument21 pagesChapter Two, Final Labour Supply NoteBereket DesalegnNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 UnemploymentDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 10 UnemploymentApril CaringalNo ratings yet
- Session 11 Unemployment Phillips CurveDocument8 pagesSession 11 Unemployment Phillips CurveGeo VargheseNo ratings yet
- Part-1 - Prices and Unemployment-02Document8 pagesPart-1 - Prices and Unemployment-02Manish NepaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Marcro EconomicsDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Marcro Economicsjimcaalemaxamed3469No ratings yet
- Unemployment: Unit HighlightsDocument22 pagesUnemployment: Unit HighlightsprabodhNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Dec 2022Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 25 Dec 2022Archita VermaNo ratings yet
- Ec12 Ch9inflationunemploymentDocument19 pagesEc12 Ch9inflationunemploymentapi-378150162No ratings yet
- Module 3 - UnemploymentDocument32 pagesModule 3 - Unemploymentnmkanjoo2743No ratings yet
- Chapter-7: Unemployment: Course Teacher: Dr. Tamgid Ahmed Chowdhury Associate Professor, SbeDocument23 pagesChapter-7: Unemployment: Course Teacher: Dr. Tamgid Ahmed Chowdhury Associate Professor, SbeAfiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Marxist Theory of UnemploymentDocument4 pagesMarxist Theory of UnemploymentSON OF WRATH HOLLOW POLNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.macromeasures PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 2.macromeasures PDFGwyneth MalagaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 UnemploymentDocument23 pagesTopic 5 Unemploymentlacthien912No ratings yet
- Un EmploymentDocument13 pagesUn EmploymentmaalikanserNo ratings yet
- Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation MC Connell Brue and Flynn-Chapter 26Document35 pagesBusiness Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation MC Connell Brue and Flynn-Chapter 26Ujayer BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Unemployment PEC100110 Principles of Economics UNILAKDocument10 pagesUnit 9 Unemployment PEC100110 Principles of Economics UNILAKalexisNo ratings yet
- Unemployment 1Document18 pagesUnemployment 1Hans MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual 1christophermortondorsfbgati100% (26)
- UnemploymentDocument30 pagesUnemploymentNorman StricksonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 UnemploymentDocument31 pagesLecture 3 Unemploymentephraim chisangaNo ratings yet
- Department of Social Work Visva-Bharati Sriniketan: Presentation On Unemployment in IndiaDocument13 pagesDepartment of Social Work Visva-Bharati Sriniketan: Presentation On Unemployment in IndiaRafikul HossainNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 13Document4 pagesLesson Proper For Week 13Sh1njo SantosNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Jobs and InflationDocument51 pagesMonitoring Jobs and InflationPetrinaNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 UnemploymentDocument3 pages2.1.3 Unemploymentfpd06972No ratings yet
- Module7 - UnemploymentDocument27 pagesModule7 - UnemploymentMaybelyn de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Theories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesTheories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesBabarNo ratings yet
- The Problem of Unemployment, Poverty and Inequality: Module - 2Document15 pagesThe Problem of Unemployment, Poverty and Inequality: Module - 2Double A CreationNo ratings yet
- Asis 4 PEDocument14 pagesAsis 4 PEsilviana maharaniNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document2 pagesTopic 4Patricia PaminsaranNo ratings yet
- Instructors - Manual - With - Solutions - Manual 15 16Document18 pagesInstructors - Manual - With - Solutions - Manual 15 16OLFA ALOUININo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Sumeet BihaniDocument18 pagesPrepared By: Sumeet Bihanibatman2407No ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - UnemploymentDocument14 pagesLecture 14 - Unemploymentzahra naheedNo ratings yet
- A Way Out of No Way: The Economic Prerequisites of the Beloved CommunityFrom EverandA Way Out of No Way: The Economic Prerequisites of the Beloved CommunityNo ratings yet
- North South University: TitleDocument11 pagesNorth South University: TitleJntNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment: Jannatul Nayeem NSU ID: 1611482030 BUS 173.4 Spring 2020Document28 pagesFinal Assignment: Jannatul Nayeem NSU ID: 1611482030 BUS 173.4 Spring 2020JntNo ratings yet
- Pol 101Document3 pagesPol 101JntNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment: Jannatul Nayeem NSU ID: 1611482030 ECO 104.11 Spring 2020Document9 pagesFinal Assignment: Jannatul Nayeem NSU ID: 1611482030 ECO 104.11 Spring 2020JntNo ratings yet
- Experiment DesignDocument13 pagesExperiment DesignJnt100% (1)
- Jannatul Nayeem 1611482030 MKT 460.5 Spring 2020 Final Assignment PDFDocument27 pagesJannatul Nayeem 1611482030 MKT 460.5 Spring 2020 Final Assignment PDFJntNo ratings yet
- His 101 Lecture 1 Introduction To HistoryDocument46 pagesHis 101 Lecture 1 Introduction To HistoryJntNo ratings yet
- Jannatul Nayeem 1611482030 Section 5 PDFDocument6 pagesJannatul Nayeem 1611482030 Section 5 PDFJntNo ratings yet
- Economic History of Bengal 3 PDFDocument37 pagesEconomic History of Bengal 3 PDFJntNo ratings yet
- Designing An ExperimentDocument6 pagesDesigning An ExperimentJntNo ratings yet
- 2 The British Impact On India, 1700-1900 PDFDocument4 pages2 The British Impact On India, 1700-1900 PDFJntNo ratings yet
- HIS 101 Courseoutline Mab2Document4 pagesHIS 101 Courseoutline Mab2JntNo ratings yet
- Bengal Renaissance 1 PDFDocument21 pagesBengal Renaissance 1 PDFJntNo ratings yet
- Suggestive Questions-Final Fall 19Document1 pageSuggestive Questions-Final Fall 19JntNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument2 pagesMethodologyJntNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Theories and ModelsDocument12 pagesConsumer Behaviour Theories and ModelsJntNo ratings yet
- MGT368Document3 pagesMGT368JntNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Presented To Wasif Sayeed Choudhury Lecturer North South UniversityDocument29 pagesOperations Management: Presented To Wasif Sayeed Choudhury Lecturer North South UniversityJntNo ratings yet
- Situation Analysis (Swot) : Strength WeaknessDocument13 pagesSituation Analysis (Swot) : Strength WeaknessJntNo ratings yet
- Omnichannel - Team JediDocument14 pagesOmnichannel - Team JediJntNo ratings yet
- Course Code: Mgt368.9: Date: 27/11/2019Document19 pagesCourse Code: Mgt368.9: Date: 27/11/2019JntNo ratings yet
- CH 14 HandoutDocument6 pagesCH 14 HandoutJntNo ratings yet
- Presenting The Textbook's Case Study On East Asia: Success and Crisis'Document36 pagesPresenting The Textbook's Case Study On East Asia: Success and Crisis'Tâm TâmNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy NotesDocument5 pagesFiscal Policy NotesJaydenausNo ratings yet
- Mount of Olives College Kakiri: InstructionsDocument28 pagesMount of Olives College Kakiri: InstructionsKaka JamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - THE GLOBALIZATION OF WORLD ECONOMICSDocument7 pagesLesson 2 - THE GLOBALIZATION OF WORLD ECONOMICSAle EalNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis - FDI in IndiaDocument6 pagesSWOT Analysis - FDI in IndianeelmtiwariNo ratings yet
- AAIB Fixed Income Fund (Gozoor) : Fact Sheet JuneDocument2 pagesAAIB Fixed Income Fund (Gozoor) : Fact Sheet Juneapi-237717884No ratings yet
- Blue Print Xii PreDocument1 pageBlue Print Xii Prebalajayalakshmi96No ratings yet
- Beauty and Personal Care in India - Analysis: Country Report - Apr 2021Document5 pagesBeauty and Personal Care in India - Analysis: Country Report - Apr 2021KAPIL MBA 2021-23 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- Agricultural Economics I PDFDocument107 pagesAgricultural Economics I PDFd.p.vijay reddyNo ratings yet
- Thailand Economic Monitor Harnessing Fintech For Financial InclusionDocument59 pagesThailand Economic Monitor Harnessing Fintech For Financial InclusionPutchong SaraNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Fundamental Factor Models Jun2010Document15 pagesThe Fundamentals of Fundamental Factor Models Jun2010Alexander GitnikNo ratings yet
- MacroeconomicsDocument4 pagesMacroeconomicskuashask2No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Nama: Ulfa Dewi PermatasariDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Nama: Ulfa Dewi PermatasarirobetNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Business and Economics: Bab 17Document22 pagesStatistics For Business and Economics: Bab 17balo100% (1)
- Unit 1 Lesson 1Document14 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 1Bj Apostol QuejaNo ratings yet
- Africam Group Presentation Uc BerkeleyDocument6 pagesAfricam Group Presentation Uc BerkeleyvargasjeffreyNo ratings yet
- Ar2005 BookDocument366 pagesAr2005 BookdemonariesNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics For M Phil EconomicsDocument7 pagesThesis Topics For M Phil Economicsafkogsfea100% (2)
- Cambridge O Level: ECONOMICS 2281/21Document8 pagesCambridge O Level: ECONOMICS 2281/21Fred SaneNo ratings yet
- Effect of Capital Formation On Economic Growth inDocument17 pagesEffect of Capital Formation On Economic Growth inAyano DavidNo ratings yet
- The Economic Transformation ASEANDocument12 pagesThe Economic Transformation ASEANAn HàNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document31 pagesCH 01limon ahmedNo ratings yet
- Vitaliy N Katsenelson CFA Vitaliy N. Katsenelson, CFA: Director of Research Investment Management Associates, IncDocument36 pagesVitaliy N Katsenelson CFA Vitaliy N. Katsenelson, CFA: Director of Research Investment Management Associates, Incssorem100% (1)
- Module 11Document2 pagesModule 11bobNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy in KenyaDocument29 pagesMonetary Policy in KenyaSimon MutekeNo ratings yet
- Econ 201 Syllabus HybridDocument3 pagesEcon 201 Syllabus HybridShemealNo ratings yet
- Post-Keynesian Macroeconomics Since The Mid 1990s: Main DevelopmentsDocument42 pagesPost-Keynesian Macroeconomics Since The Mid 1990s: Main Developments赵大牛No ratings yet
- What Is The Broken Window Fallacy?: Frederic BastiatDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Broken Window Fallacy?: Frederic BastiatptutinoNo ratings yet