Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RIP Version 1
Uploaded by
Qila SumadiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RIP Version 1
Uploaded by
Qila SumadiCopyright:
Available Formats
RIP version 1 : RIP version 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts – Chapter 5
Objectives : Objectives Describe the functions, characteristics, and operation of the RIPv1
protocol. Configure a device for using RIPv1. Verify proper RIPv1 operation. Describe how
RIPv1 performs automatic summarization. Configure, verify, and troubleshoot default routes
propagated in a routed network implementing RIPv1. Use recommended techniques to solve
problems related to RIPv1
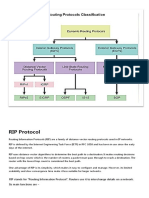
RIPv1 : RIPv1 RIP Characteristics A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol Metric
= hop count Routes with a hop count > 15 are unreachable Updates are broadcast every 30
seconds Full routing table sent with every update
RIPv1 RIP Message Format : RIPv1 RIP Message Format RIP header - divided into 3
fields -Command field -Version field -Must be zero Route Entry - composed of 3 fields
-Address family identifier -IP address -Metric
RIP Operation : RIP Operation RIP uses 2 message types: Request message -This is sent out
on startup by each RIP enabled interface -Requests all RIP enabled neighbors to send routing
table Response message -Message sent to requesting router containing routing table Rip
messages are encapsulated in a UDP segment with source and destination ports of 520
Classful Routing : Classful Routing IP addresses initially divided into classes -Class A
-Class B -Class C RIPv1 is a classful routing protocol -Does not send subnet masks in routing
updates
RIPv1 : RIPv1 Administrative Distance RIP’s default administrative distance is 120
Basic RIPv1 Configuration : Basic RIPv1 Configuration A typical practice topology
suitable for use by RIPv1 includes: - Three router set up - No PCs attached to LANs - Use of
5 different IP subnets
Basic RIPv1 Configuration : Basic RIPv1 Configuration Router RIP Command To enable
RIP enter: -Router rip at the global configuration prompt -Prompt will look like R1(config-
router)#
Specifying Networks Using RIP : Specifying Networks Using RIP Use the network
command to: Enable RIP on all interfaces that belong to this network Advertise this network
in RIP updates sent to other routers every 30 seconds Note: interface will not broadcast
updates unless associated network is advertised
Verification and Troubleshooting : Verification and Troubleshooting To verify and
troubleshoot routing -Use the following commands: -show ip route -show ip protocols -debug
ip rip
Verification and Troubleshooting : Verification and Troubleshooting show ip protocols
command -Displays routing protocol configured on router
Verification and Troubleshooting : Verification and Troubleshooting Debug ip rip
command -Used to display RIP routing updates as they are happening
Passive Interface Command : Passive Interface Command Used to prevent a router from
sending updates through an interface * Reduces traffic on a segment May be used to address
security issues (sniffers) Example: Router(config-router)#passive-interface interface-type
interface-number * Interface will still receive updates
Automatic Summarization (Modified Topology) : Automatic Summarization (Modified
Topology) The original scenario has been modified such that: Three classful networks are
used: 172.30.0.0/16 192.168.4.0/24 192.168.5.0/24 The 172.30.0.0/16 network is subnetted
into three subnets: 172.30.1.0/24 172.30.2.0/24 172.30.3.0/24 The following devices are part
of the 172.30.0.0/16 classful network address: All interfaces on R1 S0/0/0 and Fa0/0 on R2
Automatic Summarization : Automatic Summarization Boundary Routers RIP
automatically summarizes classful networks Boundary routers summarize RIP subnets from
one major network to another.
Automatic Summarization - Good : Automatic Summarization - Good Advantages of
automatic summarization: -The size of routing updates is reduced -Single routes are used to
represent multiple routes which results in faster lookup in the routing table.
Automatic Summarization - Bad : Automatic Summarization - Bad Disadvantage of
Automatic Summarization: -Does not support discontiguous networks
Will RIP Work with Subnetting? : Will RIP Work with Subnetting? Answer: Maybe!! 2
rules govern RIPv1 updates: -If a routing update and the interface it’s received on belong to
the same network then The subnet mask of the interface is applied to the network in the
routing update -If a routing update and the interface it’s received on belong to a different
network then The classful subnet mask of the network is applied to the network in the routing
update.
Default Route and RIPv1 : Default Route and RIPv1 Default routes Packets that are not
defined specifically in a routing table will go to the specified interface for the default route
Example: Customer routers use default routes to connect to an ISP router. Command used to
configure a default route is ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1
Default Route and RIPv1 : Default Route and RIPv1 Propagating the Default Route in
RIPv1 Default-information originate command -This command is used to specify that the
router is to originate default information, by propagating the static default route in RIP
update.
Removing RIP from Configuration : Removing RIP from Configuration Configuration
Details -To remove the RIP routing process use the following command No router rip -To
check the configuration use the following command Show run
Summary: Commands used by RIP : Summary: Commands used by RIP
Chapter 5 Labs : Chapter 5 Labs 5.6.1 Basic RIP Configuration 5.6.2 Challenge RIP
Configuration 5.6.3 Troubleshooting RIP
Slide 25 :
You might also like
- Rip V1Document29 pagesRip V1SomebodyNo ratings yet
- RIP v1 Routing Protocol OverviewDocument28 pagesRIP v1 Routing Protocol OverviewManjunath KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Networking Concepts - Part 5Document29 pagesNetworking Concepts - Part 5Aayush ShahiNo ratings yet
- CA Ex S2M05 RIP Version 1Document36 pagesCA Ex S2M05 RIP Version 1api-3700114No ratings yet
- Practical No. 4: Configure IP Routing Using RIPDocument13 pagesPractical No. 4: Configure IP Routing Using RIPkuldeep RajbharNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 4: Configure IP Routing Using RIPDocument13 pagesPractical No. 4: Configure IP Routing Using RIPkuldeep RajbharNo ratings yet
- Routing Information Protocol RIPDocument27 pagesRouting Information Protocol RIPomarkhanfar2No ratings yet
- Rip Version 1 (Ripv1)Document54 pagesRip Version 1 (Ripv1)AtmanNo ratings yet
- Exploration Routing Chapter 7Document27 pagesExploration Routing Chapter 7vildsmanNo ratings yet
- Routing Rip PDFDocument19 pagesRouting Rip PDFAxel LwiantoroNo ratings yet
- Ccnaexp 5Document77 pagesCcnaexp 5opsssNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Chapter 5 NotesDocument2 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 5 NotesTim Waterbury100% (1)
- Cisco CCNA Exploration V 4.0, Module 2, Chapter 5 ExamDocument7 pagesCisco CCNA Exploration V 4.0, Module 2, Chapter 5 ExamAdryana EnacheNo ratings yet
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Document8 pagesAssessment System: Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)asdasdasd123456No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 LabDocument6 pagesLecture 6 LabSerin AskecNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Chapter 5 V4.0 Answers: Admin Leave A CommentDocument9 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 5 V4.0 Answers: Admin Leave A Commentsathesh005No ratings yet
- Basic RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesBasic RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramNader AbdessayedNo ratings yet
- RIP Version 1: Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 5Document29 pagesRIP Version 1: Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 5Raheel AslamNo ratings yet
- Router: Router1 (Config-Router) # Passive-Interface Fastethernet 0/0Document13 pagesRouter: Router1 (Config-Router) # Passive-Interface Fastethernet 0/0copley50No ratings yet
- RIP and IGRPDocument24 pagesRIP and IGRPAli MohammadNo ratings yet
- Ccna2 Chapter 5Document9 pagesCcna2 Chapter 5dvemic34No ratings yet
- Rip V1 & V2Document6 pagesRip V1 & V2Sujith VSNo ratings yet
- Routing Information ProtocolDocument3 pagesRouting Information ProtocolwertoniwertonisNo ratings yet
- Exploration Routing Chapter 5Document29 pagesExploration Routing Chapter 5Anonymous CRx3B9SNo ratings yet
- RIPv2 for discontinuous networksDocument7 pagesRIPv2 for discontinuous networksJayakrishna IJNo ratings yet
- Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0) - Answers - 2012 - 2013Document8 pagesTake Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0) - Answers - 2012 - 2013Dzevad MakotaNo ratings yet
- RIP PresentationDocument43 pagesRIP PresentationNarendra KishoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 R.I.P. (Routing Information Protocol)Document21 pagesChapter 5 R.I.P. (Routing Information Protocol)omgomg_2010No ratings yet
- RIP Routing Protocol GuideDocument12 pagesRIP Routing Protocol GuideKetan GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7freehat24No ratings yet
- Lab 11 Title: RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument45 pagesLab 11 Title: RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramAhmed HameedNo ratings yet
- Lab 10Document5 pagesLab 10Nhat MinhNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA II Take AssessmentsDocument26 pagesCisco CCNA II Take AssessmentsNina VučetićNo ratings yet
- Dynamic RoutingDocument9 pagesDynamic Routingi200634 Areeba SattarNo ratings yet
- Configuring RIP: RIP Configuration Task ListDocument8 pagesConfiguring RIP: RIP Configuration Task Listtare890No ratings yet
- Route Rip PDFDocument12 pagesRoute Rip PDFAlex FloreaNo ratings yet
- RIP Version 1: © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Public ITE I Chapter 6Document36 pagesRIP Version 1: © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Public ITE I Chapter 6fauzi endraNo ratings yet
- RIP Commands ReferenceDocument22 pagesRIP Commands ReferencethulasiramaswamyNo ratings yet
- 04-RG-S7805C Switch RGOS Configuration Reference, Release 11.0 (4) B19 - IP Routing ConfigurationDocument586 pages04-RG-S7805C Switch RGOS Configuration Reference, Release 11.0 (4) B19 - IP Routing Configurationcindy yudi hermawanNo ratings yet
- G PDFDocument20 pagesG PDFokienaNo ratings yet
- Practical No.4: Routing Information Protocol - RIPDocument11 pagesPractical No.4: Routing Information Protocol - RIPSrinivas CherkuNo ratings yet
- Routing Information Protocol (Ripv1 & Ripv2)Document42 pagesRouting Information Protocol (Ripv1 & Ripv2)Sayyeda UmbereenNo ratings yet
- Configuring Routing Information ProtocolDocument14 pagesConfiguring Routing Information ProtocolTabarez AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Correct AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Correct Answersdeerhntr2267% (3)
- Network Protocols Guide - RIPDocument8 pagesNetwork Protocols Guide - RIPSameer PatelNo ratings yet
- CCNA: Semester 2 RIP: Network DiscoveryDocument8 pagesCCNA: Semester 2 RIP: Network Discoveryttna_hutNo ratings yet
- RIP ProtocolDocument4 pagesRIP ProtocolDion Odessy PaduaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Correct AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Correct Answersdeerhntr22100% (4)
- Chapter No 4 Routing Information Protocol: RIP TimersDocument11 pagesChapter No 4 Routing Information Protocol: RIP Timersjohn borusNo ratings yet
- RIP v1 Routing: CCNA Exploration Semester 2Document35 pagesRIP v1 Routing: CCNA Exploration Semester 2p316jaNo ratings yet
- CCNA2 Chap5 Practice Test QuestionsDocument7 pagesCCNA2 Chap5 Practice Test QuestionsjustkellenNo ratings yet
- RIP Basic IntroDocument8 pagesRIP Basic Introathartanveer31No ratings yet
- Distance Vector Routing Protocols: RIP, IGRP, EIGRPDocument4 pagesDistance Vector Routing Protocols: RIP, IGRP, EIGRPAdam Jian YinNo ratings yet
- CCNA2 Chapter 4,5,6 AnswersDocument5 pagesCCNA2 Chapter 4,5,6 AnswersMary Regine PableNo ratings yet
- Routing Information ProtocolDocument11 pagesRouting Information ProtocolRakin Mohammad SifullahNo ratings yet
- CCENT Chapter 14 Key TopicsDocument5 pagesCCENT Chapter 14 Key Topicshoang nguyen baNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Rfic & Mmic-0Document12 pagesRfic & Mmic-0PhilippeaNo ratings yet
- POE Research ReportDocument18 pagesPOE Research ReportJayantNo ratings yet
- Philips 32PFL3404 FuenteDocument1 pagePhilips 32PFL3404 FuenteMatias IbañezNo ratings yet
- Epec 2023 Control Module PDFDocument40 pagesEpec 2023 Control Module PDFमुकेश कुमार झाNo ratings yet
- E315 Parts List Rev GDocument3 pagesE315 Parts List Rev GChateando Con FernandoNo ratings yet
- CH 11 List ManipulationDocument46 pagesCH 11 List ManipulationROCK RACKNo ratings yet
- Roll Number 301644: Ukssv %& VH FKHZ Izr SD Iz'U I GSRQ Vyx&Vyx Izos'K I E Miflfkfr I Mkmuyksm DjsaaDocument1 pageRoll Number 301644: Ukssv %& VH FKHZ Izr SD Iz'U I GSRQ Vyx&Vyx Izos'K I E Miflfkfr I Mkmuyksm DjsaaPushpendra BiwalNo ratings yet
- Irunin 1Document8 pagesIrunin 1joyNo ratings yet
- LG L222WS Color Monitor Service ManualDocument41 pagesLG L222WS Color Monitor Service ManualDorian SvircevicNo ratings yet
- Profibus With FBP: Achieve Everything With Fewer ComponentsDocument12 pagesProfibus With FBP: Achieve Everything With Fewer ComponentsAnonymous allFud2pjfNo ratings yet
- Service manual for Vivo 45/Nippy 4 Series ventilatorsDocument82 pagesService manual for Vivo 45/Nippy 4 Series ventilatorsNandhini SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Linksys Smart Gigabit Switches: Key FeaturesDocument2 pagesLinksys Smart Gigabit Switches: Key FeaturesDjamzNo ratings yet
- VLSI Fabrication and CharacterizationDocument40 pagesVLSI Fabrication and CharacterizationKarthik RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis of The VMware VRealize Cloud Management SuiteDocument37 pagesCompetitive Analysis of The VMware VRealize Cloud Management Suiteracso1000No ratings yet
- Lab Manual WORD AND EXCELDocument14 pagesLab Manual WORD AND EXCELanish.t.pNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security: Seventh Edition by William StallingsDocument39 pagesCryptography and Network Security: Seventh Edition by William StallingsSawsan TawfiqNo ratings yet
- 02.orion XT HSSD Detector Data SheetDocument4 pages02.orion XT HSSD Detector Data SheetEDUARDONo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 Communications and Privacy: Unit 6 CommunicationDocument3 pagesWorksheet 5 Communications and Privacy: Unit 6 Communicationwh45w45hw54No ratings yet
- Efy Mar09Document148 pagesEfy Mar09indianebooks100% (9)
- Pvsyst User'S Manual: Authors: André Mermoud and Bruno Wittmer Date: January 2014Document103 pagesPvsyst User'S Manual: Authors: André Mermoud and Bruno Wittmer Date: January 2014Thai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Auto CadDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Auto CadazhiNo ratings yet
- Purpose-Built Wireless For Video Surveillance: Secure. Reliable. PredictableDocument4 pagesPurpose-Built Wireless For Video Surveillance: Secure. Reliable. PredictableMarcel Alexander PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Io Journal 3rd Quarter 2009Document40 pagesIo Journal 3rd Quarter 2009shakes21778No ratings yet
- Web Analytics - The Soul of Digital AccountabilityDocument8 pagesWeb Analytics - The Soul of Digital AccountabilitySapientNitro100% (1)
- MC908JL3ECPE Freescale Semiconductor Datasheet 18773Document172 pagesMC908JL3ECPE Freescale Semiconductor Datasheet 18773rcarrillo71No ratings yet
- ESP32 Troubleshooting GuideDocument8 pagesESP32 Troubleshooting GuideAnirudh nandiNo ratings yet
- TECTA Operator Manual - VWR10218-898Document62 pagesTECTA Operator Manual - VWR10218-898mboudi thomasNo ratings yet
- Agilent 33120A Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator: Data SheetDocument4 pagesAgilent 33120A Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator: Data SheetrommelgasparNo ratings yet
- EC Centrifugal Fan G1G133DE1902 ENGDocument5 pagesEC Centrifugal Fan G1G133DE1902 ENGWagesusilo23121986_No ratings yet
- Standard Operating ProceduresDocument4 pagesStandard Operating ProceduresPrakash KumarNo ratings yet