Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3 PDF
Uploaded by
abhi0290 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter 3.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesChapter 3 PDF
Uploaded by
abhi029Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Chapter 3
29 September 2020 02:14 PM
Characteristics of a put option are as follows:
■ The two counterparties to a put option are the long put and the short put.
■ The price at which the long put has the right to sell the asset is known as the strike price or exercise price.
■ A put option gives the long put the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset to the short put
in the future. Hence, the long put can choose in the future whether or not to exercise its right to sell.
■ The short put is obligated to purchase the underlying asset from the long put should the long put exercise
its right to sell.
■ The long put is also referred to as the “buyer” of the put option. The short put is also referred to as the
“writer” or “seller” of the put option.
■ The long put must pay a fee to the short put for providing the right. The fee is known as the “put
premium.” The put premium is paid at initiation. Other names for the put premium are the “put price” or
simply the “premium.”
■ A European-style put option provides the long put the right to exercise only at expiration. An American-style
put option provides the right to exercise either at expiration or before expiration. Both American-style and
European-style put options trade in the United States.
■ Put options trade both OTC and through exchanges.
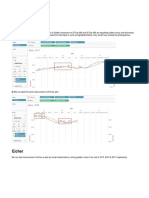
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 03:09 PM
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 03:15 PM
An equation that describes the payoff to the long put is:
New Section 1 Page 1
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 03:18 PM
The short put’s payoff at expiration can be expressed as:
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 03:20 PM
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 03:21 PM
New Section 1 Page 2
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 03:26 PM
New Section 1 Page 3
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Data Dictionary - Telecom Churn Case StudyDocument2 pagesData Dictionary - Telecom Churn Case Studyabhi029No ratings yet
- Stock AnalysisDocument8 pagesStock Analysisabhi029No ratings yet
- Agglomerative Clustering: Point Label X Y Point Label A A B B C C D D E E F FDocument2 pagesAgglomerative Clustering: Point Label X Y Point Label A A B B C C D D E E F Fabhi029No ratings yet
- Blanchard - ch02 A Tour of The BookDocument24 pagesBlanchard - ch02 A Tour of The BookaljonbudimanNo ratings yet