Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Formulas
Uploaded by
interprétation interprétation erronée0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 pageOriginal Title
Common_Formulas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 pageCommon Formulas
Uploaded by
interprétation interprétation erronéeYou are on page 1of 1
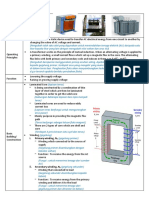
ETA® International Common Formulas
For use on all Basic Electronics Exams as well as the General Communications Technician-Level 1 (GCT1) Exam
Conversion Factors Ohm’s Law
π (Pi) = 3.14 1 meter = 3.28 feet
2π = 6.28 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters E2 E2
logπ = 0.497 1 radian = 57.3˚ R P E
ExI
I
Resonant Frequency Formulas
P
Where ƒ is in kHz, L is in microhenries, C is in microfarads I2 x R P R I2
ƒkHz = 159.2 / LC P
PxR E I
Where ƒ is in Hz, L is in Henries, C is in Farads E
1 P E
ƒresonant = 2π LC I R
I x R P/R
Frequency & Wavelength Formulas ƒ = frequency, λ = wavelength
0.5λ = 180˚ = half wave and 0.25λ = 90˚ = quarter wave
E = Voltage I = Current
ƒkHz = (3 x 108) / λmeters or ƒmHz = 984 / λfeet
P = Power R = Resistance
λmeters = (3 x 108) / ƒkHz or λfeet = 984 / ƒmHz
P = I x E, the power being dissipated by the resistor is a
c = ƒ x λ where c is the speed of light
product of the current and the applied voltage
Sine Wave Conversion Reactance Of Inductors
- Effective value (RMS) = 0.707 x Peak Value = 1.11 x Average Value Where XL is reactance, ƒ is frequency, and L is inductance
- Peak Value = 1.414 x Effective Value (RMS) = 1.57 x Average Value XL = 2 x π x ƒ x L
- Average Value over positive half period = 0.637 x Peak Value = 0.9 x Effective Value (RMS)
- Identify: Waveform, Peak (amplitude), RMS, 1 cycle over time period Time Constants
(frequency), Peak to peak, and practical average T (Greek Tau), R (ohms), C (Farads), L (Henries)
RL circuit: 1 T (sec) = L(H) / R(Ω)
RC circuit: 1 T (sec) = R(Ω) x C(F)
Compute Charge Or Quantity of Electricity
where Q is the charge (in Coulombs), C is the capacitance
(in Farads), and V is the potential difference (in Volts)
Q=CxV
Energy Storage In A Capacitor
where W is the energy (in Joules), C is the capacitance
(in Farads), and V is the potential difference (in Volts)
W = ¹⁄ C x V2
Capacitors Connected In Parallel
C = C1 + C2 +C3 +...
Voltage Gain In Decibels Capacitors Connected In Series
Gain dB = 20log (Vout / Vin) 1 / C = (1 / C1) + (1 / C2) + (1 / C3) +...
Ratio Of 2 Power Levels In Decibels Reactance Of Capacitors
Gain dB = 10log10 (P2 / P1) XC = 1 / (2 x π x ƒ x C)
Resistors In Series Impedance For A Series Circuit
R = R1 + R2 + R3... where Z is impedance
Resistors In Parallel Z = R2 + (XL - XC)2
1 / R = (1 / R1) + (1 / R2) + (1 / R3)... Impedance For R And X In Parallel
Inductors Connected In Series RX
L = L1 + L2 + L3... Z = R2 + X2
Inductors Connected In Parallel Battery Internal Resistance
1 / L = (1 / L1) + (1 / L2) + (1 / L3)... Vout = EMF - (Rint x Iout)
Sine wave figure © Eric Coates MA BSc (Hons) Used with permission © 2020 ETA® International
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- General Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Title: Units of MeasurementsDocument26 pagesGeneral Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Title: Units of MeasurementsNikah M. Tomarocon80% (5)
- Phys CH5Document19 pagesPhys CH5dockmom4No ratings yet
- A Series of Enthalpy-Entropy Charts For Natural Gases: f:1H, f:1M f:1MZDocument12 pagesA Series of Enthalpy-Entropy Charts For Natural Gases: f:1H, f:1M f:1MZDogui AldasNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Examples PDFDocument43 pagesGas Laws Examples PDFSubhash KorumilliNo ratings yet
- Power and Industrial Plant Engineering By:AlcorconDocument126 pagesPower and Industrial Plant Engineering By:AlcorconNelson Naval Cabingas77% (13)
- Analysis Sentence StartersDocument1 pageAnalysis Sentence Startersinterprétation interprétation erronéeNo ratings yet
- Oregon Department of State Lands Unclaimed Property Section 775 Summer Street Ne, Suite 100 SALEM OR 97301-1279Document2 pagesOregon Department of State Lands Unclaimed Property Section 775 Summer Street Ne, Suite 100 SALEM OR 97301-1279interprétation interprétation erronéeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Deangelisa@yosemite - Edu Follow This LinkDocument10 pagesSyllabus: Deangelisa@yosemite - Edu Follow This Linkinterprétation interprétation erronéeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Trouble With Geniuses Part2Document9 pagesChapter 4 The Trouble With Geniuses Part2interprétation interprétation erronée100% (1)
- Top Three Takeaways AssignmentDocument1 pageTop Three Takeaways Assignmentinterprétation interprétation erronéeNo ratings yet
- Emi AitsDocument31 pagesEmi AitsAnmolNo ratings yet
- Mechanics II Independent Revision ResourceDocument16 pagesMechanics II Independent Revision ResourcefejhvdhdwvwoyqiNo ratings yet
- Tubulação (Tabela)Document5 pagesTubulação (Tabela)irlonproducoesNo ratings yet
- Thomas Calvin - 4301419027 - Raymond Chang 1-5Document2 pagesThomas Calvin - 4301419027 - Raymond Chang 1-5Thomas Calvin AndjasmaraNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate The Viscosity of Blending Oils by Using Below TableDocument7 pagesHow To Calculate The Viscosity of Blending Oils by Using Below TableahmetNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesSanjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Phy.1 B.O.TDocument2 pagesPhy.1 B.O.TBWENGYE NICHOLASNo ratings yet
- Ch06 ISMDocument67 pagesCh06 ISMThai-Son LeNo ratings yet
- Ipd 32 Fans and Blowers StudentsDocument5 pagesIpd 32 Fans and Blowers StudentsAngel Joei DangananNo ratings yet
- 9709 s10 QP 43Document4 pages9709 s10 QP 43sriniyfaNo ratings yet
- Nlewis65 115 124 Class and Home Problems Nasri 43 No 2 Spring 2009 CeeDocument10 pagesNlewis65 115 124 Class and Home Problems Nasri 43 No 2 Spring 2009 CeeMarilin NuñezNo ratings yet
- L-1 Water TreatmentDocument11 pagesL-1 Water TreatmentSambhav ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Paper 6 NotesDocument9 pagesPaper 6 NotesabdulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Kinematics Part 1Document21 pagesLesson 2 - Kinematics Part 1Jonathan VillapanaNo ratings yet
- (Pengubah Ialah Satu Alat Yang Digunakan Untuk Memindahkan Tenaga Elektrik (AU) Daripada SatuDocument5 pages(Pengubah Ialah Satu Alat Yang Digunakan Untuk Memindahkan Tenaga Elektrik (AU) Daripada SatuF1006 SRIMUHUNTHANNo ratings yet
- Black Holes: (Image by A. Hamilton)Document18 pagesBlack Holes: (Image by A. Hamilton)aula misnaliaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 The Biot-Savart Law 5.2.1 Steady Currents 5.2.2 The Magnetic Field of A Steady CurrentDocument5 pages5.2 The Biot-Savart Law 5.2.1 Steady Currents 5.2.2 The Magnetic Field of A Steady CurrentAwais YousafNo ratings yet
- Lab Mini Report: Thermal-Fluid Engineering'SDocument7 pagesLab Mini Report: Thermal-Fluid Engineering'SlejiketNo ratings yet
- CapacitanceGroup3 EE5ADocument8 pagesCapacitanceGroup3 EE5AJhon Cris Corañes0% (1)
- Experiment 1 - Use of Analytical BalanceDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 - Use of Analytical BalanceMarc Diongco100% (1)
- AccelerationDocument26 pagesAccelerationBernadette MarigmenNo ratings yet
- Spec-25% GF PTFEDocument1 pageSpec-25% GF PTFEwawanNo ratings yet
- DVZ AH TMDB F.63420 BME A 100 - Rev 0Document5 pagesDVZ AH TMDB F.63420 BME A 100 - Rev 0Alcántara JorgeNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuit Analysis (EE-101) : Kirchoff'S LawsDocument36 pagesLinear Circuit Analysis (EE-101) : Kirchoff'S LawsTehseen HussainNo ratings yet
- How To Test Super CapacitorsDocument8 pagesHow To Test Super CapacitorsCazimir BostanNo ratings yet