Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economy of Pakistan
Uploaded by
mohsin iqbal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Economy of pakistan.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesEconomy of Pakistan
Uploaded by
mohsin iqbalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Datails Pakistan (4) China (23) USA (50)
Pakistan Day 23 March Independence Day,
1 October 1949
National Day (1940) 4 July (1776)
civil law influenced
common law system
common law system with by Soviet and
based on English
Islamic law (Majlis-e- continental
common law at the
Shoora) European civil law
federal level;
Legal System systems
Total Area 796,095 sq km 9,596,960 sq km 9,833,517 sq km
Coastline 1,046 km 14,500 km 19,924 km
Agricultural land 35.20% 54.7% 44.50%
Population 207.775 Mn (2017) 1,374 Mn 324 Mn
Population growth rate 1.43% 0.43% 0.81%
Median age 23.4 yr 37.1 yr 37.9 yr
Birth rate 22.3 births/1000 12.4 births/1000 12.5 births/1000
Death rate 6.4 deaths/1000 7.7 deaths/1000 8.2 deaths/1000
0-14 yr: 31.99% 0-14 yr: 17.1% 0-14 yr: 18.84%
Age structure 15-24 yr: 21.31% 15-24 yr: 13.27% 15-24 yr: 13.46%
25-54 yr: 36.87% 25-54 yr: 48.42% 25-54 yr: 39.6%
Life expectancy at birth 67.8 years 75.5 years 79.8 years
Punjabi 44.7%, Pashtun hite 79.96%, black
Han Chinese 91.6%
Ethnic groups 15.4%, Sindhi 14.1% 12.85%, Asian 4.43%
Punjabi 48%, English 79.2%,
Languages Standard Chinese
Urdu (official) 8% Spanish 12.9%,
Literacy age 15 and over Total 57.9%, Male: 69.5%
can read and write Female: 47.8%
Literacy age 10 and over Total 62.3%, Male: 72.5%
can read and write Female: 51.8%
Education expenditures 2.4% of GDP (2018)
Urbanization 38.8% 55.60% 81.6%
Rate of urbanization 2.88% 3.05% 1.02%
Health expenditures 3.3% of GDP, 2.6%(2018) 5.5% of GDP (2014) 17.1% of GDP (2014)
GDP (PPP) $312.6 bn; $305.6bn $12.24 trillion $19.4 trillion
GDP - real growth rate 5.20%, 5.8%(2017-18) 6.70% 1.60%
GDP - per capita (PPP) $ 4927.9 $15,300 $54,200
agriculture: 18.5%, 19% agriculture: 8.6% agriculture: 1.1%
GDP - composition by
industry: 20.3%, 20.6% industry: 39.8% industry: 19.4%
sector
services: 61.2%, 60.4% services: 51.6% services: 79.5%
Population below poverty 22.5% (FY2017 est.) 24.3%
3.30% 15.1% (2010 est.)
line 2015-16 ($ 2 per day)
Inflation rate (consumer
7.2%, 3.8% (FY2017) 2% 1.30%
prices)
Unemployment rate 5.79%, 5.9% (2017 est.) 3% 4.70%
Budget Revenues: RS 3,587.7 bn (9.3% of revenues: $2.3 Tr revenues: $3.363 Tr
GDP)
Total expenditures Rs 5,506.2 Bn (14.3% GDP)
Budget surplus(+) deficit(-) (-5.0%) of GDP; (-4.3%) (-3.3%) of GDP (-3.7%) of GDP
world leader in highly diversified,
textiles and apparel, food
gross value of world leading, high-
processing,
industrial output; technology
Industries pharmaceuticals,
mining and ore innovator, second-
construction materials,
processing, iron, largest industrial
paper products, fertilizer
steel, aluminum, output in the world
Industrial production
1.4%: 5.80% (2017-18) 6% 2.10%
growth rate
world leader in wheat, corn, other
cotton, wheat, rice, gross value of grains, fruits,
agricultural products
sugarcane, agricultural output; vegetables, cotton;
rice, wheat, beef, pork, poultry
Exports (reduce 1.9%.) $20.9bn, $20.48 bn (2017) $2.098 Tr $1.471 Tr
US 13%, UAE 9%, US 18%, Hong Kong Canada 18.6%,
Exports - partners Afghanistan 9%, China 14.6%, Japan 6%, Mexico 15.7%, China
8.7%, UK 5.3%, South Korea 4.5% 7.7%, Japan 4.2%
electrical and other
agricultural
textiles, rice, leather goods, machinery,
products, industrial,
Exports - commodities sporting goods, chemicals, including data
organic chemicals,
manufactures processing
capital product
equipment
Imports (4.9% reduce) $44.03 bn, $46.3 bn (2018) $1.587 Tr $2.205 Tr
electrical and other machinery, data
petroleum, petroleum
machinery, oil and processing equipt,
Imports - commodities products, machinery,
mineral fuels; vehicles, chemicals,
plastics
nuclear reactor oil, gas
South Korea 10.9%, China 21.5%, Canada
China 28.3%, Saudi Arabia
US 9%, Japan 8.9%, 13.2%, Mexico
Imports - partners 11%, UAE 10.9%, Kuwait
Germany 5.5%, 13.2%, Japan 5.9%,
5.7%
Australia 4.1% Germany 5.5%
Public debt Rs 18.17 bn 16.1% of GDP 73.8% of GDP
Energy sector circular Debt 1.362 billion
Trade Deficit (red. 7.4%) $ 23.9 bn; $25.8 (2018)
Government Debt to GDP 72.5% $1.7Tr $19.3 Tr
Current Account Balance (-$19.19 bn 2018-19) $196.4 bn -$481.2 bn
(-27% of GDP 2018-19) (-70% of GDP 2017-18)
Central bank discount rate 12.25% 4.35% 2.25%
Unemployment, youth
10.50%
ages 15-24
Electricity - imports 400 mn kWh 6.185 bn kWh 67 bn kWh
Oil - imports 150,800 bbl/day 7.599 mn bbl/day 8.567 mn bbl/day
Natural gas - proved 669.4 bn cu m 6 bn cu m 10.44 Tr cu m
reserves
Electricity - installed
App. 34,282 MW 1.646 bn kW 1.075 bn kW
generating capacity (2017)
$12.7 Bn $230 Bn $600 bn
Military expenditures
4.03% of GDP (2018) 1.3% of GDP 3.3% of GDP
Note: Macroeconomic in stability, frequent boom and bust cycles, each cycle comprised of 3-4 years of
relatively higher growth followed by a macroeconomic crisis
The outgoing five-year plan has seen an average growth of 4.7% against the target of 5.4%
External sector has shown some improvement after dismal performance in FY-2018.
The government has earmarked Rs 77.262 bn for Education Affairs and Services in the
federal budget for 2019-20 against the revised allocation of Rs 97.155 bn for the current fiscal
year, showing a decrease of around 20.5%.
Pakistan's public expenditure on education as percentage to GDP is estimated at 2.4% in
fiscal year 2018-19, which is the lowest in the region.
The government is targeting to create 10 million jobs in five years. The private sector will
play a key role in creation of jobs supported by the government. The Key areas are;
Naya Pakistan Housing Program by building 10 million houses.
10 bn Tsunami-Government country wide tree plantation Program
National Financial Inclusion Strategy to promote SMEs and digitization of Financial
services
Investment in tourism will help in job creation through development of neglected
areas
For the youth the government has launched Kamyab Jawan Program. This program
will provide low cost loans to the youth for establishing small businesses enterprises.
Energy
The installed capacity improved by 2.5% to 34,282 MW compared to last year 33,433 MW,
while generation increased by 2.1% to 87,324 GWH from 85,552 GWH.
Share in Electricity Generation
Hydroelectric 25.8% (24.4%),
Thermal 62.1% (65%),
Nuclear 8.2% (7.7%) and
renewable 3.9% (2.9%).
Sector-wise growth rates:
Agriculture: 0.85 pc (against target of 3.8pc)
Industry: 1.4pc (against target of 7.6pc)
Services 4.7pc (against target of 6.5pc)
Agriculture
The major factor in limiting the growth of Agriculture was water shortage both for Rabi and
Khariff crops which badly impacted production of major crops such as Cotton, Rice, and Sugar,
which remained behind their target productions.
The cotton crop registered a decline of 17.4% to 9.86 million bales, 11.94 Mn bales 2017-
18
Rice production remained short by 3.3% to 7.2 million ton. 7.4 Mn ton 2017-18
Sugar production stood at 67.2 million ton and witnessed a decline 19.4%. 81.1 mn ton
2017-18
Wheat crop showed some nominal growth of 0.5% to 25.2 million ton. 25.1 mn 2017-18
Maize crop showed good improvement of 6.9% to 6.3 million ton. 5.702 Mn ton 2017-18
Livestock share of 59% in agriculture and 10.91% in GDP, growth of 2.7%
growth of forestry in 7.16% due to high timber production in KPK
fishery growth 0.61% compare to 1.6% 2017-18
Industry
Industrial sector showed moderate growth of 1.4% due to decline of Large Scale
Manufacturing Sector (LSM) by 2.06% due to reduced aggregate demand
Mining and construction sector growth declined by 1.9 and 7.6% respectively.
The actual performance of economy next year will be seen in due course of time in view of
various initiatives in the field of housing, construction, SME, information technology and
tourism as well as strong expansion in credit to private sector and uninterrupted supply of
gas and power at competitive rates.
Services sector
Services sector was affected by the decline in Commodity Producing Sector and registered
a less than expected growth at 4.7%
General government services and other private services contributed to services sector by
surpassing the target and registered a growth of 8% and 7%, respectively.
Inflation
During July-May, FY-2019 inflation increased to 7.2% due to reversal in global fuel prices,
whose impact has been translated on domestic prices as well exchange rate adjustments.
The Food inflation during this period remains low to 4.23%.
From July-April 2019, headline inflation measured by the CPI averaged 7pc against the
3.77pc owing to exchange rate depreciation and higher fuel prices.
Core inflation (non-food and non-energy) was recorded at 8.1pc compared to 5.6pc in the
same period last year.
FDI and remittances
Remittances improved by 8.45% to $ 17.8 bn against 16.4 bn last year
Major role in containing the curr. account deficit to 4.03pc of GDP
Deficits
The export target for FY2019 was set at US$ 28 billion. Exports during July-April FY2019
reached to US$ 20.09 billion as compared to US$ 20.48 in July-April FY2018, decline by 1.9%
Import target for FY2019 was set to US$ 56.5 billion. Imports stood at US$ 44.03 billion in
July-April FY2019 as compared to US$ 46.30 billion, showing a decline of 4.9 percent
This helped in reducing the trade deficit by 7.3pc during July-April FY18-19, while it had
shown an expansion of 24.3pc during the corresponding period last year,
The current account deficit contracted by 27pc from July-April 2019, while it had expanded
by 70pc in the corresponding period last fiscal year.
Workers’ remittances played a major role in containing the curr. account deficit to 4.03pc
of GDP
As a short-term measure to get a breathing space, the government secured $ 9.2 bn from
friendly countries to build up buffers and to ensure timely repayment of previous loans
Revenue collection
Total revenue at Rs-35,837 bn (9.3% of GDP), while growth in total expenditures was
8.7%.
The fiscal deficit was recorded at 5pc of the GDP compared to 4.3% in last fiscal.
Decelerated performance of total revenues primarily was due to marginal growth of 1.8%
in tax revenues and negative growth of 16.7% in non-tax revenues.
The Federal Board of Revenue’s tax receipts from July-April 2019 remained at Rs-2,976 bn
against Rs-2,923 bn in the corresponding period last year, registered growth of 1.8%.
“Actual tax collection during first 10 months of the CFY remained at 67.7% of revised target
of Rs 4,398 bn,” (11.5 percent of GDP)
Provincial revenue collection rose by 1.5pc from July-March 2019.
Govt. Revenue
The FBR collections remains lower due to court stay on mobile phones, reduction in
personal income tax rates and reduced imports
Government has separated the tax policy function of FBR from tax administration.
Creation of Specialized Tax Unit for foreign assets.
Tax broadening measures.
Extensive use of information technology for data mining, detection of under reporting,
spotting tax evaders and get more people into tax net.
These efforts have helped in expansion of tax filers to more than 1.87 million.
Expenditures
The government’s total expenditure increased by 8.7% from July-March 2019 to Rs-5,506.2
bn (14.3% of GDP) against last year’s spending of Rs-5063.3 bn (14.6% of GDP).
Current expenditure posted growth of 17.7% to Rs4798.4bn (12.4% of GDP).
Development expenditure decreased to Rs-655.9 bn this fiscal compared to last year’s of
Rs-993.3 bn, exhibiting 34% negative growth compared to 23.6% positive growth recorded
last year.
The Public Sector Development Program PSDP share in total development expenditure
stood at 88% or Rs-578.5 bn in the first nine months. The same period last year saw Rs-931.4
bn expenditure.
This year’s PSDP expenditure saw a 37.9% decline, while last year witnessed 24.7% growth
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Bates V Post Office: Generic Particulars of ClaimDocument62 pagesBates V Post Office: Generic Particulars of ClaimNick Wallis75% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Importance of Steel PDFDocument3 pagesThe Importance of Steel PDFahmedd55No ratings yet
- FT Partners Research - FinTech in IndiaDocument357 pagesFT Partners Research - FinTech in IndiaPuneet KokruNo ratings yet
- What Is The Tariff Reform Program?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Tariff Reform Program?Luis GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 15 - International Outgoing Tariff - Costing AnalysisDocument95 pages15 - International Outgoing Tariff - Costing Analysismohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- 17 - CVM DashboardDocument18 pages17 - CVM Dashboardmohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- Muslim LeadersDocument87 pagesMuslim Leadersmohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- What Is Report Writing?Document7 pagesWhat Is Report Writing?mohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- Syed Ahmad Shaheed Braelvi (1786-1831) Personal LifeDocument1 pageSyed Ahmad Shaheed Braelvi (1786-1831) Personal Lifemohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management FactorzDocument8 pagesDisaster Management Factorzmohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- Analogy: Bubonic PlagueDocument3 pagesAnalogy: Bubonic Plaguemohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- Procedia Economics and Finance 26 (2015) : Dan Cristian Duran, Luminita Maria GoganDocument5 pagesProcedia Economics and Finance 26 (2015) : Dan Cristian Duran, Luminita Maria Goganmohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources of PakistanDocument4 pagesNatural Resources of Pakistanmohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- 2000 1. Make A Précis of The Following Passage in About One Third of Its Length. Suggest A Suitable Title Also.Document3 pages2000 1. Make A Précis of The Following Passage in About One Third of Its Length. Suggest A Suitable Title Also.mohsin iqbalNo ratings yet
- Introduction Tata SteelDocument2 pagesIntroduction Tata SteelNikam PranitNo ratings yet
- Katie Fitzgerald ResumeDocument1 pageKatie Fitzgerald Resumeapi-497636047No ratings yet
- Bintulu Port Cargo Throughput and Vessel CallsDocument9 pagesBintulu Port Cargo Throughput and Vessel Callsmdluqman81No ratings yet
- PFI ES 29 - 2006 EditionDocument5 pagesPFI ES 29 - 2006 EditionArcadio DuranNo ratings yet
- To SNGPL: Mol Pakistan Oil & Gas Co. B.VDocument1 pageTo SNGPL: Mol Pakistan Oil & Gas Co. B.Vadil haider khanNo ratings yet
- 17 - Heirs of Arce v. DARDocument2 pages17 - Heirs of Arce v. DARPaul Joshua SubaNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industry in IndonesiaDocument24 pagesSugar Industry in IndonesiaGunawan Abdul Basith67% (3)
- PVH Our Factory Disclosure ListDocument84 pagesPVH Our Factory Disclosure ListNhư NgọcNo ratings yet
- Sokoine University of Agriculture College of AgricultureDocument18 pagesSokoine University of Agriculture College of AgricultureNâthànîèl ÂtháílƁràinNo ratings yet
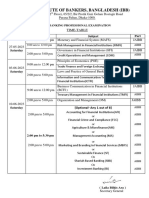
- Exam Routin of 96 Banking Deploma PDFDocument1 pageExam Routin of 96 Banking Deploma PDFMamunur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Dissertation - Amina ZNZ 1Document142 pagesDissertation - Amina ZNZ 1JuliusNeelyNo ratings yet
- 6th Lesson To Investment ManagementDocument4 pages6th Lesson To Investment ManagementWynnie RondonNo ratings yet
- The Ryotwari SystemDocument13 pagesThe Ryotwari SystemSainath SindheNo ratings yet
- Maputo Development CorridorDocument18 pagesMaputo Development CorridorRaimundo Paulo Langa100% (1)
- SAP ISR Course ContentDocument1 pageSAP ISR Course ContentSandeep SharmaaNo ratings yet
- (2013 - IJMSSR) Dangi&Kumar - Current Situation of Financial Incl. in India PDFDocument12 pages(2013 - IJMSSR) Dangi&Kumar - Current Situation of Financial Incl. in India PDFMarkus WidodoNo ratings yet
- Mining of India: BY Arun P PrasadDocument9 pagesMining of India: BY Arun P PrasadArun P PrasadNo ratings yet
- History and Structure of The Nigerian EconomyDocument3 pagesHistory and Structure of The Nigerian Economyfazetyger05No ratings yet
- Mulugeta Girma PDFDocument117 pagesMulugeta Girma PDFmelat bizuNo ratings yet
- Privatization of Insurance Sector in IndiaDocument14 pagesPrivatization of Insurance Sector in IndiaProf. R V SinghNo ratings yet
- Us Kelas 3 Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesUs Kelas 3 Bahasa InggrisRonald WeleNo ratings yet
- SB G20 011 Measuring and Recording of Turntable BearingDocument8 pagesSB G20 011 Measuring and Recording of Turntable BearingCristyan GabrielNo ratings yet
- Crop Enterprise Budget. Conventional Irrigated Alfalfa (Established)Document2 pagesCrop Enterprise Budget. Conventional Irrigated Alfalfa (Established)Geros dienosNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 On Industrial Sector of PakistanDocument20 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On Industrial Sector of PakistanMehar ZubairNo ratings yet
- Demand Forecasting of Cement IndustryDocument20 pagesDemand Forecasting of Cement IndustryShraddhaNaikNo ratings yet
- TLE-TE 10 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2 - ICT CSS WorksheetDocument3 pagesTLE-TE 10 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2 - ICT CSS WorksheetJohn King johnking.monderinNo ratings yet