0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views2 pagesCost and Management Accounting Test
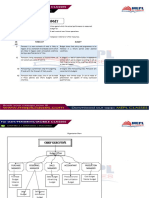
1. This document contains a test on cost and management accounting with 5 multiple choice questions and 5 true/false questions. It tests concepts like responsibility centers, budgeting approaches, budgetary control, and key limiting factors.
2. The multiple choice questions test calculations related to raw material budgets, master budgets, production budgets, and variances.
3. The true/false questions cover topics such as the purpose of budgetary control, characteristics of different budget types, and whether a key limiting factor can change over time.
Uploaded by
Amit DalalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views2 pagesCost and Management Accounting Test
1. This document contains a test on cost and management accounting with 5 multiple choice questions and 5 true/false questions. It tests concepts like responsibility centers, budgeting approaches, budgetary control, and key limiting factors.
2. The multiple choice questions test calculations related to raw material budgets, master budgets, production budgets, and variances.
3. The true/false questions cover topics such as the purpose of budgetary control, characteristics of different budget types, and whether a key limiting factor can change over time.
Uploaded by
Amit DalalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd