Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Time Value of Money - VALENTIN
Time Value of Money - VALENTIN
Uploaded by
John Christian E. ValentinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Time Value of Money - VALENTIN
Time Value of Money - VALENTIN
Uploaded by
John Christian E. ValentinCopyright:
Available Formats
Valentin, John Christian E.
BSA-2A
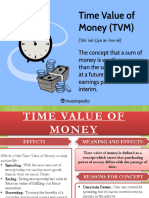
1. Timeline
A line or chart showing a company's cash inflows and cash outflows and the
business activities that caused them over a given period.
This is the timeline that the finance manager uses to determine the inflow and
outflow of the money in a given period od time so that the entity owners can
know if their business is still earning. For the investor to know if their
investment can still return and lastly for the creditors to know if is still worth to
lend them money
2. Compounding and Discounting Methods
Compounding Methods: It tells us the future value of the money or a property
depends on the given time period
For understanding the concept of compounding, first of all, you need to know
about the term future value. The money you invest today, will grow and earn
interest on it, after a certain period, which will automatically change its value in
future. So the worth of the investment in future is known as its Future Value.
Compounding refers to the process of earning interest on both the principal
amount, as well as accrued interest by reinvesting the entire amount to generate
more interest.
Compounding is the method used in finding out the future value of the present
investment. The future value can be computed by applying the compound
interest formula.
Quarterly Compounding: FV = $10,000 x [1 + (10% / 4)] ^ (4 x 1) = $11,038
Monthly Compounding: FV = $10,000 x [1 + (10% / 12)] ^ (12 x 1) = $11,047
Daily Compounding: FV = $10,000 x [1 + (10% / 365)] ^ (365 x 1) = $11,052
While in Discounting Method: tells us the present value of a property or
money
Discounting is the process of converting the future amount into its Present
Value. Now you may wonder what is the present value? The current value of
the given future value is known as Present Value. The discounting technique
helps to ascertain the present value of future cash flows by applying a discount
rate. The following formula is used to know the present value of a future sum:
Example:
Formula
R= Discount Rate
N= Number of Years
Quarterly Compounding: FV = $10,000 x [1 + (10% / 4)] ^ (4 x 1) =
$11,038
Monthly Compounding: FV = $10,000 x [1 + (10% / 12)] ^ (12 x 1) =
$11,047
Daily Compounding: FV = $10,000 x [1 + (10% / 365)] ^ (365 x 1) =
$11,052
Valentin Enterprises has to invest $ 250,000 at a quarterly interest 25%
compoundly quarterly the value of investment in 25 years.
Formula: FV = $10,000 x [1 + (10% / 4)] ^ (4 x 1) = $11,038
FV = $ 250,000 x [1 + (25% / 4)] ^ (4 x 1)
= $ 250,000x 1.27442932129
= $ 318607.33
3. Present Values and Annuity Values
Present value: Tells you how much money to fund a series of annuities payment
in the future
Formula: P=PMT×r1−((1+r)n1)
Example: Valentin Enterprise has the opportunity to receive an ordinary
annuity that pays P30,000 per year for the 30 years, with a discount rate of 5%
P= P30,000×0.06 1−((1+0.05)30)
P= 461,173.53
Annuity Due: is an annuities that was paid during the beginning of a period
Formula:
Periodic Payment when PV is known: PmtAD=PVAD[1−1(1+i)(N−1)i+1]
Periodic Payment when FV is known: PmtAD=FVAD[(1+i)N−1i](1+i)
Ordinary Annuities: is an annuities that was paid at the end of the period
which is usually used by the business entity
Formula:
Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity: Present Value = PMT x ((1 - (1 + r) ^
-n ) / r)
You might also like
- ETpedia Management - 500 Ideas For Managing An English Language SchoolDocument210 pagesETpedia Management - 500 Ideas For Managing An English Language SchoolFernando AquizeNo ratings yet
- CheckingStatement BoA 30 11 2020 30 12 2020Document3 pagesCheckingStatement BoA 30 11 2020 30 12 2020xxalias100% (3)
- Lease Addendum Promissory NoteDocument5 pagesLease Addendum Promissory NoteFOX5 VegasNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument26 pagesTime Value of MoneyBobbles D LittlelionNo ratings yet
- Why Do Sponsors Use Project Finance?: 2. How Does Project Finance Create Value? Justify With An ExampleDocument3 pagesWhy Do Sponsors Use Project Finance?: 2. How Does Project Finance Create Value? Justify With An Examplekumsisa kajelchaNo ratings yet
- Tugasan Berkumpulan Valuation Methodology (DDWF 1423) : Nama Pensyarah: Puan DR Noraini Binti RejabDocument27 pagesTugasan Berkumpulan Valuation Methodology (DDWF 1423) : Nama Pensyarah: Puan DR Noraini Binti Rejabhilman afiq100% (1)
- Time Value of MoneyDocument7 pagesTime Value of MoneyMary Ann MarianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Time Value of MoneyDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - Time Value of MoneyGalindo, Justine Mae M.No ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument40 pagesTime Value of Moneyqrrzyz7whgNo ratings yet
- TVM & CompoundingDocument8 pagesTVM & CompoundingUday BansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four TVMDocument17 pagesChapter Four TVMየሞላ ልጅNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money MPFDocument6 pagesTime Value of Money MPFSaloni AgrawalNo ratings yet
- FM CHAPTER 3 THREE. PPT SlidesDocument84 pagesFM CHAPTER 3 THREE. PPT SlidesAlayou TeferaNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Module 5Document10 pagesBusiness Finance Module 5CESTINA, KIM LIANNE, B.No ratings yet
- Financial Management Session 8Document13 pagesFinancial Management Session 8Shivangi MohpalNo ratings yet
- Planning and Evaluationl English 3Document24 pagesPlanning and Evaluationl English 3Absa TraderNo ratings yet
- Intuition Behind The Present Value RuleDocument34 pagesIntuition Behind The Present Value RuleAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Financial ManagementDocument26 pagesTerm Paper On Financial ManagementHaris MunirNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument4 pagesTime Value of MoneyTshireletso MphaneNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument26 pagesTime Value of Moneynicko marceloNo ratings yet
- Financial Management FM 1: Introduction & Time Value of MoneyDocument20 pagesFinancial Management FM 1: Introduction & Time Value of MoneyharryworldNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter-5: Future Value It Measures The Nominal Future Sum of Money That A Given Sum of Money IsDocument10 pagesNotes Chapter-5: Future Value It Measures The Nominal Future Sum of Money That A Given Sum of Money IsFariya HossainNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Notes Loan ArmotisationDocument12 pagesTime Value of Money Notes Loan ArmotisationVimbai ChituraNo ratings yet
- Finman Modules Chapter 5Document9 pagesFinman Modules Chapter 5Angel ColarteNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money - MbaDocument36 pagesTime Value of Money - MbaFranchezka PegolloNo ratings yet
- FM Midterm NotesDocument9 pagesFM Midterm NotesMj NuarinNo ratings yet
- Planning and Evaluationl English 4Document40 pagesPlanning and Evaluationl English 4Absa TraderNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Ii: Chapter 5 (Fundamental of Corporate Finance) Introduction To Valuation: The Time Value of MoneyDocument33 pagesFinancial Management Ii: Chapter 5 (Fundamental of Corporate Finance) Introduction To Valuation: The Time Value of MoneyEldi JanuariNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Lecture 4thDocument34 pagesFinancial Management Lecture 4thMansour NiaziNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument38 pagesTime Value of Moneytomikovan110% (1)
- Time Value of Money - TVMDocument21 pagesTime Value of Money - TVMTh'bo Muzorewa ChizyukaNo ratings yet
- Session 10: Unit II: Time Value of MoneyDocument49 pagesSession 10: Unit II: Time Value of MoneySamia ElsayedNo ratings yet
- 1time Value AnalysisDocument78 pages1time Value AnalysisSay SayNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document51 pagesChap 2Eba GetachewNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument18 pagesTime Value of MoneyJunaid SubhaniNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow ValuationsDocument14 pagesCash Flow ValuationsRao Shahid TufailNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3-Time Value of Money - 29908Document39 pagesPresentation 3-Time Value of Money - 29908Chin Keanna BuizonNo ratings yet
- Study Material For Corporate FinanceDocument62 pagesStudy Material For Corporate FinanceAnant JainNo ratings yet
- The Time Value of Money: Money NOW Is Worth More Than Money LATER!Document37 pagesThe Time Value of Money: Money NOW Is Worth More Than Money LATER!Meghashyam AddepalliNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting and FinancingDocument21 pagesCapital Budgeting and FinancingCérine AbedNo ratings yet
- Mba 4 YerDocument3 pagesMba 4 YerRashidNo ratings yet
- 4) - Are Shares of A Single Foreign Company Issued in The U.S. (ADR or American Depository Receipt)Document8 pages4) - Are Shares of A Single Foreign Company Issued in The U.S. (ADR or American Depository Receipt)mohanraokp2279No ratings yet
- Time Value SolnDocument34 pagesTime Value SolnAlim Ahmed Ansari100% (1)
- Time Value of Money - GitmanDocument7 pagesTime Value of Money - GitmanJasmine FalibleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Valuation: The Time Value of Money Chapter OutlineDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Valuation: The Time Value of Money Chapter OutlineEman SamirNo ratings yet
- Winter Semester 2023-24 - MGT2006 - TH - AP2023246000029 - 2024-01-20 - Reference-Material-IDocument24 pagesWinter Semester 2023-24 - MGT2006 - TH - AP2023246000029 - 2024-01-20 - Reference-Material-Isujithsai2004No ratings yet
- Time Value of Money: DR. Mohamed SamehDocument22 pagesTime Value of Money: DR. Mohamed SamehRamadan IbrahemNo ratings yet
- 3b5a3lecture 3 Time Value of MoneyDocument34 pages3b5a3lecture 3 Time Value of MoneyApril MartinezNo ratings yet
- Class Notes in Basic FinanceDocument23 pagesClass Notes in Basic FinanceOnat PNo ratings yet
- The Time Value of Money - The BasicsDocument64 pagesThe Time Value of Money - The BasicsTaqiya NadiyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Time Value of MoneyDocument4 pagesModule 1 Time Value of MoneyChristianNo ratings yet
- Concept of Time Value of Money (TVM) Need / Reasons For Time Value of MoneyDocument34 pagesConcept of Time Value of Money (TVM) Need / Reasons For Time Value of MoneyRasumathi SNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Ahmed HassanDocument41 pagesTime Value of Money Ahmed HassanKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money.-1Document6 pagesTime Value of Money.-1Darlington ChikanzaNo ratings yet
- Draft Jawapan Cases (Managerial Finance) Set9 Sem2 Sesi20222023 Bangi - YdDocument10 pagesDraft Jawapan Cases (Managerial Finance) Set9 Sem2 Sesi20222023 Bangi - YdAhmad SuffianNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money - Group 2Document40 pagesTime Value of Money - Group 2Ron Andi RamosNo ratings yet
- The Time Value of Money: Topic 3Document35 pagesThe Time Value of Money: Topic 3lazycat1703No ratings yet
- Lecture Time Value of MoneyDocument44 pagesLecture Time Value of MoneyAdina MaricaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Time Value of MoneyDocument22 pagesLecture 3 - Time Value of MoneyJason LuximonNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument60 pagesTime Value of MoneyJash ChhedaNo ratings yet
- An Overview: I. Financial ManagementDocument15 pagesAn Overview: I. Financial ManagementNoor Cahyo WNo ratings yet
- Ch2 - Time Value of MoneyDocument37 pagesCh2 - Time Value of MoneyAmrish KumarNo ratings yet
- The Time Value of MoneyDocument29 pagesThe Time Value of Moneymasandvishal50% (2)
- Time Value of MoneyDocument38 pagesTime Value of MoneyLaiba KhanNo ratings yet
- Summer Breeding 2021Document2 pagesSummer Breeding 2021John Christian E. ValentinNo ratings yet
- A Compilation of Written OutputDocument8 pagesA Compilation of Written OutputJohn Christian E. ValentinNo ratings yet
- A Compilation of Written OutputDocument8 pagesA Compilation of Written OutputJohn Christian E. ValentinNo ratings yet
- Operman. Jc.1Document6 pagesOperman. Jc.1John Christian E. Valentin100% (1)
- Final MaheshDocument3 pagesFinal MaheshOnkar AroteNo ratings yet
- Passion Reborn": Internship Report On Bank of PunjabDocument99 pagesPassion Reborn": Internship Report On Bank of PunjabAleena Shah100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENT COST OF CAPITAL - Chapter 14 - Resti Aulia - 1182003031Document4 pagesASSIGNMENT COST OF CAPITAL - Chapter 14 - Resti Aulia - 1182003031Faydil ImanNo ratings yet
- 51 Mohd Ifham Khan-Study On GST&its ImplicationDocument100 pages51 Mohd Ifham Khan-Study On GST&its ImplicationFaisal ArifNo ratings yet
- Home Affordable Refinance Faqs: December 20, 2011Document29 pagesHome Affordable Refinance Faqs: December 20, 2011Pedro BenitezNo ratings yet
- PRS Express 20210223 (No 76)Document3 pagesPRS Express 20210223 (No 76)Kelvin ChiNo ratings yet
- SecC - Group-6 - FA Project Report - Godrej Consumer ProductsDocument14 pagesSecC - Group-6 - FA Project Report - Godrej Consumer ProductsTao LoheNo ratings yet
- Insolvency QuestionsDocument1 pageInsolvency Questionsben85296No ratings yet
- Epp 6Document15 pagesEpp 6Sharmaine UalatNo ratings yet
- Common Stock and Investment Banking ProcessDocument26 pagesCommon Stock and Investment Banking ProcessRamji BhandariNo ratings yet
- Coffee Table Booklet 19012024Document244 pagesCoffee Table Booklet 19012024Antony ANo ratings yet
- FAR Handout Investment PropertyDocument4 pagesFAR Handout Investment PropertyPIOLA CAPINANo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: MANISHA SIKKA - I Would Also Like To Express My Thanks To My Guide in ThisDocument77 pagesAcknowledgement: MANISHA SIKKA - I Would Also Like To Express My Thanks To My Guide in ThisAnil BatraNo ratings yet
- Moniepoint and Our Business UnitsDocument8 pagesMoniepoint and Our Business UnitssomilpixelNo ratings yet
- PFRS 10, Consolidated Financial StatementsDocument32 pagesPFRS 10, Consolidated Financial Statementsjulia4razoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Finance 6th Edition Leach Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument45 pagesEntrepreneurial Finance 6th Edition Leach Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFinverse.zinkthxzut100% (15)
- A Project Report On Comparison Between HDFC Bank Amp Icici BankDocument75 pagesA Project Report On Comparison Between HDFC Bank Amp Icici BankSAHIL AGNIHOTRINo ratings yet
- PWC Indonesia Corporate Profile 2014Document22 pagesPWC Indonesia Corporate Profile 2014cerberusberceuse100% (1)
- Estimate MH05EJ0630Document4 pagesEstimate MH05EJ0630Swapnil DoiphodeNo ratings yet
- Concept of State and Regional FinanceDocument15 pagesConcept of State and Regional FinancePutri SariNo ratings yet
- Itr Fy 22-23Document6 pagesItr Fy 22-23Omkar kaleNo ratings yet
- Cheaptry Cheaptry: Question & AnswerDocument9 pagesCheaptry Cheaptry: Question & AnswerAlec AndersenNo ratings yet
- Options Pricing Using Binomial TreesDocument12 pagesOptions Pricing Using Binomial TreesGouthaman Balaraman100% (10)
- Case Analysis: IridiumDocument11 pagesCase Analysis: IridiumNEMUEL DE ROJAS BAYSANTOSNo ratings yet
- Zero Balance FreedomDocument23 pagesZero Balance FreedomALI MORGAN93% (43)