Professional Documents
Culture Documents
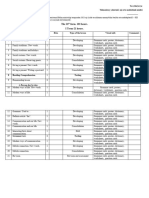
GRADUATE ANALYTICAL & PROBLEM-SOLVING ASSESSMENT RUBRIC (MGMT 700 Case Analysis-100 Points Available)
Uploaded by
falguniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GRADUATE ANALYTICAL & PROBLEM-SOLVING ASSESSMENT RUBRIC (MGMT 700 Case Analysis-100 Points Available)
Uploaded by
falguniCopyright:
Available Formats
Student’s Name: __________________________________________________________ Evaluator’s Name: ____________________________________________________
Date: _________________________ Course: _______________________ 3/06/2008
GRADUATE ANALYTICAL & PROBLEM-SOLVING ASSESSMENT RUBRIC (MGMT 700 Case Analysis- 100 points available)
Exceeds Standards Meets Standards Fails to Meet Standards
Identification of Symptoms (10 Identifies symptoms clearly, with no confusion Identifies majority of symptoms (at least 5). There is Identifies few, if any
%) ½ page maximum between symptoms and problems (5 or more). There little confusion between symptoms and problems. symptoms (4 or less). There
Symptoms are indicators of is no confusion between symptoms and problems. may be confusion between
problems. "Clusters” of symptoms Symptoms are clustered, with each group of symptoms, problems and/ or
aid in pointing toward underlying symptoms pointing toward an underlying problem. recommendations.
problems.
(10) (8) (6)
Problem Statements (20%) 2-3 substantial problems faced by the company’s At least 1 of the company’s substantial problems is 2 or more of the following
½ page maximum decision-makers are identified, and stated in terms identified and stated in terms that are actionable by errors apply:
Problems should be stated in that are actionable by the company’s leadership. the company’s leadership
terms that are actionable by the *Problems stated may refer
decision-maker for the analysis. to environmental
conditions
A good problem definition keeps *Symptoms are stated as the
the case analysis tightly problems.
structured because everything *Recommendations are
discussed after this point must be stated as problems.
related to the problem(s) stated in * Problems may not be
this section. stated in single, concise,
complete sentences.
Each problem is stated in one * More than 3 problems
sentence, and is not given in the stated may be included.
form of a question. There should (20) (15) (12)
be no more than 3 problems.
Problem Analysis (15%) Analysis includes all of the following: Analysis includes 2 of the following: Analysis includes 1 of the
¾ page maximum * 2-3 stated problems are analyzed thoughtfully * 1 problem is analyzed thoughtfully OR 2 or more items listed in the next
Problems are dissected to analyze * At least 1 strategic analysis tool applied problems are covered superficially. column.
key factors. * Relevant financial analysis is applied (Financial * At least 1 strategic analysis tool applied
ratios or other financial analysis approach) * Relevant financial analysis is applied (Financial
(15) ratios or other financial analysis approach) (10) (5)
Identification of Alternatives Identifies a comprehensive set of thoughtful Identifies majority of alternatives (4-5 alternatives), Identifies few, if any
(15%) alternatives, excluding “Do Nothing” alternatives (6 excluding “Do Nothing” alternatives. alternatives (3 or less
This is for brainstorming. alternatives). May have only 1 set of alternatives for more than one alternatives) listed or not all
There is a set of alternatives for each problem. problem. aspects of identified
problems are addressed.
(15) (12) (10)
© 2008, C. Nielsen, Merrick School of Business, University of Baltimore
Student’s Name: __________________________________________________________ Evaluator’s Name: ____________________________________________________
Date: _________________________ Course: _______________________ 3/06/2008
Evaluation of Alternatives Pros and cons for alternatives are provided. Pros and cons for alternatives are provided. Most of Pros & cons for few, if any
(15%) Arguments are convincing, supported & the arguments are convincing & supported. alts or only 1 alt. for each
Arguments are provided for and comprehensive. May be missing a few pros and/or cons. problem; Missing significant
against each alternative. discussion of alternative
(15) (12) pros or cons. (10)
Recommended Course of Action Student demonstrates the ability to articulate and Student demonstrates the Partial courses Actions rely heavily on
(20%) 2 page minimum defend his analysis and recommendations. Student ability to articulate and of action; and/or hiring, or setting up
Develop the most effective, provides a comprehensive course of action, with defend analysis and Actions committee(s)/ team(s) and
efficient, and feasible substantiated feasibility that is likely to solve all of recommendations. recommended do others to decide how best to
combination of alternatives to the priority problems and lead to above average Student provides a not include solve the problems.
solve the problems within returns in this industry with intensifying competition. course of action, specifics to fully OR
boundaries of the firm's Student demonstrates ability to integrate concepts with substantiated address/resolve Brief statements are made
objectives. Do NOT recommend and functional tools from three or more business feasibility that is identified problems about what needs to be
doing research, hiring a disciplines to solve complex business problems. likely to solve at done, but few specifics are
consultant, or setting up a team or least one of the provided.
com./task force to study the identified problems OR
situation. You are the consultants. and lead to above Feasibility of some actions
average returns in can be questions
this industry. OR
Student Recommendations include
demonstrates ability actions not evaluated in
to integrate concepts previous sections.
and functional tools
from at least two
business disciplines
to solve complex
business problem
20) (16) (14) (10)
Implementation Plan (5 %) Timeline and those responsible are identified and Timeline is adequate but responsibilities are not Timeline with those
Who is to do what; timeframe. detailed. identified OR responsibilities are identified by the responsible not provided. (0)
Individuals/depts. are named. (5) timeline is not adequate. (3)
Scoring Key: Total Score: __________
_______ Exceeds Standards 90 – 100
______ Meets Standards 70 – 89
______ Fails to Meet Standards ≤69
© 2008, C. Nielsen, Merrick School of Business, University of Baltimore
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AEC 2018 Aluminum Extrusion ManualDocument191 pagesAEC 2018 Aluminum Extrusion ManualJuan Andrés Díaz RiveroNo ratings yet
- A319 - AWM - IntroductionDocument76 pagesA319 - AWM - Introductionklallali31100% (3)
- Asics Chasing A 2020 VisionDocument57 pagesAsics Chasing A 2020 Visionfalguni33% (3)
- Edexcel GCE Core 2 Mathematics C2 Advanced Subsidary May 2006 6664/01 Question PaperDocument20 pagesEdexcel GCE Core 2 Mathematics C2 Advanced Subsidary May 2006 6664/01 Question Paperrainman875100% (1)
- Kumpulan 100 Soal TOEFL Written ExpressiDocument8 pagesKumpulan 100 Soal TOEFL Written ExpressiPuji AmbarNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 4 Quarter 1 Week 5: CompetencyDocument10 pagesMATHEMATICS 4 Quarter 1 Week 5: CompetencyJhenzNo ratings yet
- Central ProblemDocument5 pagesCentral ProblemfalguniNo ratings yet
- Manual Bomba KoomeyDocument95 pagesManual Bomba KoomeyDiego De JesusNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalogue 422 ESG - Mar-18Document29 pagesParts Catalogue 422 ESG - Mar-18Ws Anandapuram AnakapalliNo ratings yet
- Deep ExcavationDocument59 pagesDeep ExcavationIsbelNo ratings yet
- Problem Statement: Secondary IssuesDocument15 pagesProblem Statement: Secondary IssuesfalguniNo ratings yet
- 560-000-Pi-T-001 - 1 - Simbologia PDFDocument1 page560-000-Pi-T-001 - 1 - Simbologia PDFismylive100% (1)
- Warehouse Order ProcessingDocument67 pagesWarehouse Order ProcessingYogitha BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Marketing-Essay PHPDocument1 pageMarketing-Essay PHPfalguniNo ratings yet
- Equipment No Estimate Date ISO Code Repair Company Pool Currency Repair CostDocument2 pagesEquipment No Estimate Date ISO Code Repair Company Pool Currency Repair CostfalguniNo ratings yet
- Jan 2019 (BD-APL)Document2 pagesJan 2019 (BD-APL)falguniNo ratings yet
- Note On Sensory MarketingDocument2 pagesNote On Sensory MarketingfalguniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior LearningDocument13 pagesConsumer Behavior LearningfalguniNo ratings yet
- The New Coke StrategyDocument3 pagesThe New Coke StrategyfalguniNo ratings yet
- Note Sensory Marketing Shaping Consumer Perception Behavior PreviewDocument1 pageNote Sensory Marketing Shaping Consumer Perception Behavior PreviewfalguniNo ratings yet
- Is A Wearable, Voice and Motion-Controlled Android Device That Resembles A Pair of Eyeglasses and Displays Information Directly in The User's FieldDocument3 pagesIs A Wearable, Voice and Motion-Controlled Android Device That Resembles A Pair of Eyeglasses and Displays Information Directly in The User's FieldfalguniNo ratings yet
- MBA - Case Analysis RubricDocument2 pagesMBA - Case Analysis RubricfalguniNo ratings yet
- Introducing New CokeDocument24 pagesIntroducing New CokefalguniNo ratings yet
- Intro To CB PDFDocument7 pagesIntro To CB PDFfalguniNo ratings yet
- 201809151404251 (1)Document1 page201809151404251 (1)falguniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: MKT 634 - Consumer Behavior and Managerial Decision MakingDocument8 pagesSyllabus: MKT 634 - Consumer Behavior and Managerial Decision MakingfalguniNo ratings yet
- Scent and Brand Memory PDFDocument17 pagesScent and Brand Memory PDFfalguniNo ratings yet
- A) Write Fully Working Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Program Using Java. ExampleDocument6 pagesA) Write Fully Working Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Program Using Java. ExampleGeleta MitikuNo ratings yet
- Playbox Certified Profiles - v3Document5 pagesPlaybox Certified Profiles - v3Cincu CristianNo ratings yet
- Crizal RX and Stock Lens Availability ChartDocument9 pagesCrizal RX and Stock Lens Availability ChartArvind HanaNo ratings yet
- Tingkat Konsumsi Energi, Karbohidrat, Protein, Lemak (Azzarah, DKK)Document21 pagesTingkat Konsumsi Energi, Karbohidrat, Protein, Lemak (Azzarah, DKK)dimasNo ratings yet
- Whole Digital Communication PPT-libreDocument319 pagesWhole Digital Communication PPT-librePiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Capgemini Proposal TemplateDocument14 pagesCapgemini Proposal TemplatePhillip100% (1)
- 10 Synp.2023Document9 pages10 Synp.2023jangahkmNo ratings yet
- Davies & Hull 1976 - The Zoological Collections of The Oxford University MuseumDocument146 pagesDavies & Hull 1976 - The Zoological Collections of The Oxford University MuseumMiguelillo_HernandezNo ratings yet
- Variability in The Project Completion DateDocument12 pagesVariability in The Project Completion DateNguyễn Quốc ViệtNo ratings yet
- Are We Ready For Robot SexDocument17 pagesAre We Ready For Robot SexkaiNo ratings yet
- Altron CCTV Product Catalogue v4.0Document112 pagesAltron CCTV Product Catalogue v4.0AsikusaynNo ratings yet
- Europass Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument2 pagesEuropass Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationNatasa BudisinNo ratings yet
- Nicol, Abigial, Komal - Maths Finial SbaDocument14 pagesNicol, Abigial, Komal - Maths Finial SbavanessajageshwarNo ratings yet
- Catalogue HeizkaDocument48 pagesCatalogue Heizkavotinh20687No ratings yet
- Wa0001Document8 pagesWa0001varshasharma05No ratings yet
- Conflict Management Case SudyDocument3 pagesConflict Management Case SudyNovrialdiNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes RaDocument11 pagesLearning Outcomes Raapi-349210703No ratings yet
- Adding Library Objects To Sbuilder BY Jon Masterson Scruffyduck SceneryDocument17 pagesAdding Library Objects To Sbuilder BY Jon Masterson Scruffyduck SceneryInterim InterimNo ratings yet
- GlobalDocument9 pagesGlobaldaily foot ball highlightsNo ratings yet
- IGS System-1Document11 pagesIGS System-1manojNo ratings yet