0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views2 pagesParameters Arterial Blood Gas: Interpreting An Abg
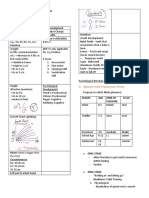
This document provides guidelines for interpreting arterial blood gas (ABG) parameters, including pH, PaCO2, PaO2, and HCO3 levels. It describes uncompensated, partially compensated, and fully compensated states based on whether pH and the respiratory or metabolic systems are within normal ranges. Uncompensated states occur when pH is abnormal and the opposite system is normal. Partially compensated states occur when pH is abnormal and the opposite system is also abnormal. Three examples are provided to demonstrate interpreting ABG results based on these guidelines.
Uploaded by
Micah MagallanoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views2 pagesParameters Arterial Blood Gas: Interpreting An Abg
This document provides guidelines for interpreting arterial blood gas (ABG) parameters, including pH, PaCO2, PaO2, and HCO3 levels. It describes uncompensated, partially compensated, and fully compensated states based on whether pH and the respiratory or metabolic systems are within normal ranges. Uncompensated states occur when pH is abnormal and the opposite system is normal. Partially compensated states occur when pH is abnormal and the opposite system is also abnormal. Three examples are provided to demonstrate interpreting ABG results based on these guidelines.
Uploaded by
Micah MagallanoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd