Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GATE 2021 Syllabus For Electronics & Communication Engineering (ECE)
Uploaded by
Ahzam Zobairi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views10 pagesThe document provides information on the GATE 2021 syllabus for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE). It discusses the 8 sections that will be covered in the exam, including Engineering Mathematics, Networks Signals and Systems, Electronic Devices, Analog Circuits, Digital Circuits, Control Systems, Communications and Electromagnetics. Candidates are advised to review the syllabus topics in order to devise an effective exam preparation strategy. The syllabus will help applicants understand the scope of topics that may appear in the exam.
Original Description:
Gate for ece
Original Title
37749
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information on the GATE 2021 syllabus for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE). It discusses the 8 sections that will be covered in the exam, including Engineering Mathematics, Networks Signals and Systems, Electronic Devices, Analog Circuits, Digital Circuits, Control Systems, Communications and Electromagnetics. Candidates are advised to review the syllabus topics in order to devise an effective exam preparation strategy. The syllabus will help applicants understand the scope of topics that may appear in the exam.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views10 pagesGATE 2021 Syllabus For Electronics & Communication Engineering (ECE)
Uploaded by
Ahzam ZobairiThe document provides information on the GATE 2021 syllabus for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE). It discusses the 8 sections that will be covered in the exam, including Engineering Mathematics, Networks Signals and Systems, Electronic Devices, Analog Circuits, Digital Circuits, Control Systems, Communications and Electromagnetics. Candidates are advised to review the syllabus topics in order to devise an effective exam preparation strategy. The syllabus will help applicants understand the scope of topics that may appear in the exam.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
GATE 2021 Syllabus for Electronics &
Communication Engineering (ECE)
Updated on: May 18, 2020
Rakhee Sharma 82 Views
Devise an effective preparation strategy for GATE 2021
with Electronics & Communication Engineering (EC)
Syllabus. Read more details here.
GATE 2021 syllabus f or Electronics and Communication
Engineering (ECE) branch will be released by the of f icial
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
exam conducting authority in the month of September
2021. The details regarding GATE 2021 exam conducting
body is not out yet. Candidates seeking admission in
MTech course through GATE ECE exam must be aware
of the syllabus in order to start their preparation and
scoring good marks.
The GATE 2021 syllabus f or Electronics and
Communication Engineering (ECE) consists section-wise
topics. Knowing GATE syllabus f or ECE will help
candidates in making a good preparation strategy which
will help them achieve a desired goals. As per the
syllabus guidelines available on the of f icial website,
Electronics and Communication Engineering Syllabus has
eight sections: Engineering Mathematics, Networks
Signals and Systems, Electronic Devices, Analog
Circuits, Digital Circuits, Control Systems,
Communications and Electromagnetics. Along with GATE
2021 Electronics and Communication Engineering
syllabus, candidates are also advised to check the GATE
2021 exam pattern f or ef f ective exam preparation.
GATE 2020 Syllabus For ECE – General Aptitude
This section of GATE Syllabus includes questions based
on Verbal Ability and Numerical Ability. The dif f erent
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
topics included in the GATE syllabus f or General Aptitude
are same f or all the exams. Have a look:
Verbal Ability: English grammar, sentence completion,
verbal analogies, word groups, instructions, critical
reasoning and verbal deduction
Numerical Ability: Numerical computation, numerical
estimation, numerical reasoning and data interpretation
GATE 2021 Syllabus for Electronics and
Communication Engineering (ECE)
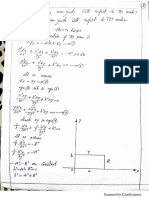
Section 1: Engineering Mathematics
Linear Algebra: Vector space, basis, linear dependence
and independence, matrix algebra, eigenvalues and Eigen
vectors, rank, solution of linear equations – existence
and uniqueness.
Calculus: Mean value theorems, theorems of integral
calculus, evaluation of def inite and improper integrals,
partial derivatives, maxima and minima, multiple integrals,
line, surf ace and volume integrals, Taylor series.
Dif f erential Equations: First order equations (linear and
nonlinear), higher order linear dif f erential equations,
Cauchy's and Euler's equations, methods of solution
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
using variation of parameters, complementary f unction
and particular integral, partial dif f erential equations,
variable separable method, initial and boundary value
problems.
Vector Analysis: Vectors in plane and space, vector
operations, gradient, divergence and curl, Gauss's,
Green's and Stoke’s theorems.
Complex Analysis: Analytic f unctions, Cauchy's integral
theorem, Cauchy's integral f ormula; Taylor's and
Laurent's series, residue theorem.
Numerical Methods: Solution of nonlinear equations,
single and multi-step methods f or dif f erential equations,
convergence criteria.
Probability and Statistics: Mean, median, mode and
standard deviation; combinatorial probability, probability
distribution f unctions - binomial, Poisson, exponential
and normal; Joint and conditional probability; Correlation
and regression analysis.
Section 2: Networks, Signals and Systems
Network solution methods: Nodal and mesh analysis;
Network theorems: superposition, Thevenin and Norton’s,
maximum power transf er; Wye-Delta transf ormation;
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
Steady state sinusoidal analysis using phasors; Time
domain analysis of simple linear circuits; Solution of
network equations using Laplace transf orm; Frequency
domain analysis of RLC circuits; Linear 2-port network
parameters: driving point and transf er f unctions; State
equations f or networks.
Continuous-time signals: Fourier series and Fourier
transf orm representations, sampling theorem and
applications; Discrete-time signals: discrete-time Fourier
transf orm (DTFT), DFT, FFT, Z-transf orm, interpolation
of discrete-time signals; LTI systems: def inition and
properties, causality, stability, impulse response,
convolution, poles and zeros, parallel and cascade
structure, f requency response, group delay, phase delay,
digital f ilter design techniques.
Section 3: Electronic Devices
Energy bands in intrinsic and extrinsic silicon; Carrier
transport: dif f usion current, drif t current, mobility and
resistivity; Generation and recombination of carriers;
Poisson and continuity equations; P-N junction, Zener
diode, BJT, MOS capacitor, MOSFET, LED, photo diode
and solar cell; Integrated circuit f abrication process:
oxidation, dif f usion, ion implantation, photolithography
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
and twin-tub CMOS process.
Section 4: Analog Circuits
Small signal equivalent circuits of diodes, BJTs and
MOSFETs; Simple diode circuits: clipping, clamping and
rectif iers; Single-stage BJT and MOSFET amplif iers:
biasing, bias stability, mid f requency small signal analysis
and f requency response; BJT and MOSFET amplif iers:
multi-stage, dif f erential, f eedback, power and
operational; Simple op-amp circuits; Active f ilters;
Sinusoidal oscillators: criterion f or oscillation, single-
transistor and op- amp conf igurations; Function
generators, wave-shaping circuits and 555 timers;
Voltage ref erence circuits; Power supplies: ripple removal
and regulation.
Section 5: Digital Circuits
Number systems; Combinatorial circuits: Boolean
algebra, minimization of f unctions using Boolean
identities and Karnaugh map, logic gates and their static
CMOS implementations, arithmetic circuits, code
converters, multiplexers, decoders and PLAs; Sequential
circuits: latches and f lip-f lops, counters, shif t-registers
and f inite state machines; Data converters: sample and
hold circuits, ADCs and DACs; Semiconductor memories:
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
ROM, SRAM, DRAM; 8-bit microprocessor (8085):
architecture, programming, memory and I/O interf acing.
Section 6: Control Systems
Basic control system components; Feedback principle;
Transf er f unction; Block diagram representation; Signal
f low graph; Transient and steady-state analysis of LTI
systems; Frequency response; RouthHurwitz and Nyquist
stability criteria; Bode and root-locus plots; Lag, lead and
lag-lead compensation; State variable model and solution
of state equation of LTI systems.
Section 7: Communications
Random processes: autocorrelation and power spectral
density, properties of white noise, f iltering of random
signals through LTI systems; Analog communications:
amplitude modulation and demodulation, angle modulation
and demodulation, spectra of AM and FM, super
heterodyne receivers, circuits f or analog
communications; Inf ormation theory: entropy, mutual
inf ormation and channel capacity theorem.
Digital communications: PCM, DPCM, digital
modulation schemes, amplitude, phase and f requency
shif t keying (ASK, PSK, FSK), QAM, MAP and ML
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
decoding, matched f ilter receiver, calculation of
bandwidth, SNR and BER f or digital modulation;
Fundamentals of error correction, Hamming codes;
Timing and f requency synchronization, inter-symbol
interf erence and its mitigation; Basics of TDMA, FDMA
and CDMA.
Section 8: Electromagnetics
Electrostatics; Maxwell’s equations: dif f erential and
integral f orms and their interpretation, boundary
conditions, wave equation, Poynting vector; Plane waves
and properties: ref lection and ref raction, polarization,
phase and group velocity, propagation through various
media, skin depth;
Transmission lines: equations, characteristic
impedance, impedance matching, impedance
transf ormation, Sparameters, Smith chart
Waveguides: modes, boundary conditions, cut-of f
f requencies, dispersion relations; Antennas: antenna
types, radiation pattern, gain and directivity, return loss,
antenna arrays; Basics of radar; Light propagation in
optical f ibers.
Click here to download GATE 2021 Syllabus for
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
Mechanical Engineering
GATE Exam Pattern 2021 Highlights
GATE Exam
Details
Structure
Number of General Aptitude and the choice of
sections engineering branch
Duration of 180 minutes (60 minutes per
exam section)
Aptitude Engineering, Mathematics,
Sections
Subject specif ic questions
Language of
English
question paper
Number of 4 choices in case of MCQ
answer choices No choices in case of NAT
Mode of
Online (Computer-based test)
examination
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) -
+1 & 2 marks f or the correct answer;
1/3 mark will be deducted f or 1 mark
Marking questions and 2/3 mark will be
scheme deducted f or 2 marks questions
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
Numeric Answer Type (NAT) - +1 & 2
marks f or the correct answer; no
negative marking
Disclaim e r: This PDF is auto -generated based o n the info rmatio n
available o n Shiksha as o n 0 5-Jun-20 20 .
You might also like
- The Fast Track to Your Extra Class Ham Radio License: Covers All FCC Amateur Extra Class Exam Questions July 1, 2020 Through June 30, 2024From EverandThe Fast Track to Your Extra Class Ham Radio License: Covers All FCC Amateur Extra Class Exam Questions July 1, 2020 Through June 30, 2024No ratings yet
- Electronics For You Express 2 2021Document76 pagesElectronics For You Express 2 2021moez0% (1)
- Kanodia EC Solved PaperDocument508 pagesKanodia EC Solved PaperPratik Datta100% (4)
- Yamaha xp7000 5000 Power Amplifier Service Manual PDFDocument92 pagesYamaha xp7000 5000 Power Amplifier Service Manual PDFRomlly Voice Elektro100% (3)
- Postgraduate SyllabusDocument9 pagesPostgraduate SyllabussabitavabiNo ratings yet
- Select Instrum TransfmerDocument75 pagesSelect Instrum TransfmerJheny B. Bayon100% (1)
- Lab Exercise 1Document3 pagesLab Exercise 1Cy RilNo ratings yet
- 2009 NFPA 70E Arc Flash CalculatorII 1Document4 pages2009 NFPA 70E Arc Flash CalculatorII 1AlvinSotoRíosNo ratings yet
- NTA UGC NET Electronic Science SyllabusDocument3 pagesNTA UGC NET Electronic Science Syllabusgrk.elrNo ratings yet
- Vlsi DesignDocument115 pagesVlsi DesignAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Drowsiness DetectionDocument20 pagesDrowsiness Detectionmdmujeeb1324No ratings yet
- 2GR-FE Engine CKP Sensor CodesDocument7 pages2GR-FE Engine CKP Sensor CodesYdelkadiasmela Dominguezmorel100% (1)
- E BombDocument20 pagesE BombVijayShan100% (1)
- E BombDocument20 pagesE BombVijayShan100% (1)
- Handy-A Help PDFDocument247 pagesHandy-A Help PDFAmmar SyrianNo ratings yet
- SDFDocument18 pagesSDFManda SwamyNo ratings yet
- Gate Ece Syllabus C0e015f0Document5 pagesGate Ece Syllabus C0e015f0Anbu SelvanNo ratings yet
- GATE ECE 2021 SyllabusDocument7 pagesGATE ECE 2021 SyllabusvipulNo ratings yet
- GATE 2017 EC Syllabus Sections & TopicsDocument4 pagesGATE 2017 EC Syllabus Sections & TopicsbnacNo ratings yet
- Quick Query: Target-Gate 2015Document4 pagesQuick Query: Target-Gate 2015Shubham KaushikNo ratings yet
- GATE Syllabus For Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) - All About EducationDocument4 pagesGATE Syllabus For Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) - All About EducationSai SarathNo ratings yet
- Gate 2011 Preparation: A Complete Guide A Set Of Μmust Read¶ Articles For M.Tech Aspirants Number Of Students Appeared In Gate 2010 Gate 2010 Qualifying Marks Highest Marks In Gate 2010Document3 pagesGate 2011 Preparation: A Complete Guide A Set Of Μmust Read¶ Articles For M.Tech Aspirants Number Of Students Appeared In Gate 2010 Gate 2010 Qualifying Marks Highest Marks In Gate 2010HimaBindu ValivetiNo ratings yet
- Here Are Total 9 Sections in The GATE SyllabusDocument4 pagesHere Are Total 9 Sections in The GATE SyllabusPiyush JhawarNo ratings yet
- Gate PatternDocument4 pagesGate PatternTharun kondaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For GATE 2011 Exam For ECE BranchDocument3 pagesSyllabus For GATE 2011 Exam For ECE Branchameerunnisa123No ratings yet
- PHD Admission Syllabus ECE 2021Document3 pagesPHD Admission Syllabus ECE 2021abdul jawadNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS FOR FACULTY RECRUITMENT TEST ACROSS DEPARTMENTSDocument24 pagesSYLLABUS FOR FACULTY RECRUITMENT TEST ACROSS DEPARTMENTSSaurabh AroraNo ratings yet
- MSC ElectronicsDocument3 pagesMSC Electronicsabishek singhNo ratings yet
- Ap RcetDocument4 pagesAp RcetManu ManuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus for Electronics and Communication Engineering Recruitment ExamDocument3 pagesSyllabus for Electronics and Communication Engineering Recruitment ExammrameshmeNo ratings yet
- APRCETDocument3 pagesAPRCETManu ManuNo ratings yet
- Target-GATE: Tell Your FriendsDocument4 pagesTarget-GATE: Tell Your FriendsAth SydNo ratings yet
- GATE 2017 Electronics and Communications - PDF 28 PDFDocument3 pagesGATE 2017 Electronics and Communications - PDF 28 PDFHima SekharNo ratings yet
- GATE 2017 Electronics and CommunicationsDocument3 pagesGATE 2017 Electronics and CommunicationsstephanNo ratings yet
- GATE 2022 Syllabus For Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) - Check Here!Document15 pagesGATE 2022 Syllabus For Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) - Check Here!PurvaNo ratings yet
- Ece Ae Annexure II CDocument3 pagesEce Ae Annexure II CsandyNo ratings yet
- ECE GATE 2014 exam topicsDocument2 pagesECE GATE 2014 exam topicsganeshkirankumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For General Aptitude (GA) : (Common To All Papers)Document4 pagesSyllabus For General Aptitude (GA) : (Common To All Papers)Ankur SinghNo ratings yet
- CBSE UGC NET June-December 2018 Syllabus for Electronic ScienceDocument3 pagesCBSE UGC NET June-December 2018 Syllabus for Electronic SciencePiyush ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsandCommunicationEngineering 64 PDFDocument3 pagesElectronicsandCommunicationEngineering 64 PDFVenkatesh PeruthambiNo ratings yet
- Ap RsetDocument3 pagesAp RsetsujushNo ratings yet
- Syll Lec Elecroeng 29 09 2014Document2 pagesSyll Lec Elecroeng 29 09 2014Dharmendra MehtaNo ratings yet
- GATE ECE Syllabus (Electronics & Communication Engineering)Document4 pagesGATE ECE Syllabus (Electronics & Communication Engineering)Agnibha DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Gate EcDocument2 pagesGate EcsravanthiNo ratings yet
- EC Electronics and Communications: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsDocument3 pagesEC Electronics and Communications: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsVladNo ratings yet
- GATE 2019 Syllabus For Electronics & Communication Engineering (ECE) - Check HereDocument12 pagesGATE 2019 Syllabus For Electronics & Communication Engineering (ECE) - Check Heresushmitha vNo ratings yet
- Gate Syllabus EC ImpDocument7 pagesGate Syllabus EC Impmanikantamnk11No ratings yet
- Buet MS EeeDocument12 pagesBuet MS EeeA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMAN100% (1)
- Electronics Communication 06Document32 pagesElectronics Communication 06ayush jadaunNo ratings yet
- APPGECET-2019 Electronics & Communication Engineering (EC)Document2 pagesAPPGECET-2019 Electronics & Communication Engineering (EC)Charan UkkuNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering - Ies (Paper - I)Document4 pagesElectronics & Telecommunication Engineering - Ies (Paper - I)Archana TripathiNo ratings yet
- EC Electronics and Communications EngineeringDocument2 pagesEC Electronics and Communications EngineeringS RajuNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication - SyllabusDocument6 pagesElectronics and Communication - SyllabusDeepa ShreeNo ratings yet
- Course DescriptionDocument2 pagesCourse Descriptionturrquoise182No ratings yet
- EC Engineering Math SignalsDocument2 pagesEC Engineering Math SignalsMohan Kumar NNo ratings yet
- Common Recruitment Examination June 2013: DeityDocument10 pagesCommon Recruitment Examination June 2013: DeitydannycbsNo ratings yet
- Handbook 1 B.tech Ece III Sem Quantity 180Document71 pagesHandbook 1 B.tech Ece III Sem Quantity 180akttripathiNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communications Engineering: Part-BDocument3 pagesElectronics and Communications Engineering: Part-BpdnkiranNo ratings yet
- GATE 2013 Syllabus For ECEDocument4 pagesGATE 2013 Syllabus For ECESmithNo ratings yet
- Ies Indian Engineering Services Electronics Ece Syllabus General Ability TestDocument3 pagesIes Indian Engineering Services Electronics Ece Syllabus General Ability TestpalleshankerNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: B.Tech. V SemesterDocument27 pagesSyllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: B.Tech. V SemesterTanmaySharmaNo ratings yet
- RRB SSE Exam 2015 PatternDocument3 pagesRRB SSE Exam 2015 Patternanandmoon273No ratings yet
- Paper I (General Aptitude) Objective Duration: 1 1/2 Hours: Click Here For Model QuestionsDocument2 pagesPaper I (General Aptitude) Objective Duration: 1 1/2 Hours: Click Here For Model QuestionsVivek MauryaNo ratings yet
- RGPV Syllabus For 4th Sem Mechanical Branch - KopyKitab ResourcesDocument11 pagesRGPV Syllabus For 4th Sem Mechanical Branch - KopyKitab ResourcesCrimsontyphoon11No ratings yet
- EC Electronics and Communications: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsDocument4 pagesEC Electronics and Communications: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsvamshiNo ratings yet
- MTech CS 2011 exam syllabus and sample questionsDocument312 pagesMTech CS 2011 exam syllabus and sample questionsShivam ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ies Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesIes Syllabus PDFKrishanjeet BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus DCRUSTDocument38 pagesSyllabus DCRUSTSachin MalikNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Syllabus: GENERAL ABILITY TEST (Common For All Branches)Document3 pagesElectronics & Telecommunication Engineering Syllabus: GENERAL ABILITY TEST (Common For All Branches)pawantwrNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For IES in Electronics&Communication PaperDocument4 pagesSyllabus For IES in Electronics&Communication PaperRitesh Kumar BhadaniNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem UIETDocument8 pages4th Sem UIETrock80069No ratings yet
- B TechopenelectivesforiiiyearDocument118 pagesB TechopenelectivesforiiiyearsunilkumareceNo ratings yet
- CSIR-CIMFR Application Form for Scientist PostDocument9 pagesCSIR-CIMFR Application Form for Scientist PostVishnoo PrathapNo ratings yet
- Microwave and Radar Engineering: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesMicrowave and Radar Engineering: Course Description and ObjectivesAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii: Yagi-Uda Antenna (Array With Parasitic Elements)Document49 pagesUnit-Ii: Yagi-Uda Antenna (Array With Parasitic Elements)Ahzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Microwave AssignmentDocument12 pagesMicrowave AssignmentAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Li Fi The Future TechnologyDocument13 pagesLi Fi The Future TechnologyPraveen Kumar100% (1)
- Unmanned Railway Crossing SystemDocument10 pagesUnmanned Railway Crossing SystemAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Sample PP TXDocument2 pagesSample PP TXsakisNo ratings yet
- Space ElevatorDocument27 pagesSpace Elevatordannybenny005No ratings yet
- Appendix A: Certificate from Head of the Department/ InstituteDocument1 pageAppendix A: Certificate from Head of the Department/ InstituteAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Cost-Effective Mission OperationsDocument11 pagesCost-Effective Mission OperationsAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- An Emerging Material For Future Technology: Seminar ONDocument19 pagesAn Emerging Material For Future Technology: Seminar ONAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Jntuh 4-1 ECE R13 & R15 Syllabus PDFDocument16 pagesJntuh 4-1 ECE R13 & R15 Syllabus PDFAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic PulseDocument7 pagesElectro Magnetic PulseAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Aecs The Final Lab WorkDocument27 pagesAecs The Final Lab WorkAhzam ZobairiNo ratings yet
- Z92JDocument63 pagesZ92JJose Luis Coderque SalasNo ratings yet
- B-Web9500 Technical Manual 01 2013 en UsDocument84 pagesB-Web9500 Technical Manual 01 2013 en UsLiszeth AlcazarNo ratings yet
- Type C NoteDocument15 pagesType C NoteThota SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Transition Series: DescriptionDocument4 pagesTransition Series: DescriptionJamal ShaikNo ratings yet
- The Resistor Cube Equivalent Resistance Conundrum - RF CafeDocument7 pagesThe Resistor Cube Equivalent Resistance Conundrum - RF Cafeyasir9909No ratings yet
- Ras70 3BDocument4 pagesRas70 3BEdwin LimNo ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio TV Sony KDL 60W600B Chassis RB2GDocument47 pagesManual de Servicio TV Sony KDL 60W600B Chassis RB2Gtaz1mxNo ratings yet
- Registers and Counters for Digital Logic DesignDocument42 pagesRegisters and Counters for Digital Logic DesignDayanand Gowda KrNo ratings yet
- ESP3212 Wifi Bluetooth Combo ModuleDocument9 pagesESP3212 Wifi Bluetooth Combo ModuleSasha-wNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document67 pagesUnit 1ராஜலிங்கம் பாலகிருஷ்ணன்No ratings yet
- Irc3380 2880-pcDocument192 pagesIrc3380 2880-pcAndrei MarinasNo ratings yet
- A 8bit Sequential MultiplierDocument6 pagesA 8bit Sequential MultiplierAnh Trai Em ỐcNo ratings yet
- IRM8601Document9 pagesIRM8601Oprina MonicaNo ratings yet
- Slimline Plus: Wiring DevicesDocument14 pagesSlimline Plus: Wiring DevicesAndhika Hafizh PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet lm741Document6 pagesDatasheet lm741Luis RossoNo ratings yet
- What Is Damping in Process Transmitters Learning Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDocument2 pagesWhat Is Damping in Process Transmitters Learning Instrumentation and Control EngineeringNGASSAKI ATONGUI Christ HubertNo ratings yet
- Deplian - FISIOWAVE 042012 EN PRDocument4 pagesDeplian - FISIOWAVE 042012 EN PRAroelNo ratings yet
- RosenstarkDocument13 pagesRosenstarkSimone MolinaroNo ratings yet
- Cne Project GRP 05Document25 pagesCne Project GRP 05bhaskarpagare247No ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 SCPH-70004 Technical SpecDocument2 pagesPlayStation 2 SCPH-70004 Technical SpecSonu Rai83% (6)