100% found this document useful (1 vote)
428 views13 pagesEssentials of Material Management
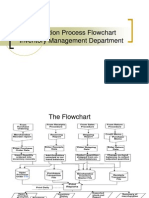
Material management involves planning, procuring, storing, and coordinating materials to support business operations. It aims to provide the right materials of appropriate quality and quantity at the lowest cost while minimizing waste. Key functions of material management include planning and inventory control as well as purchasing, transportation, and handling of materials. Material management has become increasingly important over time to enhance productivity and reduce costs. Its objectives are to decrease expenses, improve profitability, and streamline production processes.
Uploaded by
harabassCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
428 views13 pagesEssentials of Material Management
Material management involves planning, procuring, storing, and coordinating materials to support business operations. It aims to provide the right materials of appropriate quality and quantity at the lowest cost while minimizing waste. Key functions of material management include planning and inventory control as well as purchasing, transportation, and handling of materials. Material management has become increasingly important over time to enhance productivity and reduce costs. Its objectives are to decrease expenses, improve profitability, and streamline production processes.
Uploaded by
harabassCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd