Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Lightweight Canopy at Victoria Plaza
The Lightweight Canopy at Victoria Plaza
Uploaded by
Paul0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesThe Lightweight Canopy at Victoria Plaza
The Lightweight Canopy at Victoria Plaza
Uploaded by
PaulCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
ec 275)
THE LIGHTWEIGHT CANOPY
AT VICTORIA PLAZA
A large American financial
concern, Salomon Brothers, has
been converting the atrium
space of recently-built
speculative offices over Vietoria
In recent years tension structures have
been in favour, as much for architectural as
technical reasons, Their visual qualities
hhave been as important as their structural
advantages. But, in some cases the
structure has almost become a decorative
element with litle technical justification.
Imitating the obvious features of some of
the original designs, but lacking their
Station into a dealing hall. John
Thornton describes the
cable-stayed canopy structure
at the heart of the conversion.
Photographs by Richard Bryant.
technical rigour, they remain unconvincing.
‘Victoria Plaza is built over the platforms
of Vietoria Station and contains two atrium
‘spaces, the larger of which was to be
‘converted into a dealing room. This room
had to be roofed. For this, Anthony Hunt
Associates and Heery Architects and
Engineers, designed a tension structure
that is both eonvineing and justifiable
1.24 One problem in tension
“structure design's the effect of
wind ult. nb, the
J wopegaaes
SSiedldol fff harlem
sraity oF wind ads, cause
ovement of the columns and lots
of support to adjoining spans. A
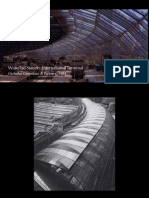
2A view ofthe atria with ts
‘new canopy The vaults are
‘ezmental to leave openings for
‘stoke Incase af ire, vents can
‘open inthe root af the atrium.
Why a tension structure?
‘The main problem facing the designers was
that the existing foundations would not
permit any increase in load; there was,
however, alink block within the atrium, Its
removal released load capacity for the
‘canopy, but a transfer structure at level one
‘meant that this was available only ina line
of three foundations.
‘This naturally led to a structure
supported by a few columns over these
foundations, which suited the general
preference for column-free spaces in
dealing rooms. Hunt's looked at a number
of options for the canopy, but only the
tension-assisted umbrella could be kept
within the depth of the spandrel beams
surrounding the atrium. It also helped keep
‘the weight down to 128 tonnes, under the
184 tonne limit imposed by the foundations.
Being internal, it did not have to cope
‘with the two problems that particularly
affect tension structures, 1, and this
permitted a simple arrangement. The first
of these problemsis that the tension system
for gravity loads becomes inoperative under
wind uplift; the supported structure has to
span further or a secondary tension system
has to be provided, 11. The second problem
is that unbalanced live loads in one span
‘cause uplift in another, 1¢; in this case the
live load was small, Umbrella structures
also tend to fall over, but here the canopy
‘ould be propped horizontally from the
surrounding building,
‘The structure itself consists of three
Vierendeel box girders forming spines
which carry rib beams. Masts pass through
the two outer spines and support them at
this point. Rod ties from the top of the
masts hold the spines at intervals, There
were to have been three masts, but at alate
stage the central one was removed to
improve the dealing space. The triple spine
scheme was retained because it gave the
best overall layout and the central spine is
now entirely suspended. Although this has
complicated the e arrangements, stil
looks logical and consistent. The masts have
ball and socket joints at their base and at
canopy level to allow movement without
inducing bending. This entire structure
is steel,
‘The ribs support vaulted louvres made of
corrugated steel sheet on hollow seetion
frames. They are clad underneath with
perforated aluminium ceiling panels, while
the top surface of the canopy is covered.
with vertical aluminium louvres. These are
close together over the gaps between main
louvres to control light; elsewhere the
spacing, is opened out to give visual unity.
‘Ventilation and lighting are supplied from
above, with aecess walkways on the spine
‘beams. Aluminium was used extensively in
‘both the walkways and service systems to
save weight. As the canopy isa roof toa
sprinklered space with no occupancy above,
it was not necessary to treat the steel
against fire in any way.
‘A tension structure uses discrete
components of beam, tie and mast to give
structural depth, The bulk of these
individual components is much less than
that of a more monolithie structure. This
was an advantage here since the canopy had
to be brought into the building through a
[5 window opening, The structure was,
Aesigned to be broken down into smal
pieces to make this possible and to make its
removal just as easy if need be (the initial
lease is only three years), A Vierendee!
girder, although less effieient than a
conventional tus, isa good choice in these
Framework, butin this case the device was
an internally threaded eylinder). The load
‘was correctly distributed between rods and
girder when the girder was level, so it was
only a matter of adjusting the turnbuekles,
Thad been thought that the structure
circumstances, since a conventional truss
requires splices in the diagonals as well as
the chords, whieh can look awkward,
particularly if they occur frequently
‘might be levelled while temporarily
ballasted with a load equivalent to that
which would be finally applied; in the event
itproved simpler to adjust the ties at
intervals as load was added, This shows an
‘Assembly advantage of a simple system such as this,
‘The stracture was assembled on a where itcan easily be seen when the loads
scaffolding platform. The tension inthe __arecorrect and where adjusting one rod
rods was adjusted by means of turnbuekles does not cause other rods to need
(strietly speaking, a turnbuckle isan open readjustment. A highly interactive tension
3 General arrangement ofthe
‘canopy structure. Three
Vierendel box geders are
suspended from the two masts
and composite stee/concrete
‘ants span between the
‘4 Detlef the bear and vat.
5 Louvre and walkways run over
‘the vaults and beams Lighting
and ventilation services are
carried in the canopy.
{Cross-section trough
Vierendeet girders. Attachment to
the side walls gives lateral but no
sertial support.
1 Data ofthe masthead. The
complesty ofthe assembly flows
from the engineering approach
taking the problems in sequence, 7
18 The canopy 25 seem from the
ew dealing rom.
ohn Thornton structural
Engineer working for Ove Arup
Sod Partnors
structure which requires precise laads in its
various elements and which might require
strain gauges to check these loads could
‘easily make erection the most difficult part
of the project,
‘Working toa tight programme has had
consequences on the finished structure. The
rib tubes were to have been tapered to
reflect the bending forces but there were
problems with the spinning machine. To
keep to programme they were then changed
to stepped straight tubes, which look quite
heavy. Bolts were substituted for some of
the smaller pins and welds in the tubes were
left unground. There is nothing wrong with
this, butit creates a certain inconsisteney in
detailing refinement.
Details play an important part in the
overall effect of a structure such as this
which takes effort, skill and time. With
hindsight, one can see the risks when
time is short.
Design approach
‘The engineer has two possible approaches
to the design of such a structure. Even in
such an apparently simple design these will
affect the appearance. One is to work with
the underlying structural principles to
‘minimise and simplify. The other is to solve
the problems in sequence, which tends to
give a layering of elements and a more
complicated appearance, 7. The latter
approach seems to be characteristie of
Hunt's structures. Take three examples,
First, the louvres are deep enough to look
asif they could have been made to span
further without support from the ribs. This.
makes the distribution of load between
them and the primary structure ambiguous.
second, the number and angle of the ties
and the way they have all been brought to
the masthead makes a complex assembly.
‘The distinctive wide shape of the east forks
was generated by the need for clearance.
Finally, the spines have been made
continuous past the masts, rather than
being pinned at this point. Apart from
affecting the appearance of the junction this
creates the visual quality of the canopy
being a continuous element supported on
‘columns and itself supporting a mast and tie
system which strengthens it. The
alternative pinned solution would have
accentuated the mast and given greater
‘emphasis to the suspended nature of the
‘canopy. Again, the choice of structure was
that which tended to ambiguity
Faced with an unusual problem, the
designers have produced a tension structure
which is appropriate and uncontrived while
being well detailed,
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5808)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On The Blast Resistance of Laminat - 2012 - International Journal of Solids andDocument20 pagesOn The Blast Resistance of Laminat - 2012 - International Journal of Solids andPaulNo ratings yet
- Tractive Rolling Contact Mechanics of - 2012 - International Journal of SolidsDocument17 pagesTractive Rolling Contact Mechanics of - 2012 - International Journal of SolidsPaulNo ratings yet
- CRN-SPC-CVL-713026361-377 - Boundary Fences PDFDocument17 pagesCRN-SPC-CVL-713026361-377 - Boundary Fences PDFPaulNo ratings yet
- Supplement To AGRD Part 6B Roadside EnvironmentDocument9 pagesSupplement To AGRD Part 6B Roadside EnvironmentPaulNo ratings yet
- Industry Alert - VBA - Feb 2016Document6 pagesIndustry Alert - VBA - Feb 2016PaulNo ratings yet
- Safety Factor For StoneDocument4 pagesSafety Factor For StonePaulNo ratings yet
- Stick Electrode Welding GuideDocument44 pagesStick Electrode Welding GuidePaulNo ratings yet
- FLIR T810441-En-Us gUIDEDocument39 pagesFLIR T810441-En-Us gUIDEPaulNo ratings yet
- Building Enclosure Commissioning: What's The Big Deal?Document44 pagesBuilding Enclosure Commissioning: What's The Big Deal?PaulNo ratings yet
- Influences of Longitudinal Magnetic Field On Wave Propa - 2010 - Applied MathemaDocument12 pagesInfluences of Longitudinal Magnetic Field On Wave Propa - 2010 - Applied MathemaPaulNo ratings yet
- Modeling of MIG MAG Welding With Experimental Validation - 2010 - Applied MathemDocument17 pagesModeling of MIG MAG Welding With Experimental Validation - 2010 - Applied MathemPaulNo ratings yet
- Bolted Joint Design: Home Screws Index PageDocument5 pagesBolted Joint Design: Home Screws Index PagePaulNo ratings yet
- Editorial Board - 2010 - Applied Mathematical ModellingDocument1 pageEditorial Board - 2010 - Applied Mathematical ModellingPaulNo ratings yet
- Bolted Conn. With Hot-Dip Galv. Steel Memb.Document14 pagesBolted Conn. With Hot-Dip Galv. Steel Memb.PaulNo ratings yet
- FISCHER Anchor Design-Pages-192-261Document71 pagesFISCHER Anchor Design-Pages-192-261PaulNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt FAZ: Approved ForDocument6 pagesAnchor Bolt FAZ: Approved ForPaulNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematical Modelling: Junli Liu, Tailei ZhangDocument12 pagesApplied Mathematical Modelling: Junli Liu, Tailei ZhangPaulNo ratings yet
- Waterloo Station PDFDocument9 pagesWaterloo Station PDFPaul100% (1)
- 5.9 Anti Graffiti Coatings and TreatmentsDocument5 pages5.9 Anti Graffiti Coatings and TreatmentsPaulNo ratings yet
- Architectural Powder - Mike WithersDocument36 pagesArchitectural Powder - Mike WithersPaulNo ratings yet